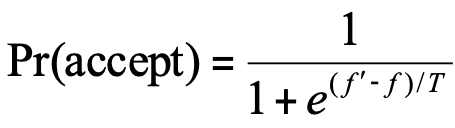This Java tool was coded as an individual project and obtained an A* for the CS2004 Algorithms and their Applications module in the Year 2 of a degree in computer sciences.
Travelling Salesman Problem is an algorithm that calculates the shortest path between two points given a list of data points and the distance between each pair, only visiting each set once and returning to the origin. This TSP tool for Java calculates the shortest path in each of the twenty-seven datasets which have from 48 to 442 data points using the following algorithms:
- Random Mutation Hill Climber
- Random Restart Hill Climber
- Stochastic Hill Climber
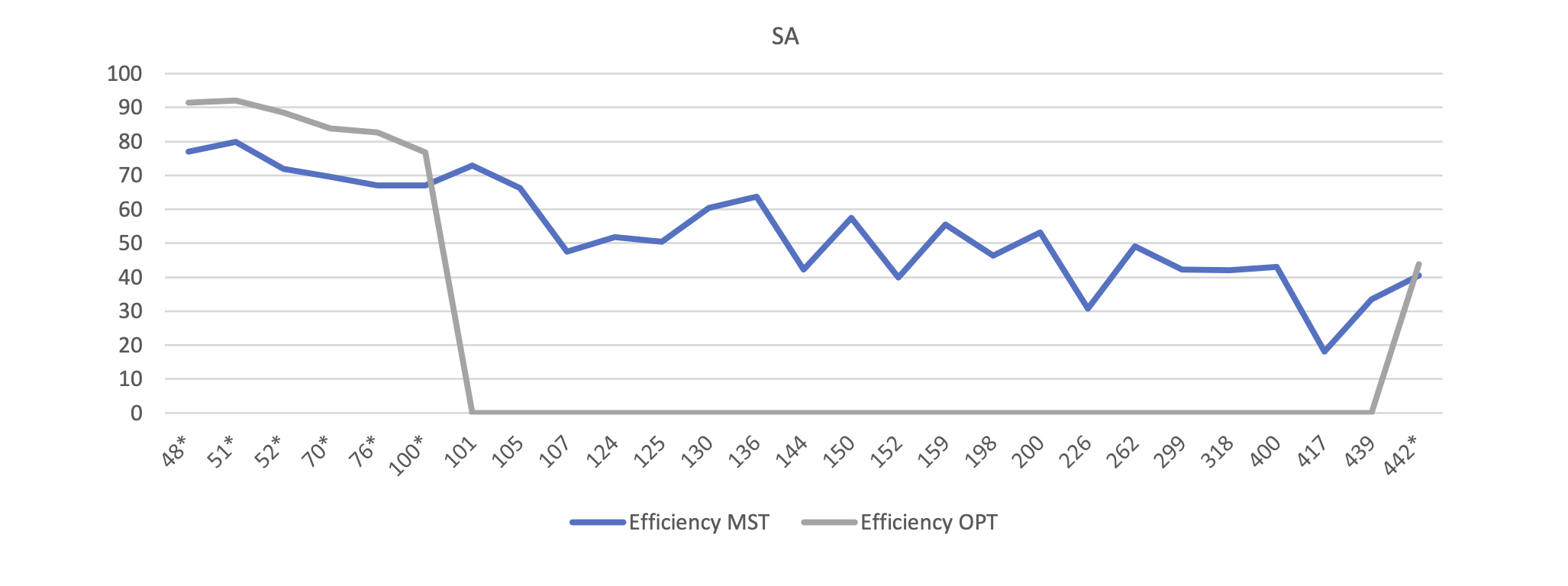
- Simulated Annealing
- MST = Minimum Spanning Tree
- OPT = Optimal solution
- LO1. Understand fundamental issues concerned with computation and algorithms
- LO2. Describe and evaluate both classic algorithms and meta-heuristic algorithms.
- LO3. Successfully implement classic sorting, searching, graph traversal or non-population meta-heuristic algorithms
- LO4. Take real-world problems and identify relevant characteristics to guide the selection of an appropriate algorithm
- Download or clone the repository
- Open the folder with your favourite IDE.
- Go to src/gui/GUI.java
- Run the main method.
- Select the size of the dataset in the top left corner.
- Modify parameters.
- You can either tap START to run all of them or tap on each algorithm lable to run individually.
- Go back to step 2 until you obtian optimal results.
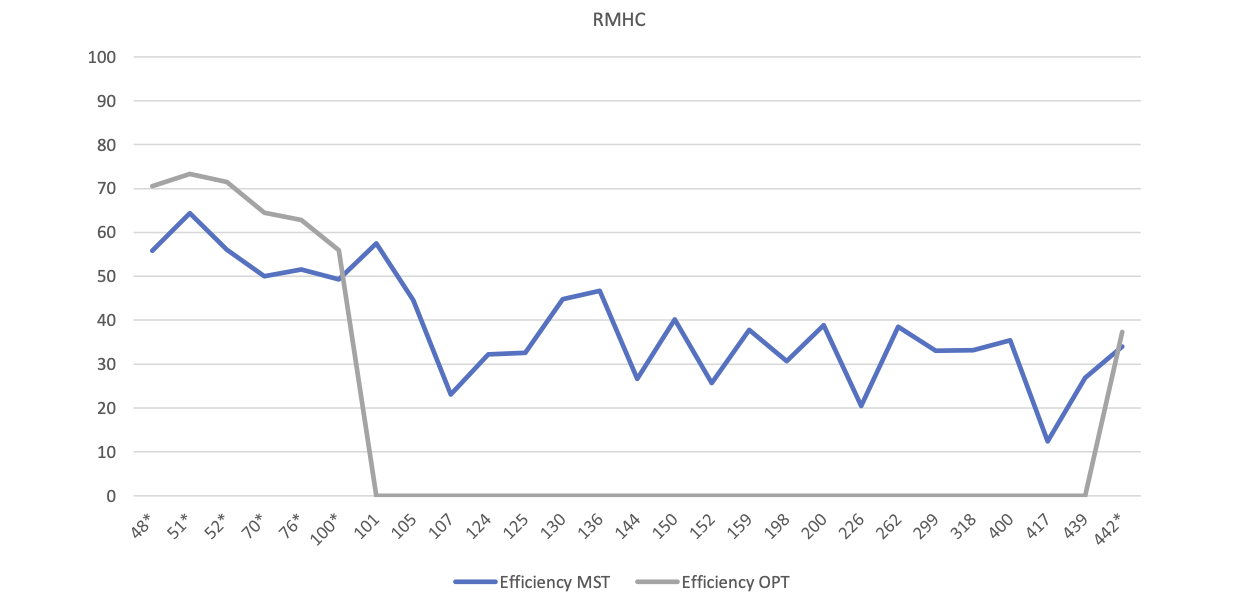
This model fashions a randomly generated path, then apply a small change several times. It is located on src/core/RMHC.java.
- Generate random path
- Apply small change
- Compare fitness
- Store path with lowest fitness
- Repeat “I” times
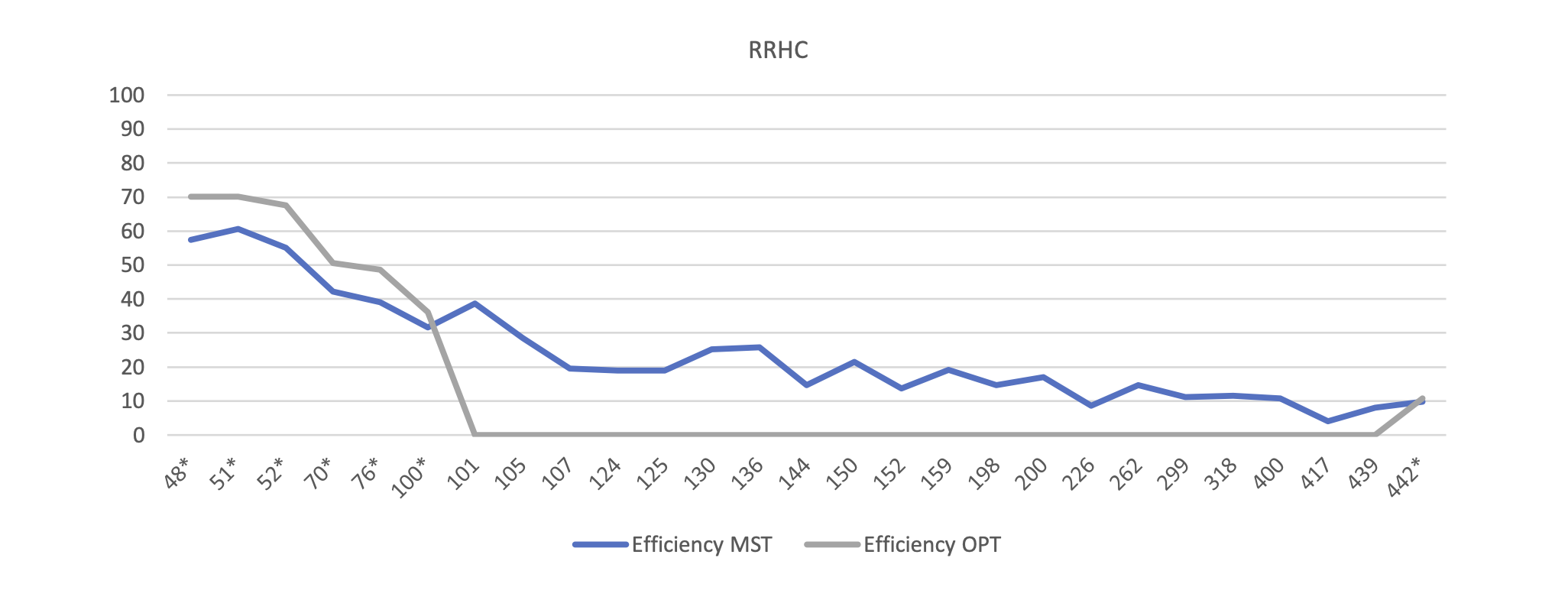
The Random Restart Hill Climber model is an extension of the previous Random Mutation Algorithm. This method run the Random Mutation X times and the Random Mutation produces Y changes to the path. The multiplication of X and Y should be equal to the total number of iterations. It is located on src/core/RRHC.java.
- Generate random path
- Run RMHC Y times
- Choose the most efficient path
- Repeat X times.
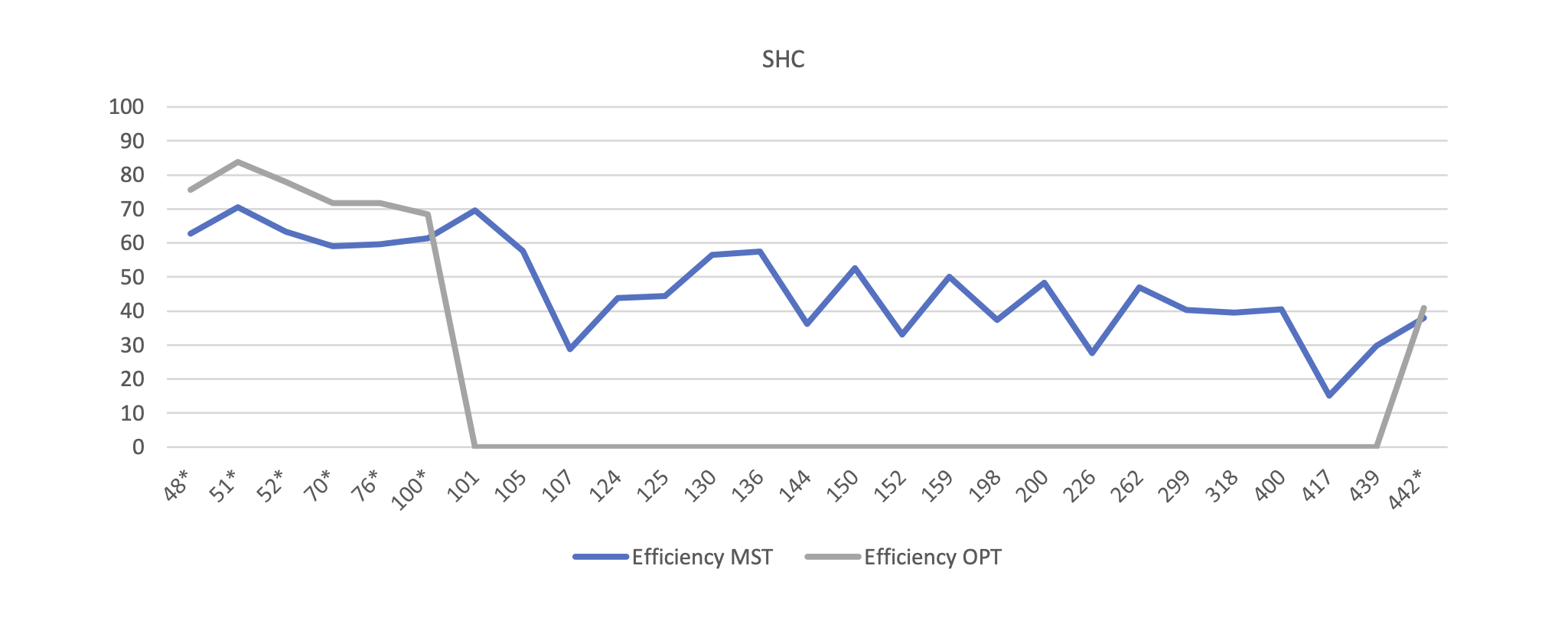
This method works similar the Random Mutation Hill Climber. After applying the small change, it calculates the probability using the new and old fitness in this formula. It is located on src/core/SHC.java.
Then compares the probability with a number randomly generated between 0 and 1. If the probability Is greater than the randomly generated number, the new path is admitted.
Given the optimal temperature for the data set 48 which is 45, I have used the following formula to find the constant which is 1.63x10^-3.
Size * K = T;
This method allows a worse solution to be accepted so that local maximums can be circumnavigated. It contains 3 main parameter that has to be calculated for this method to be more efficient.src/core/SA.java.
- Temperature. This parameter is indicates the initial temperature which should to be high as it will be decreased throughout the process. I have used the following formula to calculate the initial temperature:
Temp = MST – (Size * Max distance) / Any number to scale down
-
Minimum Temperature. This parameter should be as low as possible as it will help to bring the initial temperature down to 0.
-
Cooling Rate. This variable is calculated using the minimum and initial temperature and the number of iterations.