-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 109
Commands
Commands are defined by attaching it to a regular Python function. The command is invoked by the user who send a message similar to the function name. For example, in the given command:
async def cmd_hi(self, ctx):
await ctx.respond("Hello")so that the command will invoked when a user send a /hi.
Since a command needs to be inside a class.
A command must always have at least two parameter, self the plugin instance as the first and ctx which is the Context as the second one.
Since we create a command with Python function name, we also have argument passing behaviour by the function parameters. Note that only command function that have this ability. An event listener will not have this feature.
The most basic parameters is a positional parameter.
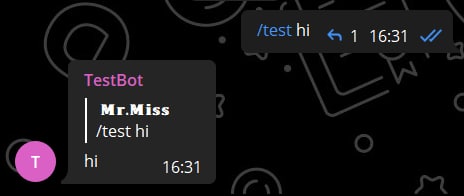
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, arg):
await ctx.respond(arg)There are no limitation on this kind of parameter. You can have it as much as you want. The parameter is default to NoneType if the command message have no argument.
You can use this when you want to parse the rest of the message text to become one variable.
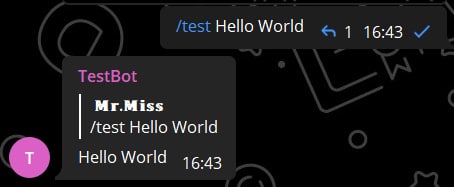
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, *, arg):
await ctx.respond(arg)By default, the Keyword-Only arguments are stripped from whitespace. Because of that the parameter is default to empty string ("") unlike the positional parameters. And take a note that ## you can only have one keyword-only argument for each command.
We try our best to make plugin creation easy. Sometimes a commands need an argument to make it properly. Hence, we're introducing a Converters.
Converters comes in several types:
- A callable object that takes an argument and returns with a different type.
- This can be your own function or something like
boolandint.
- This can be your own function or something like
- A custom converter class that inherits
anjani.util.converter.Converter
We specify a converters by using something called a function annotation introduced on PEP 3107.
A basic converter is a callable that takes in an argument and change it into something else.
For example, if we wanted to add two numbers together, we could request that they are turned into integers for us by specifying the converter:
async def cmd_add(self, ctx, num1: int, num2: int):
await ctx.respond(num1 + num2)To prevent ambiguities of bool E.G: when a non-empty string evaluated as True. We modify this a bit so that it evaluate based on the content of the argument as you can see below.
if arg in ("yes", "true", "enable", "on", "1"):
return True
if arg in ("no", "false", "disable", "off", "0"):
return FalseConverter also works with any callable that takes a single parameter.
def lower(arg):
return arg.lower()
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, text: to_lower):
await ctx.respond(text)You are free to modify an argument on that function. You also have a choice to use async (async def) or sync (def) function.
Sometimes the basic converter doesn't have enough information you need. For example you need the command.Context. In that case we provide a Converter class to do all that jobs. Defining a a custom converter of this require to have the Converter.__call__ method and this must be an Asynchronous method.
An example of advanced converter:
from anjani.utils.converter import Converter
class MediaGroup(Converter):
async def __call__(self, ctx: command.Context):
replied_id = ctx.message.reply_to_message.message_id
chat_id = ctx.chat.id
return await ctx.bot.client.get_media_group(chat_id, replied_id)
class Testing(plugin.Plugin):
name = "Testing"
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, arg: MediaGroup):
print(arg)
for i in arg:
await ctx.respond(arg)We provide a several pyrogram types converter. This converter might be have the most use case on the commands:
Under the hood, those are implemented with Advanced Converter as above. Below are our converter of those pyrogram types:
| Pyrogram Types | Converter |
|---|---|
User |
UserConverter |
Chat |
ChatConverter |
ChatMember |
ChatMemberConverter |
Use example of Pyrogram Converters:
from pyrogram.types import ChatMember
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, member: ChatMember):
await ctx.send(f"User joined on {member.joined_date}")You can also use the converter we provide to use in your custom converter:
from anjani.util import converter
class UserFullname(converter.UserConverter):
async def __call__(self, ctx):
user = await super().__call__(ctx)
user.fullname = user.first_name + (user.last_name or "") # add fullname attribute to user
return user
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, member: UserFullname):
await ctx.send(f"User joined on {member.joined_date}")If you're working with type hinting, we have two accepted type hinting typing.Union and ``typing.Optional`. But currently we only convert to one of the types with left-to-right priority.
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, user: typing.Optional[pyrogram.types.User]):
# Do somethingasync def cmd_test(self, ctx, user: typing.Union[pyrogram.types.User, None]):
# Do somethingIf you want to have a default value apart from the default value we provide (None), you can give a default value by your own.
async def cmd_test(self, ctx, number: int = 0):
# Do somethingWiki of Anjani © Copyright 2021, UserBotIndo