| layout | title |
|---|---|
../../layouts/CheatSheet.astro |
IoT Cheatsheet |
IoT stands for Internet of Things, which means accessing and controlling daily usable equipments and devices using Internet. Let's us look closely at our mobile device which contains GPS Tracking, Mobile Gyroscope, Adaptive brightness, Voice detection, Face detection etc. These components have their own individual features, but what about if these all communicate with each other to provide a better environment? For example, the phone brightness is adjusted based on my GPS location or my direction. Connecting everyday things embedded with electronics, software, and sensors to internet enabling to collect and exchange data without human interaction called as the Internet of Things (IoT). The term "Things" in the Internet of Things refers to anything and everything in day to day life which is accessed or connected through the internet. IoT is an advanced automation and analytics system which deals with artificial intelligence, sensor, networking, electronic, cloud messaging etc. to deliver complete systems for the product or services. The system created by IoT has greater transparency, control, and performance.
Basing on the devices that connect over the internet, IoT has three categories
-
The devices that can collect and send the information
-
The devices that collect and respond to the information
-
The devices that can equip both of the above features
-
The devices that can collect and send the information: One word substitute for devices that can collect and send the information will be ‘sensors’. There are numerous sensors available like temperature sensors, motion sensors, different quality measurement sensor and it can be any one of them or a combination of them. These sensors are intelligent and can collect the information for us to take the decision. Like our senses like sight, taste, touch, etc the machinery sensor will make machines feel the senses and respond.
-
The devices that collect and respond to the information: There are many machines that will act upon after receiving the information like a printer connected to your desktop which will respond upon print request. Similarly, the signal from the car key will make your car door to respond and open. There will be endless examples of such devices. So we can actually trigger the machines with the command which can be complex or simple and if the machines are designed with a good algorithm then will respond aptly unless the extreme
-
The devices that can equip both of the above features: The actual power of IoT is from these kinds of devices that can do both of the above-discussed features. The sensor will collect the information and the devices intelligently should respond with the intervention of humans. Like depending on the output of the moisture sensor from the soil, the irrigation system should by default try to operate on the motor without the involvement of the actual farmer. And if this irrigation system is connected to the internet and is able to receive the whether details then it will be smarter and action on the motor will be more efficient now. Achieving this kind of efficiency is the target of these organizations which work on IoT.
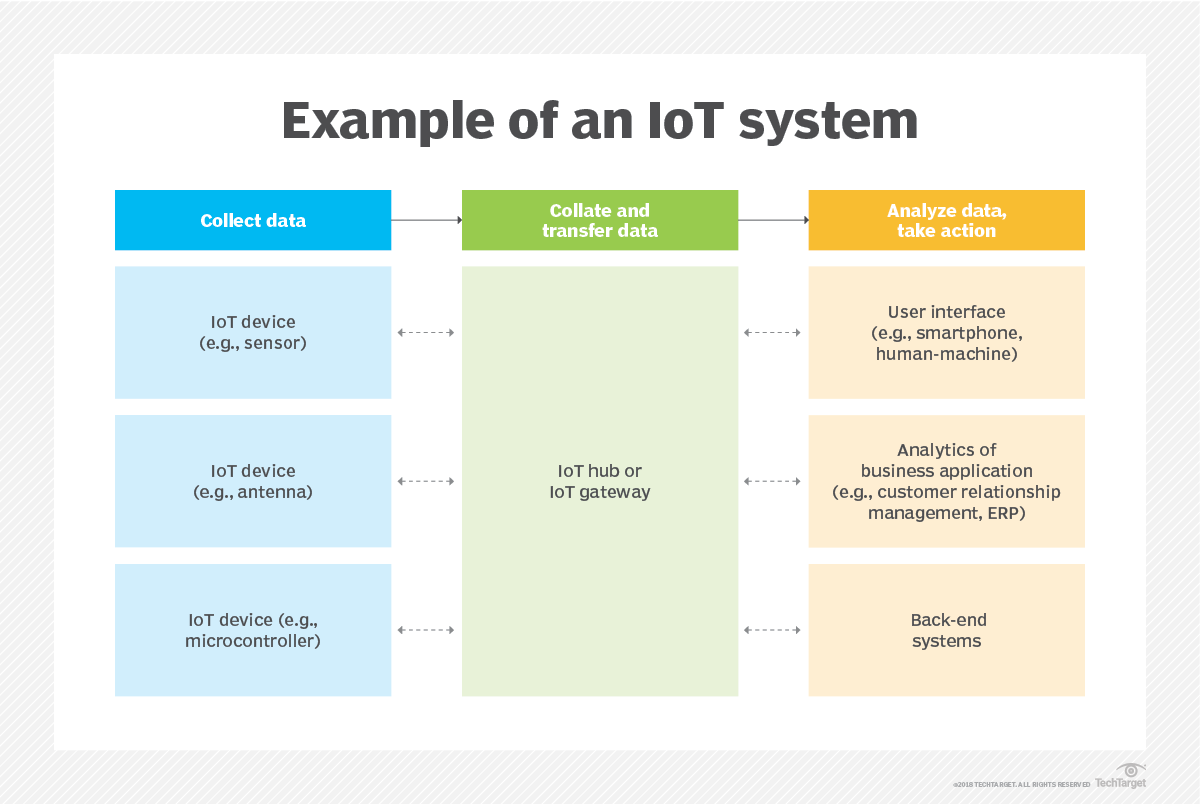
An IoT ecosystem consists of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems, such as processors, sensors and communication hardware, to collect, send and act on data they acquire from their environments. IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device where data is either sent to the cloud to be analyzed or analyzed locally. Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they get from one another. The devices do most of the work without human intervention, although people can interact with the devices -- for instance, to set them up, give them instructions or access the data.
it's important to note the biggest challenges facing IoT security. IoT devices were not built with security in mind, leading to potential vulnerabilities in a multiple device system. In the majority of cases, there is no way to install security software on the device itself. In addition, they sometimes ship with malware on them, which then infects the network they are connected to.
Some network security doesn’t have the ability to detect IoT devices connected to it and/or the visibility to know what devices are communicating through the network.
IoT security wasn’t really taken seriously until recently after many hacking attacks resulted in catastrophic consequences. Since IoT security vulnerabilities are like a welcome sign to hackers, many IoT security measures are now being taken to close security holes and prevent security breaches at the device level, nipping the problem in the bud before it has time to wreak havoc. Here are some IoT security best practices businesses can adopt to protect their devices.
- Change default passwords
This initial step to improving IoT security may seem quite obvious, but there are businesses that forget to change the passwords they were originally given. Once the passwords have been updated, they should be changed regularly. A business can even set up forced password changing after a certain amount of time has elapsed to ensure accounts are properly protected. A password vault can be used to protect the passwords and means that employees don’t end up writing them down. This closes off one way that cybercriminals could potentially use to enter the network to obtain sensitive information.
- Make sure the software is protected
Devices connected to IoT can be secured by implementing active security measures in their software. Providing security measures such as password protection for accessing the software is one of the ways to safeguard devices from potential attacks. It is also important to not let IoT devices initiate network connections on their own – critical data could end up being leaked if programs aren’t blocked behind firewalls or have restricted use. Any devices and software installed on them need to be checked on a regular basis to ensure there are no threats lurking or that no security gaps have formed. Keeping software up-to-date is imperative in the fight against IoT security risks.
- Defend against IoT identity spoofing
Hackers have and continue to become cleverer over the years, which is very disadvantageous for IoT security. Many disguise their computers as trustworthy devices, meaning that businesses must verify the identity of the IoT devices they connect with to make sure they are legitimate. By simply accepting all connections, the business is at high risk of being spoofed or hacked and once criminals have found their way into the network, it can be hard to get rid of them.
- Use encrypted protocols
Very few devices use encrypted communications as part of their initial configuration. They are more likely to use normal web protocols that communicate in plain text, which makes it easy for hackers to observe them and spot weaknesses. This is why it is crucial for all web traffic to use HTTPS, transport layer security (TLS), Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), DNS security extensions, and other secure protocols when communicating over the internet. Devices that connect to mobile apps should also use encrypted protocols and data stored on flash drives should be encrypted as an IoT security measure. Only by encrypting data can you be sure that malware hasn’t infected the device.
IoT related work is carried out by three types of professionals
-
The network specialists who manage connectivity
-
The data analysts who collect data from the devices and interpret it
-
The engineers who develop the platforms, software, hardware, and systems that allow these devices to work.
IoT developers fall into the last category; these individuals are responsible for overseeing the production of the devices or sensors. It includes most prominent programming software that allows the device at hand to both connect with other systems as well as function accurately on its own. Though responsibilities will vary considerably depending on the industry, other job roles may include designing, coding, and testing features of products that are meant for connecting to other devices. Some projects may also require developing embedded software that’s cloud-compatible, to allow products to integrate accurately with one another.
An IoT developer maintains the skills of analyzing and gathering a huge amount of data for interpreting the pattern and predicting the result. With the rise in complexity, AI is used for managing the tasks and autonomous decisions are made with AI as well. The algorithms of machine learning, on the other hand, are used for creating smarter devices with the help of data sensors.
IoT developers possess the skills of machine learning and big data management that helps them in making predictions based on the identification of data patterns. Every company needs skilled IoT developerswho can harvest the data from the IoT sensors and connected devices.
Web and mobile applications are created with the help of high-level languages, with Java, Swift, and Node.js among the top languages for IoT app development services. GPS programming skills are in high demand, as are various IoT applications, including wearables and smart vehicles, that track location. IoT developers keep track of emerging frameworks and developer kits that they can utilize for rapid prototyping, as well as IoT platforms to provide foundation and means to automate developing, deploying, maintaining, and operating IoT applications.
In the last decade or so, we have observed the explosion in the data industry. We have seen security issues at the top of the list of priorities of every business. Especially in the IoT industry, because consumers want to be sure if their information and data is safe. To keep the data private and safe, they have to be familiar with public key infrastructure, ethical hacking, vulnerability assessment, network security etc. A specialization in cybersecurity is another significant role for an IoT developer. Whether it is IoT data collection or processing, it's an essential part of developing IoT devices and the key to the success of the business.
The underlying idea behind IoT and Cloud computing is to increase efficiency in the day to day tasks, without interrupting the quality of the data being collected or transferred. Since the relationship is shared, both the services complement each other perfectly. The IoT becomes the source of the data, while the Cloud becomes the destination for it to be stored. Due to the interconnected network in IoT, there is also a large amount of data to handle. It requires secure data storage which poses a huge challenge for IoT developers. This is the reason why the IoT industry has professionals who are expert in or have a previous history of working with cloud computing technologies for better analysis-ready data storage and management solutions.
BI (business intelligence), is changing, as a result of the IoT. Data has become a new kind of currency in the modern-day world, and about everything we do in life and business generates data. We see every connected machine and smart devices generate incomprehensible amounts of information every second of the day. With so many devices consuming and sending and receiving terabytes of new information, the true potential of "big data” will be accomplished. Organizations try to collect, store and analyze smart device data streams for actionable intelligence business. IoT professionals with skills in sensor data analysis, data centre management, predictive analytics, PaaS, as well as programming skills in popular big data platforms like Apache Hadoop and NoSQL are ideally suitable to meet the needs.
IoT sensors and applications can be retrieved with the help of smart devices. There are several networking tools and techniques needed to connect them efficiently with the apps. IoT professionals generally acquire networking expertise. The sensors associated with the internet of things environment connect with the ecosystem around them. The collected information is sent to get examined. The communication network design needs to be sound, reliable and secure. Therefore, internet Protocol networking is one of the essential skills sets acquired by IoT developers In addition to network design, the developer has practical knowledge of network standards, protocols, and technologies. It includes Wi-Fi, Low Energy Bluetooth, Zigbee, RFID technologies used in consumer applications, and in Low Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN) technologies like LoRa.
Designing a valuable and intuitive user experience for an IoT system in itself can be challenging given the complicated nature and modernity of this technology. Creating UI/UX design for IoT mobile application development is particularly sensitive.I So it becomes necessary that the design of the interface between user and device is user friendly and equally efficient. This skill set of IoT developers comes in handy to make the quality of product efficient. Some of the skill sets they have as a UX/UI designer on the internet of things development are responsive design and service design. If anything goes wrong, UI must be furnished enough to supervise users. Hence, one of the challenges for IoT developers is to develop skills to build intuitive and sophisticated UI with easy-to-understand and interactive elements.
In most of the automated solution, sensors are responsible for exchanging the live data to a digitally connected system. Developers working with IoT development platforms have detailed knowledge and precise understanding of how sensors operate and integrate into the IoT-powered architecture. IoT developers are skilled in wireless solutions and embedded systems and related functionalities
Here are the top IoT tools and platforms for IoT developers and development.
Eclipse IoT is an open-source platform that allows IoT developers and IoT development companies to develop applications in Java. With the help of Eclipse IoT, you can build IoT Devices, Cloud Platforms, and Gateways. This tool focuses on the development, adoption, and promotion of open-source IoT technologies.
Node-RED is a simple and open-source visualization tool built on Node.JS which is used to connect the devices, services, and APIs together for the Internet of Things. Node-RED is a user-friendly interface, developed by IBM’s Emerging Technology department, allowing you to connect, hardware, an API or an online service with tight integration. It helps you connect the devices easily and quickly, helps deal with the flow of the data, and integrates with APIs.
Tessel 2 is a robust IoT platform that is used to build basic IoT solutions and prototypes. It integrates additional sensors and modules. This board has the capacity to hold up to a dozen modules including RFID, GPS, camera, and accelerometer.
This Tessel is very easier for those developers who are familiar with Node.JS programming. This way, Tessel can be used to host several servers and hardware firmware IoT solutions. You can leverage all the libraries of Node.JS to unveil a host of devices in minutes with Tessel.
Arduino is an open-source prototyping platform offering both IoT hardware and software. Arduino is a hardware specification that can be applied to interactive electronics and a set of software which includes the Integrate Development Environment (IDE) and the Arduino programming language. It’s one of the most preferable IDEs in all IoT development tools which is easy and simple to use.
Arduino can be your first choice if you are planning to build a computer that can sense and control more of the physical world when compared to your normal stand-alone computing device.
Kinoma Create is a device that allows establishing a connection between two devices without having too high programming knowledge in JavaScript. Kinoma Create consists of many features that are required for developing small IoT applications like connecting light, temperature or movement sensors for a specific purpose with mobile notifications in case of any alterations.
Kinoma Create has some fundamental components which are as follows:
- Touch screen
- ARM SoC 800 MHz processor
- Bluetooth and integrated WiFi
- Several ports to connect peripherals, including a USB 2.0 port
- Memory of 128 MB and flash memory of 16 MB
- MicroSD card slot
- Speaker and microphone features
- Linux distribution
Based on Data Art’s AllJyone, Device Hive is a free open-source Machine to Machine (M2M) communication framework. Launched in 2012, it’s considered one of the most preferred platforms for IoT app development. Since Device Hive is a cloud-based API, you can control it remotely without having network configuration. A similar thing applies to the libraries, portals, and management protocols.
Home Assistant is an open-source tool that is used for home automation and functions with a Python-based coding system. Mobile or desktop browser can easily have their control over the IoT system developed with this tool. It’s very easy to set up and is trusted for operations, security, and privacy. The software supports any systems which are running on Python 3.