RUS version here (РУС версия здесь)
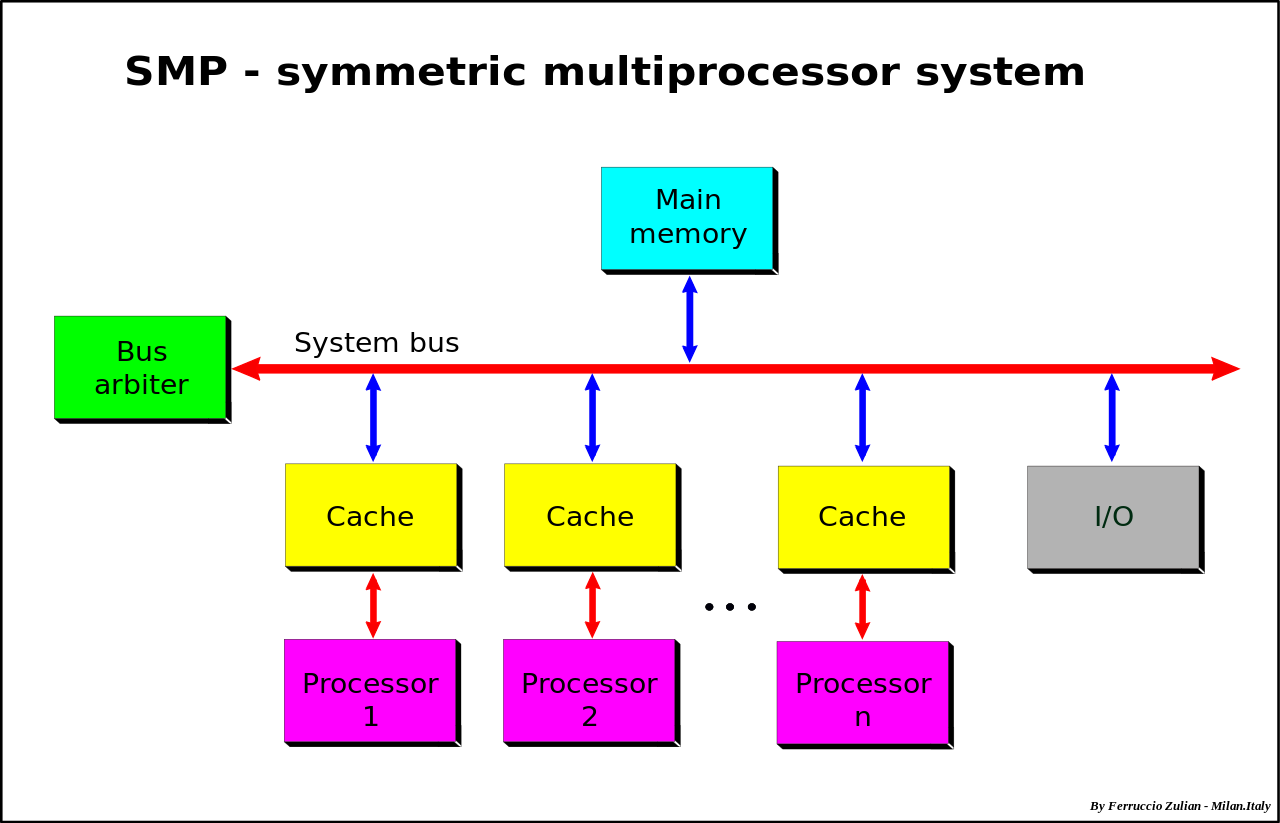
This repository contains a draft of a laboratory work devoted to the development of a model of a memory subsystem in a symmetric multiprocessor system. The application is implemented in the C++ programming language using the Qt library, which provides cross-platform support and high performance.
- Cache replacement policies: Algorithms used to manage the cache of information, thereby improving system performance.
- Coherence protocol: Rules for device interaction in a distributed system.
- MESIF Protocol: A cache coherence protocol developed by Intel, providing 5 states of each cache line.
- Bus snooping: A mechanism for tracking transactions over the system bus in order to maintain cache coherence.
- Calculation cache: A component that stores data to quickly respond to future requests.
- System bus: A bus connecting the main components of a computer system.
- LFU (Least Frequently Used): A caching algorithm that removes the element with the lowest frequency of use from the cache.
The following abbreviations and designations are used in this report:
- MESI - Modified (M), Exclusive (E), Shared (S), Invalid (I).
- MESIF - Modified (M), Exclusive (E), Shared (S), Invalid (I), Forward (F).
- SMP – Symmetric Multiprocessor Systems.
- LRU - Least Recently Used (linearly replaceable unit).
- LFU - Least Frequently Used.
- RWITM - Read With Intent To Modify.
The MESIF protocol extends the classic MESI (Modified, Exclusive, Shared, Invalid) by introducing the Forward (F) state. This significantly improves parallel processing, since the cache line in the Forward state can respond to all read requests once, which minimizes network traffic and access conflicts.
- Advantages of Forward State:
- Reduced traffic due to centralized cache response.
- Software localization of data increases the likelihood of data reuse without additional requests.
- The transition of the Forward state to the newest copy improves temporary locality and caching efficiency.
The LFU (Least Frequently Used) algorithm used in this paper optimizes cache management by throwing out the elements that were used the least often, based on the number of accesses, and not the time of last use as in LRU.
Strategies for Handling Misses and Hits:
- When reading (read miss), the query searches for the desired row first in the caches of neighboring processors, then moving to the main memory if the necessary state is missing in the cache.
- Write miss means loading a string from memory with subsequent modification and transfer to the Modified state.
Initialization and Cache Management:
- The initial state of all cache lines is Invalid.
- The read and write functions perform a status check, allowing you to process requests correctly without excessive bus access.
These mechanisms significantly improve data consistency in multiprocessor systems and optimize reading and writing processes in conditions of high competition for resources.
- Cache in multiprocessor systems. Cache coherence. MESI Protocol (https://habr.com/ru/articles/183834 /) - Habr (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Communication protocol (https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Communication_protocol ) - Wikipedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Cache computing (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_ (computing)) - Wikipedia (dateof access: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF protocol (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MESIF_protocol ) - Wikipedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Cache coherence protocols (examples) (https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_coherency_protocols_ (examples)) - Wikipedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- MESI Cache Coherency Protocol (https://www.scss.tcd.ie/Jeremy.Jones/vivio/caches/MESIHelp.htm) - VivioJS (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF (https://dbpedia.org/page/MESIF_protocol ) - DBpedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF Memory Coherence Protocol (https://studopedia.ru/18_51713_protokol-kogerentnosti-pamyati-MESIF.html ) - Studopedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF Cache Coherency Protocol 2012.pdf (https://www.scss.tcd.ie/Jeremy.Jones/vivio/caches/Andrew%20Hay%20MESIF%20Cache%20Coherency%20Protocol%202012.pdf) - Andrew Hay (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Covers.fm (https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/goodman/TechnicalReports/MESIF-2009.pdf ) - (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF protocol (https://www.semanticscholar.org/topic/MESIF-protocol/3555123 ) - Semantic Scholar (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Cache replacement policies (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_replacement_policies ) - Wikipedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Memory II (https://teccxx.neocities.org/mx1/memory2 ) - D.R. Kuvshinov (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Cache Memory (https://books.ifmo.ru/file/pdf/883.pdf ) - (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- At least frequently used (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Least_frequently_used ) - Wikipedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
- Line-replaceable unit (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Line-replaceable_unit ) - Wikipedia (date of access: 16/04/2024)
The project is distributed under the MIT license, which allows you to use, copy, modify and distribute this software product both in closed and open form, provided that the authorship is indicated.
Данный репозиторий содержит проект лабораторной работы, посвященной разработке модели подсистемы памяти в симметричной многопроцессорной системе. Приложение реализовано на языке программирования C++ с использованием библиотеки Qt, что обеспечивает кросс-платформенную поддержку и высокую производительность.
- Политики замены кэша: Алгоритмы, используемые для управления кэшем информации, повышая тем самым производительность системы.
- Протокол когерентности: Правила взаимодействия устройств в распределённой системе.
- Протокол MESIF: Протокол когерентности кэша разработанный Intel, предусматривающий 5 состояний каждой строки кэш-памяти.
- Bus snooping: Механизм для отслеживания транзакций по системной шине в целях поддержания когерентности кэша.
- Кэш вычисления: Компонент, который хранит данные для быстрого ответа на будущие запросы.
- Системная шина: Шина, соединяющая основные компоненты компьютерной системы.
- LFU (Least Frequently Used): Алгоритм кэширования, удаляющий из кэша элемент с наименьшей частотой использования.
В настоящем отчете применяют следующие сокращения и обозначения:
- MESI - Модифицированная (M), Эксклюзивная (E), Разделяемая (S), Недействительная (I).
- MESIF - Модифицированная (M), Эксклюзивная (E), Разделяемая (S), Недействительная (I), Прямая (F).
- SMP – симметричные многопроцессорные системы.
- LRU - Least Recently Used (линейно-заменяемый блок).
- LFU - Least Frequently Used (наименее часто используемый).
- RWITM - Read with Intent to Modify.
Протокол MESIF расширяет классический MESI (Modified, Exclusive, Shared, Invalid), введя состояние Forward (F). Это существенно улучшает параллельную обработку, поскольку кэш-линия в состоянии Forward может однократно отвечать на все запросы чтения, что минимизирует сетевой трафик и конфликты доступа.
- Преимущества Forward State:
- Снижение количества трафика благодаря централизованному ответу кэша.
- Программная локализация данных увеличивает вероятность повторного использования данных без дополнительных запросов.
- Переход Forward состояния к новейшей копии улучшает временную локальность и эффективность кэширования.
Алгоритм LFU (Least Frequently Used), использованный в данной работе, оптимизирует управление кэшем за счет выброса элементов, которые использовались наименее часто, основываясь на количестве обращений, а не времени последнего использования как в LRU.
Стратегии Обработки Промахов и Попаданий:
- При чтении (read miss), запрос ищет нужную строку сначала в кэшах соседних процессоров, переходя затем к основной памяти, если необходиое состояние в кэше отсутствует.
- Запись (write miss) подразумевает загрузку строки из памяти с последующим изменением и переводом в состояние Modified.
Инициализация и Управление Кэшем:
- Исходное состояние всех кэш-линий — Invalid.
- Функции чтения и записи проводят проверку состояний, позволяя корректно обрабатывать запросы без избыточного обращения по шине.
Эти механизмы значительно улучшают согласованность данных в многопроцессорных системах и оптимизируют процессы чтения и записи в условиях высокой конкуренции за ресурсы.
- Кэш в многопроцессорных системах. Когерентность кэша. Протокол MESI (https://habr.com/ru/articles/183834/) - Habr (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Communication protocol (https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Communication_protocol) - Wikipedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Cache computing (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_(computing)) - Wikipedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF protocol (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MESIF_protocol) - Wikipedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Cache coherency protocols (examples) (https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_coherency_protocols_(examples)) - Wikipedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- MESI Cache Coherency Protocol (https://www.scss.tcd.ie/Jeremy.Jones/vivio/caches/MESIHelp.htm) - VivioJS (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF (https://dbpedia.org/page/MESIF_protocol) - DBpedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Протокол когерентности памяти MESIF (https://studopedia.ru/18_51713_protokol-kogerentnosti-pamyati-MESIF.html) - Студопедия (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF Cache Coherency Protocol 2012.pdf (https://www.scss.tcd.ie/Jeremy.Jones/vivio/caches/Andrew%20Hay%20MESIF%20Cache%20Coherency%20Protocol%202012.pdf) - Andrew Hay (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Covers.fm (https://www.cs.auckland.ac.nz/goodman/TechnicalReports/MESIF-2009.pdf) - (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- MESIF protocol (https://www.semanticscholar.org/topic/MESIF-protocol/3555123) - Semantic Scholar (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Cache replacement policies (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_replacement_policies) - Wikipedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Память II (https://teccxx.neocities.org/mx1/memory2) - Кувшинов Д.Р. (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Cache Memory (https://books.ifmo.ru/file/pdf/883.pdf) - (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Least frequently used (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Least_frequently_used) - Wikipedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
- Line-replaceable unit (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Line-replaceable_unit) - Wikipedia (дата обращения: 16/04/2024)
Проект распространяется под лицензией MIT, что позволяет использовать, копировать, модифицировать и распространять данный программный продукт как в закрытой, так и в открытой форме, при условии указания авторства.