- Add Trackier SDK to your app
- Implement and initialize the SDK
- Events Tracking
- Defer Start SDK
- Disable Organic Tracking
- Uninstall Tracking
- SDK Signing
- Keys Hiding
- Deeplinking Android
- Getting Campaign Data
- Proguard Settings
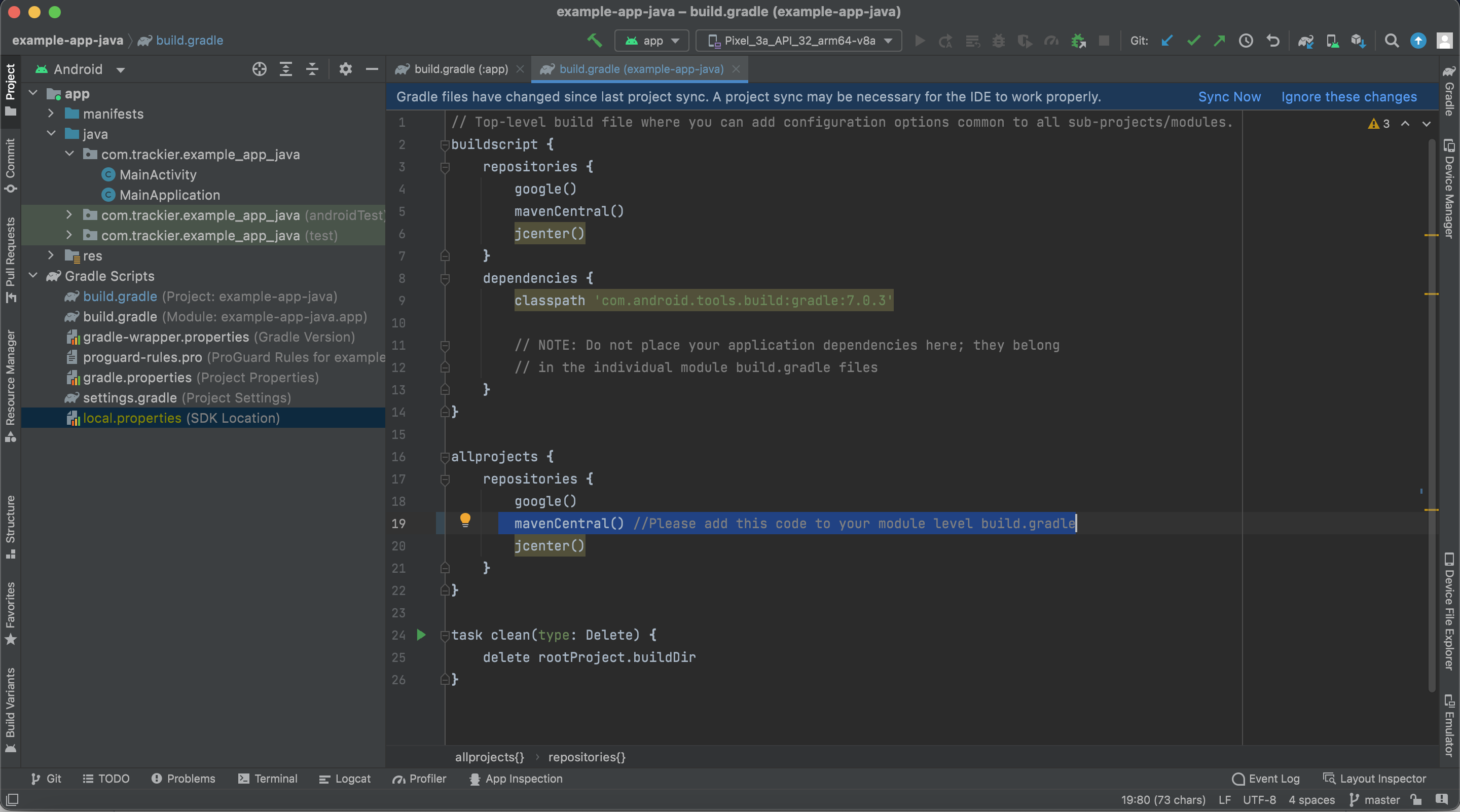
Add the code below to Module level app build.gradle before dependencies
repositories {
mavenCentral() // Please add this code to your module level build.gradle
}Below are the for screenshot reference.
Screenshot[1]
You can find the latest version here
implementation 'com.trackier:android-sdk:1.6.60' // Add this Trackier SDK dependency in the build.gradleAlso, please check the screenshot[2] in the below section for reference.
Add the Android Install Referrer as a dependency. You can find the latest version here
dependencies {
// make sure to use the latest SDK version:
// https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.trackier/android-sdk
implementation 'com.trackier:android-sdk:1.6.60' // Add this Trackier SDK dependency in the build.gradle
implementation 'com.android.installreferrer:installreferrer:2.2' // Add this install referrer dependency in the build.gradle
}Sync the project to retrieve the dependencies – see the following screenshot.
Screenshot[2]

dependencies {
// ...
implementation "com.miui.referrer:homereferrer:1.0.0.6"
}
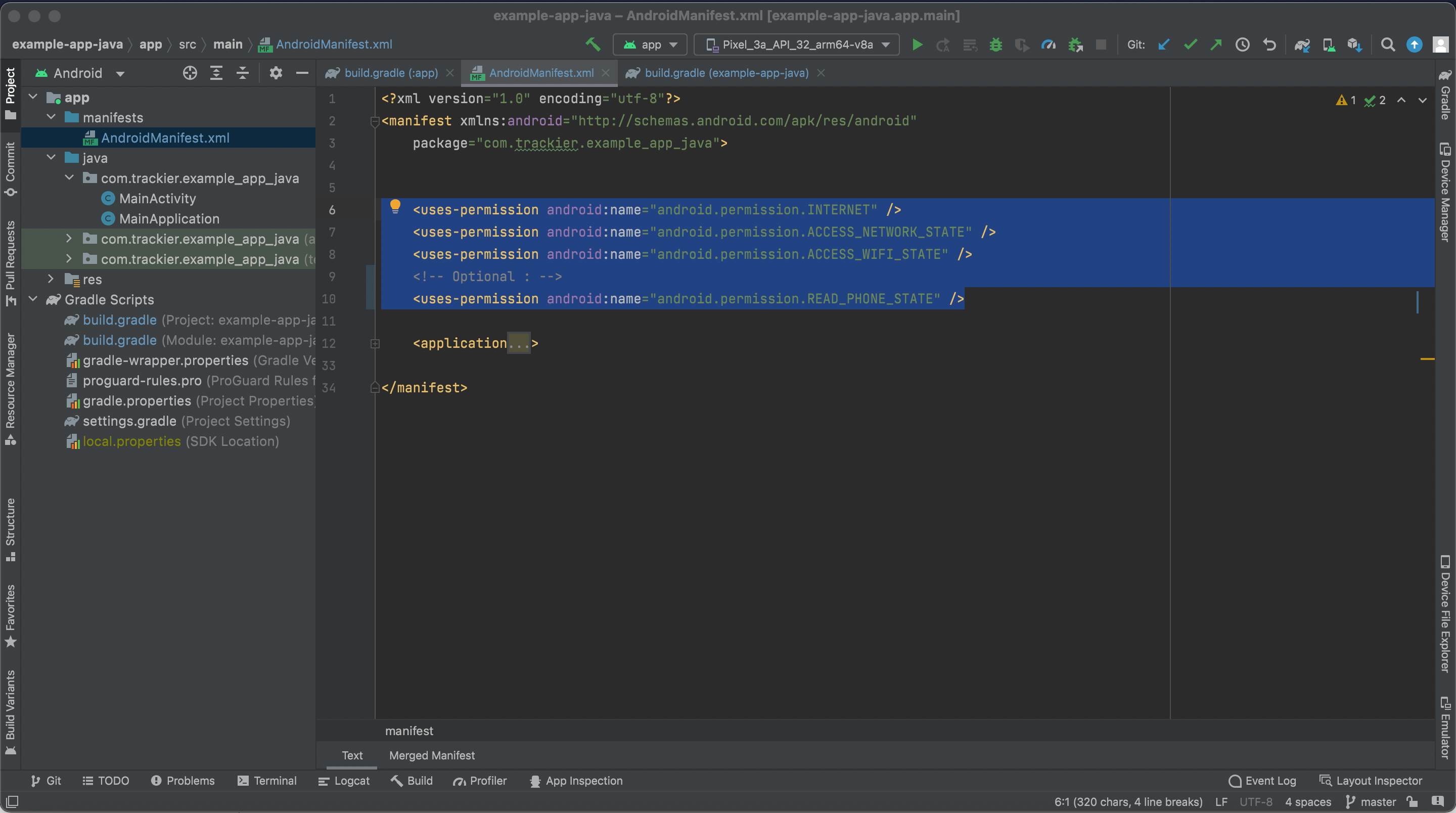
Trackier SDK need the following below permission in the manifest.xml.
Please add the below permission in your app project manifest.xml. if they are not added.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<!-- Optional : -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE" />Below are the Screenshot for the reference
Screenshot[3]
Trackier SDK need the advertising id from the application.
For achieving this, you need to add some line of code in the build.gradle and also in Manifest.xml for read the Advertising id from the application which is mentioned below
- Add the google advertising id dependency in your app build.gradle
dependencies {
// This can be added where the SDK dependency has been added
implementation 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-ads-identifier:18.0.1'
}Below are the Screenshot for the reference
ScreenShot[4]
- Update your Android Manifest file by adding the following permission. This is required if your app is targeting devices with android version 12+
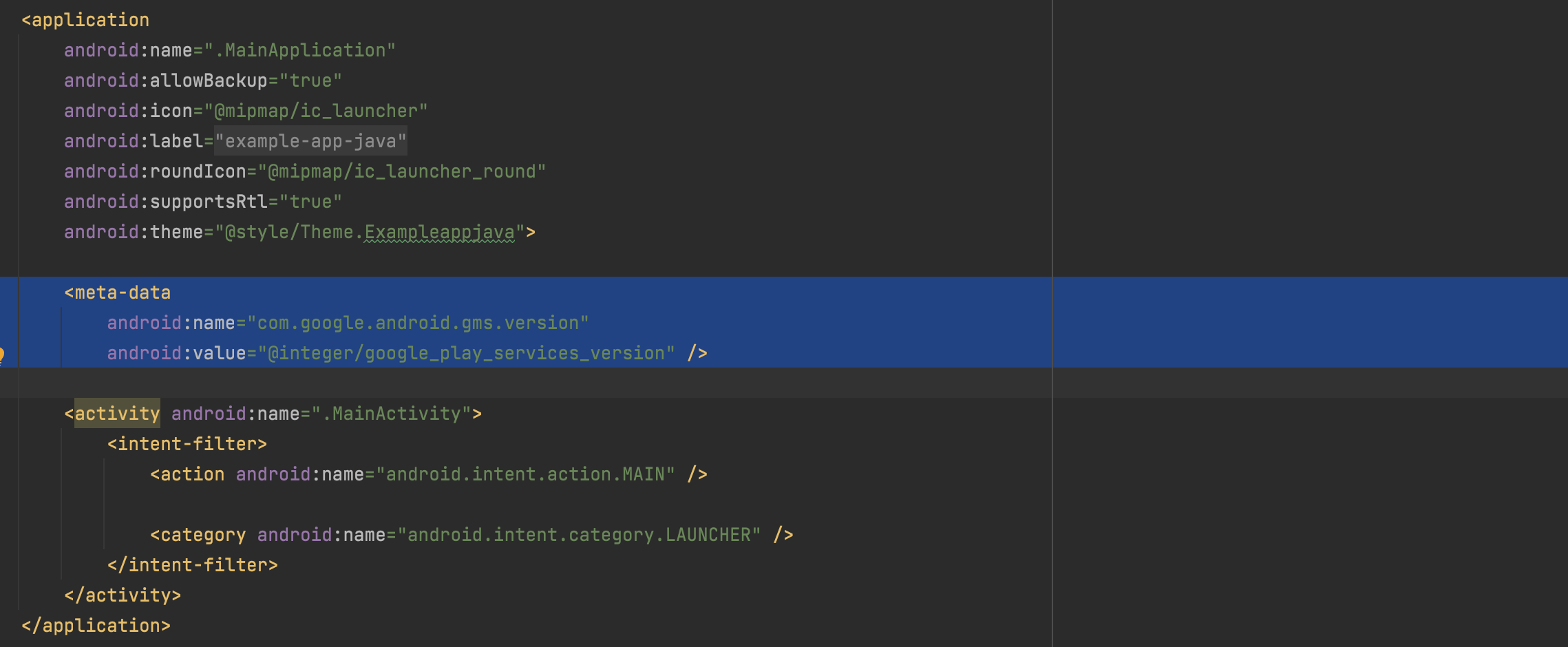
<uses-permission android:name="com.google.android.gms.permission.AD_ID"/>- Add meta data inside the application tag (If not already added)
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> // Add this meta-data in the manifest.xml under Application tag.Below are the screenshot of application tag in manifest.xml for the reference
Screenshot[5]
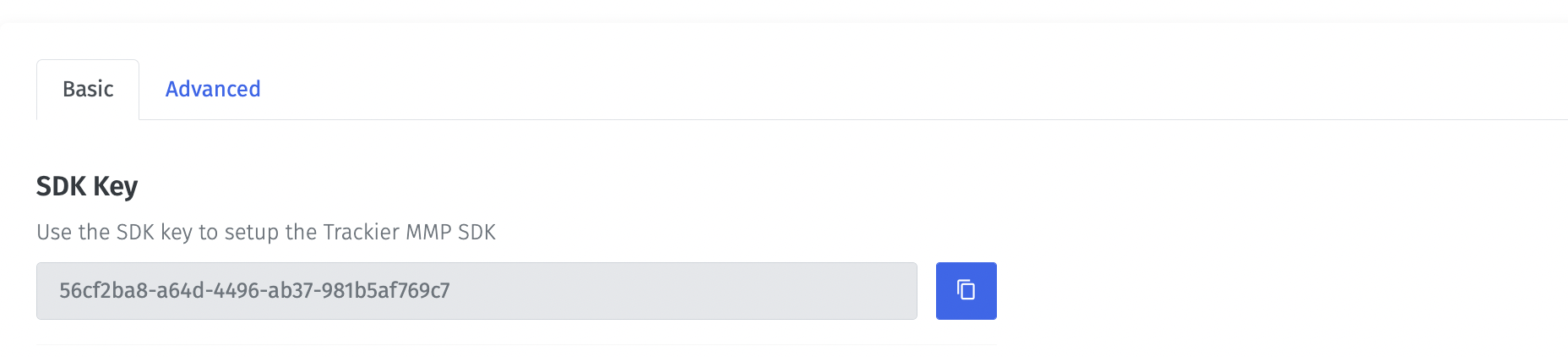
For initialising the Trackier SDK. First, We need to generate the SDK key from the Trackier MMP panel.
Following below are the steps to retrieve the SDK key:-
- Login your Trackier Panel and select your application.
- In the Dashboard, Click on the
SDK Integrationoption on the left side of panel. - Under on the SDK Integration, You will be get the SDK Key.
After follow all steps, Your SDK key look like the below screenshot
Screenshot[6]
We recommend initializing the SDK inside the app’s global application class. This allows the SDK to initialize in all scenarios, including deep linking.
For initializing the SDK in your app project. Add the initialize function code in the global application class.
If your project app does not have application class in your project. Follow the below steps
- Create a new class that extends the
Application - Open the
AndroidManifest.xmlfile of your project app and find the<application>elements - Add the attribute
android:nameand set it to the name of your new application class.
In our Trackier example app, we use Application class named as MainApplication.
We configured the manifest file as like mentioned in below:-
<application
android:name=".MainApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Exampleappjava">
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
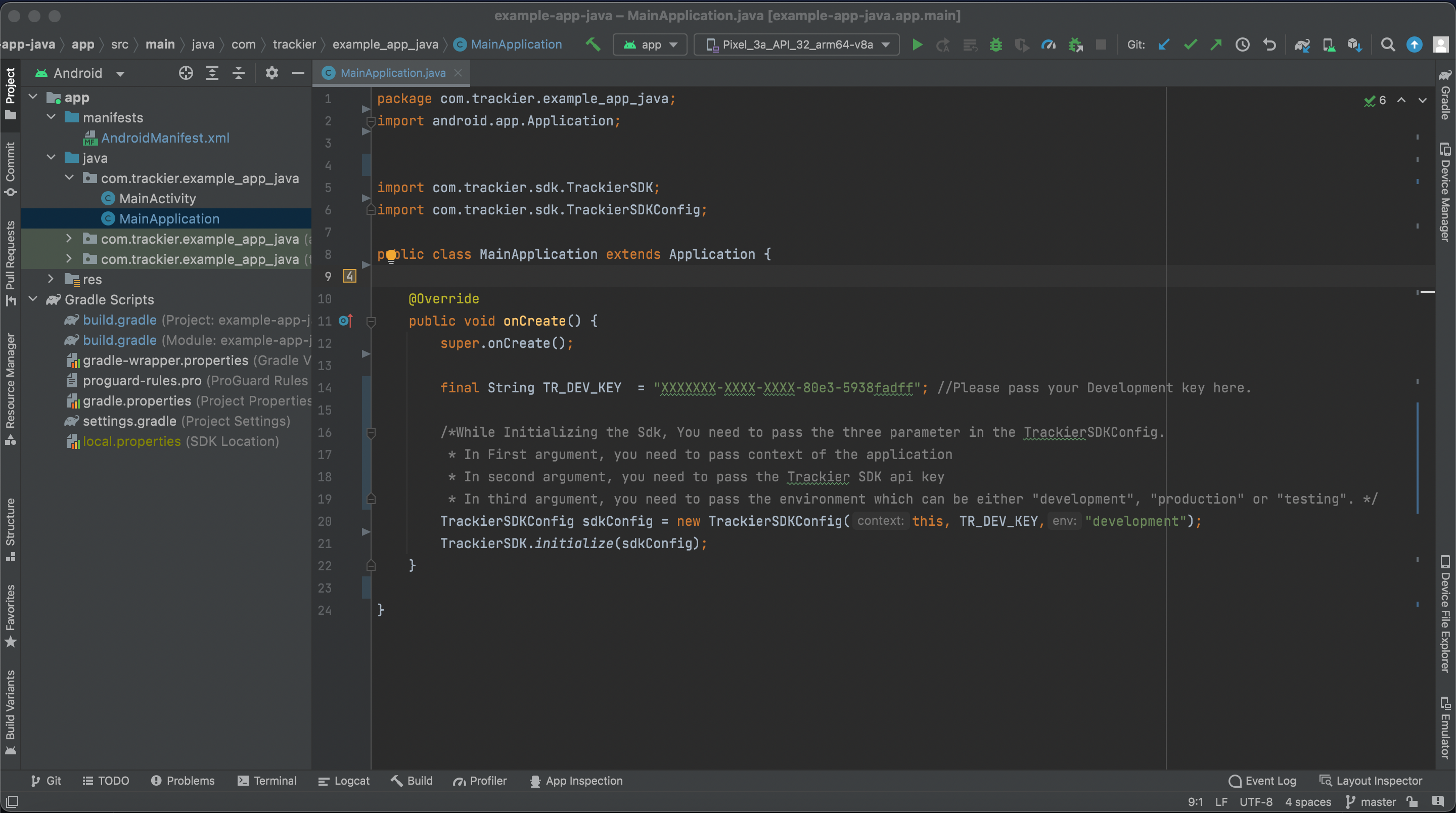
After following the above steps, you need to add the following code in the MainApplication class under onCreate() method.
Check the below example code for the SDK initializations.
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig;
public class MainApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
final String TR_SDK_KEY = "XXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-80e3-5938fadff"; // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
TrackierSDKConfig sdkConfig = new TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY,"development");
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig);
}
}
Screenshot for the above initializing code:-
Screenshot[7]
Important: it is crucial to use the correct SDK key when initializing the SDK. Using the wrong SDK key or an incorrect SDK key impact all traffic sent from the SDK and cause attribution and reporting issues.
We recommend initializing the SDK inside the app’s global application class. This allows the SDK to initialize in all scenarios, including deep linking.
For initializing the SDK in your app project. Add the initialize function code in the global application class.
If your project app does not have application class in your project. Follow the below steps
- Create a new class that extends the
Application - Open the
AndroidManifest.xmlfile of your project app and find the<application>elements - Add the attribute
android:nameand set it to the name of your new application class.
In our Trackier example app, we use Application class named as MainApplication.
We configured the manifest file as like mentioned in below:-
<application
android:name=".MainApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Exampleappkotlin">
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.gms.version"
android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" />
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
After following the above steps, you need to add the following code in the MainApplication class under onCreate() method.
Check the below example code for the SDK initializations.
import android.app.Application
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig
class MainApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
val TR_SDK_KEY: String = "xxxx-xx-4505-bc8b-xx" // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
val sdkConfig = TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY, "development")
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig)
}
}
Screenshot for the above initializing code of Trackier example app:-
Important: it is crucial to use the correct SDK key when initializing the SDK. Using the wrong SDK key or an incorrect SDK key impact all traffic sent from the SDK and cause attribution and reporting issues.
Trackier events trackings enable to provides the insights into how to user interacts with your app. Trackier SDK easily get that insights data from the app. Just follow with the simple events integration process
Trackier provides the Built-in events and Customs events on the Trackier panel.
Built-in Events - Built-in events are the list of constants events which already been created on the dashboard. You can use directly to track those events. Just need to implements events in the app projects.
Screenshot[9]

import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierEvent;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button eventTrack, eventTrackWithCurrency;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
eventTrack =(Button) findViewById(R.id.event_track);
eventTrack.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
eventsTracking();
}
});
}
private void eventsTracking(){
// Below are the example of built-in events function calling
// The arguments - "TrackierEvent.LOGIN" passed in the Trackier event class is Events id
TrackierEvent event = new TrackierEvent(TrackierEvent.LOGIN);
/* Below are the function for the adding the extra data,
You can add the extra data like login details of user or anything you need.
We have 10 params to add data, Below 5 are mentioned */
event.param1 = "Param 1";
event.param2 = "Param 2";
event.param3 = "Param 3";
event.param4 = "Param 4";
event.param5 = "Param 5";
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event);
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: event_track ");
}
}Note:- Argument in Trackier event class is event Id.
You can integrate inbuilt params with the event. In-built param list are mentioned below:-
orderId, revenue, currency, param1, param2, param3 ,param4, param5, param6, param7, param8, param9, param10.
import android.os.*
import android.util.Log
import android.widget.Button
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierEvent
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val btn_event_track = findViewById(R.id.event_track) as Button
val btn_event_curr_track = findViewById<Button>(R.id.event_curr_track)
btn_event_track.setOnClickListener {
eventsTracking()
}
}
fun eventsTracking(){
// Below are the example of built-in events function calling
// The arguments - "TrackierEvent.LOGIN" passed in the Trackier event class is Events id.
val event = TrackierEvent(TrackierEvent.LOGIN)
/* Below are the function for the adding the extra data,
You can add the extra data like login details of user or anything you need.
We have 10 params to add data, Below 5 are mentioned */
event.param1 = "Param 1";
event.param2 = "Param 2";
event.param3 = "Param 3";
event.param4 = "Param 4";
event.param5 = "Param 5";
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event)
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: event_track ")
}
}
Note:- Argument in Trackier event class is event Id.
You can integrate inbuilt params with the event. In-built param list are mentioned below:-
orderId, revenue, currency, param1, param2, param3 ,param4, param5, param6, param7, param8, param9, param10.
Customs Events - Customs events are created by user as per their required business logic. You can create the events in the Trackier dashboard and integrate those events in the app project.
Screenshot[10]

import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierEvent;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button eventTrack;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
eventTrack =(Button) findViewById(R.id.event_track);
eventTrack.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
customEventsTracking();
}
});
}
private void customEventsTracking(){
// Below are the example of customs events function calling
// The arguments - "sEMWSCTXeu" passed in the event class is Events id
TrackierEvent event = new TrackierEvent("sEMWSCTXeu");
/* Below are the function for the adding the extra data,
You can add the extra data like login details of user or anything you need.
We have 10 params to add data, Below 5 are mentioned */
event.param1 = "Param 1";
event.param2 = "Param 2";
event.param3 = "Param 3";
event.param4 = "Param 4";
event.param5 = "Param 5";
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event);
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: event_track ");
}
}
mport android.os.*
import android.util.Log
import android.widget.Button
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierEvent
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val btn_event_track = findViewById(R.id.event_track) as Button
val btn_event_curr_track = findViewById<Button>(R.id.event_curr_track)
btn_event_curr_track.setOnClickListener {
customEventsTrcking()
}
}
fun customEventsTrcking() {
// Below are the example of customs events function calling
// The arguments - "sEMWSCTXeu" passed in the event class is Events id
val event = TrackierEvent("sEMWSCTXeu")
/* Below are the function for the adding the extra data,
You can add the extra data like login details of user or anything you need.
We have 10 params to add data, Below 5 are mentioned */
event.param1 = "Praram Name";
event.param2 = "Param 2";
event.param3 = "Param 3";
event.param4 = "Param 4";
event.param5 = "Param 5";
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event)
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: event_curr_track ")
}
}
Trackier allow user to pass the revenue data which is generated from the app through Revenue events.
It is mainly used to keeping record of generating revenue from the app and also you can pass currency as well.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button eventTrack;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
eventTrack =(Button) findViewById(R.id.event_track);
eventTrack.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
revenueEventsTracking();
}
});
}
private void revenueEventsTracking(){
// Below are the example of inbuilt events function calling
// The arguments - "TrackierEvent.LOGIN" passed in the event class is Events id
TrackierEvent event = new TrackierEvent("sEMWSCTXeu");
// Passing the revenue events be like below example
event.revenue = 2.5; // Pass your generated revenue here.
event.currency = "USD"; // Pass your currency here.
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event);
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: event_track ");
}
}
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val btn_event_track = findViewById(R.id.event_track) as Button
val btn_event_curr_track = findViewById<Button>(R.id.event_curr_track)
btn_event_curr_track.setOnClickListener {
revenueEventsTrcking()
}
}
fun revenueEventsTrcking() {
// Below are the example of customs events function calling
// The arguments - "sEMWSCTXeu" passed in the event class is Events id
val event = TrackierEvent("sEMWSCTXeu")
// Passing the revenue events be like below example
event.revenue = 2.5 // Pass your generateed revenue here.
event.currency = "USD" // Pass your currency here.
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event)
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: event_curr_track ")
}
}
private void customEventsTracking(){
// Below are the example of inbuilt events function calling
// The arguments - "TrackierEvent.LOGIN" passed in the event class is Events id
TrackierEvent event = new TrackierEvent("sEMWSCTXeu");
// Passing the extra data through customs params
HashMap<String,Object> eventCustomParams= new HashMap<>();
eventCustomParams.put("customParam1","xxxxxx");
eventCustomParams.put("customParam2","xxxxxx");
event.ev = eventCustomParams; // Pass the reference to the ev
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event);
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: event_track ");
}- First create a mutable map
- Pass its reference to event.ev param of event
- Pass event reference to trackEvent method of TrackierSDK
Trackier allows to pass additional data like Userid, Email to SDK so that same can be correlated to the Trackier Data and logs.
Just need to pass the data of User Id, Email Id and other additional data to Trackier SDK function which is mentioned below:-
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button eventTrack, eventTrackWithCurrency;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
userDetails();
}
private void userDetails(){
TrackierEvent event = new TrackierEvent("sEMWSCTXeu");
TrackierSDK.setUserId("XXXXXXXX"); // Pass the UserId values here
TrackierSDK.setUserEmail("abc@gmail.com"); // Pass the user email id in the argument.
TrackierSDK.setUserName("abc");
TrackierSDK.setUserPhone("983293829");
/* Passing the additional data */
HashMap<String,Object> userDetails = new HashMap<>();
userDetails.put("Name","Sanu"); // You can pass the Username data.
userDetails.put("UserMobile","873287XXXX"); // You can pass user mobile number
TrackierSDK.setUserAdditionalDetails(userDetails);
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event);
}
}
import android.os.*
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
userDetails()
}
fun userDetails(){
/* Passing the UserId and UserEmail Data */
TrackierSDK.setUserId("XXXXXXXX") // Pass the UserId values here
TrackierSDK.setUserEmail("abc@gmail.com") // Pass the user email id in the argument.
/* Passing the Additional Data */
val userAdditionalDetails: MutableMap<String,Any> = mutableMapOf()
userAdditionalDetails.put("UserName","ABC") // You can pass the Username data.
userAdditionalDetails.put("MobileNumber","8878328XXX") // You can pass user mobile number
TrackierSDK.setUserAdditionalDetails(userAdditionalDetails) // Pass the userAdditionalDetails reference in this method.
}
}
Trackier allow for passing the additional user details like UserName, Mobile Number, UserAge, UserGender etc. . You need to first make a hashmap and pass it in setUserAdditionalDetails function. The example are in mentioned below
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.Button;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button eventTrack, eventTrackWithCurrency;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
userDetails();
}
private void userDetails(){
HashMap<String,Object> userDetails = new HashMap<>();
userDetails.put("Name","Sanu"); // You can pass the Username data.
userDetails.put("UserMobile","873287XXXX"); // You can pass user mobile number
TrackierSDK.setUserAdditionalDetails(userDetails);
}
}import android.os.*
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
userDetails()
}
fun userDetails(){
val userAdditionalDetails: MutableMap<String,Any> = mutableMapOf()
userAdditionalDetails.put("UserName","ABC") // You can pass the Username data.
userAdditionalDetails.put("MobileNumber","8878328XXX") // You can pass user mobile number.
TrackierSDK.setUserAdditionalDetails(userAdditionalDetails) // Pass the userAdditionalDetails reference in this method.
}
}
Trackier uninstall functionality is used to track the uninstall of the application from the devices. It is very useful for tracking the quality of the user.
private FirebaseAnalytics mFirebaseAnalytics;
FirebaseAnalytics mFirebaseAnalytics = FirebaseAnalytics.getInstance(this);
mFirebaseAnalytics.setUserProperty("ct_objectId", Objects.requireNonNull(TrackierSDK.getTrackierId())); - Add the above code to your app to set up a common identifier.
- Set the
app_removeevent as a conversion event in Firebase. - Use the Firebase cloud function to send uninstall information to Trackier MMP.
- You can find the support article here.
It is customized way to initialized the sdk. It is required when you need to fire the install in specific page. After implementing this feature, SDK will not initialize on the time of application open.
import android.app.Application;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
final String TR_SDK_KEY = "XXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-80e3-5938fadff"; // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
TrackierSDKConfig sdkConfig = new TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY, "development");
// Passing User Information on time of initialization
sdkConfig.setManualMode(true);
TrackierSDK.setLocalRefTrack(true, "_");
TrackierSDK.setUserId("XXXXXXXX"); // Pass the UserId values here
TrackierSDK.setUserEmail("abc@gmail.com"); // Pass the user email id in the argument.
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig);
}
}
import android.app.Application
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig
import kotlin.reflect.jvm.internal.impl.load.kotlin.JvmType
class MainApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
val TR_SDK_KEY: String = "xxxx-xx-4505-bc8b-xx" // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
val sdkConfig = TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY, "development")
sdkConfig.setManualMode(true)
TrackierSDK.setLocalRefTrack(true,"_")
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig)
// Passing User Information on time of initialization
TrackierSDK.setUserId("XXXXXXXX") // Pass the UserId values here
TrackierSDK.setUserEmail("abc@gmail.com") // Pass the user email id in the argument.
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig)
}
}
- Set manual mode to true by passing true boolean value to setManualMode.
- The second method is to associate user email in which .
Note:- Make sure to take EXTERNAL_STORAGE_READ permission before enabling this feature. For reference you can see example directory
Now you can explicitly fire Install whenever desired,
TrackierSDK.fireInstall(); // Call this function on the specific Activity, wherever you want to fire the install. TrackierSDK.fireInstall() // Call this function on the specific Activity, wherever you want to fire the install.
This features is used to disable the Organic traffic. Just need to call the sdkConfig.disableOrganicTracking(true); function and pass boolean true value in it.
Please follow the below example:-
import android.app.Application;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
final String TR_SDK_KEY = "XXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-80e3-5938fadff"; // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
TrackierSDKConfig sdkConfig = new TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY, "development");
sdkConfig.disableOrganicTracking(true); // Pass true value for disable organic tracking.
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig);
}
}
import android.app.Application
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig
import kotlin.reflect.jvm.internal.impl.load.kotlin.JvmType
class MainApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
val TR_SDK_KEY: String = "xxxx-xx-4505-bc8b-xx" // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
val sdkConfig = TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY, "development")
sdkConfig.disableOrganicTracking(true); // Pass true value for disable organic tracking/
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig)
}
}
Following below are the steps to retrieve the secretId and secretKey :-
- Login your Trackier Panel and select your application.
- In the Dashboard, click the three dot in left bottom.
- You can see the SDK key there and click on Advanced tab to generate the Id and Key.
- Click on the Add secret key button to generate the Id and key.
Please check on the below screenshot
Screenshot[11]

Check below the example code for passing the secretId and secretKey to the SDK
import android.app.Application;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainApplication extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
final String TR_SDK_KEY = "XXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-80e3-5938fadff"; // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
TrackierSDKConfig sdkConfig = new TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY, "development");
sdkConfig.disableOrganicTracking(true); // Pass true value for disable organic tracking.
/* For SDK Signing */
sdkConfig.setAppSecret("xxxx","xxxx-xxx"); // Pass the secretId and secretKey
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig);
}
}
import android.app.Application
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig
import kotlin.reflect.jvm.internal.impl.load.kotlin.JvmType
class MainApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
val TR_SDK_KEY: String = "xxxx-xx-4505-bc8b-xx" // Please pass your SDK key here.
/* While Initializing the SDK, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
val sdkConfig = TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_SDK_KEY, "development")
sdkConfig.disableOrganicTracking(true); // Pass true value for disable organic tracking/
/* For SDK Signing */
sdkConfig.setAppSecret("xxxx","xxxx-xxx") // Pass the secretId and secretKey
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig)
}
}
1. Hiding the keys using NDK. Just follow the below steps for hiding SDK Key, Secret ID and Secert Key.
1.Add plugin to your module level build.gradle:
id "com.klaxit.hiddensecrets" version "0.2.0"
It will look like the below code
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'org.jetbrains.kotlin.android'
id "com.klaxit.hiddensecrets" version "0.2.0"
}
Then sync project with gradle files. When you open the gradle tasks, you will see that hideSecret task is available
Screenshot:

- Then run the following command for hiding Keys:
SDK Key:
./gradlew hideSecret -Pkey=pass_your_sdkkey -PkeyName=SDKKey
Secret Id:
./gradlew hideSecret -Pkey=pass_your_secretId -PkeyName=SecretId
Secret Key:
./gradlew hideSecret -Pkey=pass_your_secretKey -PkeyName=SecretKey
keyName parameter is optional, a random name is generated by default. You could also provide the package name.
You will see that Secrets class is added to your project:
class Secrets {
// Method calls will be added by gradle task hideSecret
// Example : external fun getWellHiddenSecret(packageName: String): String
companion object {
init {
System.loadLibrary("secrets")
}
}
external fun getSDKKey(packageName: String): String
external fun getSecretId(packageName: String): String
external fun getSecretKey(packageName: String): String
}
- Add the following to your module level build.gradle:
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path "src/main/cpp/CMakeLists.txt"
}
}
Then it will look like this:
android {
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path "src/main/cpp/CMakeLists.txt"
}
}
This will enable C++ files compilation. You can get the secret key like this:
val sdkKey = new Secrets().getSDKKey(packageName)
val secretId = new Secrets().getSecretId(packageName)
val secretKey = new Secrets().getSecretKey(packageName)
Create one folder in project under src → main, folder name - jni
- Then, add three below file in jni folder Android.mk Application.mk keys.c
- Then, add the following code in respective file
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := keys
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := keys.c
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
APP_ABI := all
#include <jni.h>
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_myapplication_MainApplication_getKey(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance) {
return (*env)-> NewStringUTF(env, "sanugupta");
}
externalNativeBuild {
ndkBuild {
path "src/main/jni/Android.mk"//path of Android.mk file
}
}
static {
System.loadLibrary("keys");
}
public native String getKey(); //You can create more function accordind to need.
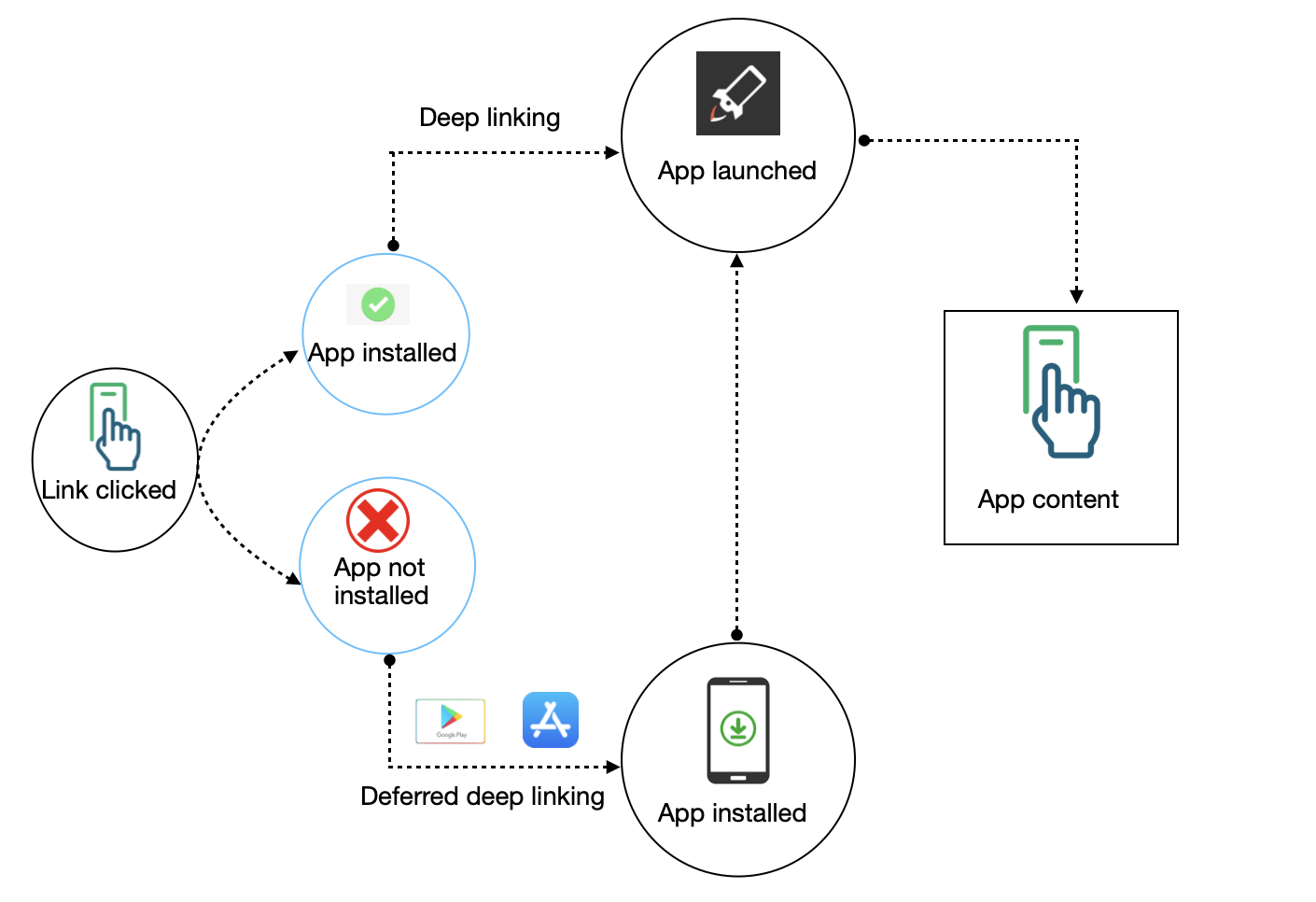
Deep linking is a techniques in which the user directly redirect to the specific pages of the application by click on the deeplink url.
There are two types deeplinking
-
Normal deeplinking - Direct deep linking occurs when a user already has your app installed on their device. When this is the case, the deep link will redirect the user to the screen specified in the link.
-
Deferred deeplinking - Deferred deep linking occurs when a user does not have your app installed on their device. When this is the case, the deep link will first send the user to the device app store to install the app. Once the user has installed and opened the app, the SDK will redirect them to the screen specified in the link.
Please check below the Deeplinking scenario
If a user already has your app on their device, it will open when they interact with a tracker containing a deep link. You can then parse the deep link information for further use. To do this, you need to choose a desired unique scheme name.
You can set up a specific activity to launch when a user interacts with a deep link. To do this:
- Assign the unique scheme name to the activity in your AndroidManifest.xml file.
- Add the intent-filter section to the activity definition.
- Assign an android:scheme property value with your preferred scheme name.
For example, you could set up an activity called FirstActivity to open like this:
<activity
android:name=".Activity.FirstProduct"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:host="trackier.u9ilnk.me"
android:pathPrefix="/product"
android:scheme="https" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
To open your app when a user clicks on a tracker URL, add its scheme name to the Trackier tracker as a deep_link parameter. A tracker URL without any extra information might look like this:
https://trackier.u9ilnk.me/product?dlv=FirstProduct&quantity=10&pid=sms
After follow the above example, your app will open when a user interacts with a trackier URL and it will launch the FirstProduct activity as per our example. You will receive information about the deep_link parameter content inside the FirstProduct class.
The SDK will deliver deep link information within the Intent object of your activity. It uses either the activity's onCreate or onNewIntent methods to do this. Once you have launched your app and triggered one of these methods, you can access the deep link content. You can then use this information in other places in your app.
You can extract deep link content from either of these methods like this:
Using the onCreate method:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.product_first);
Intent intent = getIntent();
Uri data = intent.getData();
// data.toString() -> This is your deep_link parameter value.
if (!(data == null)){
TrackierSDK.parseDeepLink(data);
}
}
Using the onNewIntent method:
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
super.onNewIntent(intent);
Uri data = intent.getData();
// data.toString() -> This is your deep_link parameter value.
}
Deferred deep linking happened, when a user does not have your app installed on their device. When the user clicks a trackier URL, the URL will redirect them to the Play Store to download and install your app. When the user opens the app for the first time, the SDK will read the deep_link content.
The Trackier SDK opens the deferred deep link by default. just need to add some code in application class just after initilazation of Trackier SDk
Below are the example of the code :-
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Intent;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import com.trackier.sdk.DeepLink;
import com.trackier.sdk.DeepLinkListener;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDK;
import com.trackier.sdk.TrackierSDKConfig;
public class MainApplication extends Application {
DeepLinkListener deepLinkListener=new DeepLinkListener() {
@Override
public void onDeepLinking(@NonNull DeepLink deepLink) {
if(deepLink.getDeepLinkValue().equalsIgnoreCase("DeepLinkActivity")){ //This activity/class name should be same as mmp unlink dlv.
Intent intent= new Intent(MainApplication.this, MainActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
};
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
final String TR_DEV_KEY = "XXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-80e3-5938fadff"; //Please pass your Development key here.
/*While Initializing the Sdk, You need to pass the three parameter in the TrackierSDKConfig.
* In First argument, you need to pass context of the application
* In second argument, you need to pass the Trackier SDK api key
* In third argument, you need to pass the environment which can be either "development", "production" or "testing". */
TrackierSDKConfig sdkConfig = new TrackierSDKConfig(this, TR_DEV_KEY, "development");
sdkConfig.setDeepLinkListener(deepLinkListener);
sdkConfig.disableOrganicTracking(true); // Pass true value to disable organic tracking.
TrackierSDK.initialize(sdkConfig);
}
}
For getting the campaign data, We have a function that return the campaign data. Please check below the example code.
eventTrackWithCurrency.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
TrackierEvent event = new TrackierEvent(TrackierEvent.UPDATE);
event.param1 = "Praram Name";
event.revenue = 0.5;
event.currency = "USD";
String ad = TrackierSDK.getAd();
String adId = TrackierSDK.getAdID();
String camp = TrackierSDK.getCampaign();
String campID = TrackierSDK.getCampaignID();
String adSet = TrackierSDK.getAdSet();
String adSetID = TrackierSDK.getAdSetID();
String channel = TrackierSDK.getChannel();
String p1 = TrackierSDK.getP1();
String p2 = TrackierSDK.getP2();
String p3 = TrackierSDK.getP3();
String p4 = TrackierSDK.getP4();
String p5 = TrackierSDK.getP5();
String clickId = TrackierSDK.getClickId();
String dlv = TrackierSDK.getDlv();
String pid = TrackierSDK.getPid();
String isRetargetting = TrackierSDK.getIsRetargeting();
TrackierSDK.trackEvent(event);
Log.d("TAG", "onClick: eventTrackWithCurrency");
}
});
Code for kotlin
btn_event_track.setOnClickListener(View.OnClickListener {
val event = TrackierEvent(TrackierEvent.UPDATE)
event.param1 = "Praram Name"
event.revenue = 0.5
event.currency = "USD"
val ad: String = getAd()
val adId: String = getAdID()
val camp: String = getCampaign()
val campID: String = getCampaignID()
val adSet: String = getAdSet()
val adSetID: String = getAdSetID()
val channel: String = getChannel()
val p1: String = getP1()
val p2: String = getP2()
val p3: String = getP3()
val p4: String = getP4()
val p5: String = getP5()
val clickId: String = getClickId()
val dlv: String = getDlv()
val pid: String = getPid()
val isRetargetting: String = getIsRetargeting()
trackEvent(event)
})It is mandatory to add this setting in android app when your app is using proguard. Add below code in proguard file.
-keep class com.trackier.sdk.** { *; }
-keep class com.google.android.gms.common.ConnectionResult {
int SUCCESS;
}
-keep class com.google.android.gms.ads.identifier.AdvertisingIdClient {
com.google.android.gms.ads.identifier.AdvertisingIdClient$Info getAdvertisingIdInfo(android.content.Context);
}
-keep class com.google.android.gms.ads.identifier.AdvertisingIdClient$Info {
java.lang.String getId();
boolean isLimitAdTrackingEnabled();
}
-keep public class com.android.installreferrer.** { *; }