-
objdump is used to disassmble the executable file to get the assembly langauges instructions that are generated after compliation of the source code.
-
The executable file on Linux is called as ELF.(executable and linkable format) Objdump helps in anaylsing the activation records, the ELF headers and in general all the arithematic operations that are performed by the CPU.
$ objdump -d exe # this will disassmble the exe file
$ objdump -D exe # disassamble all the instructions in ELF-
The ELF file contains a single contiguous block of memory which is loaded by kernel code when the process is initiated, and contains the data and instruction for the CPU to execute.
-
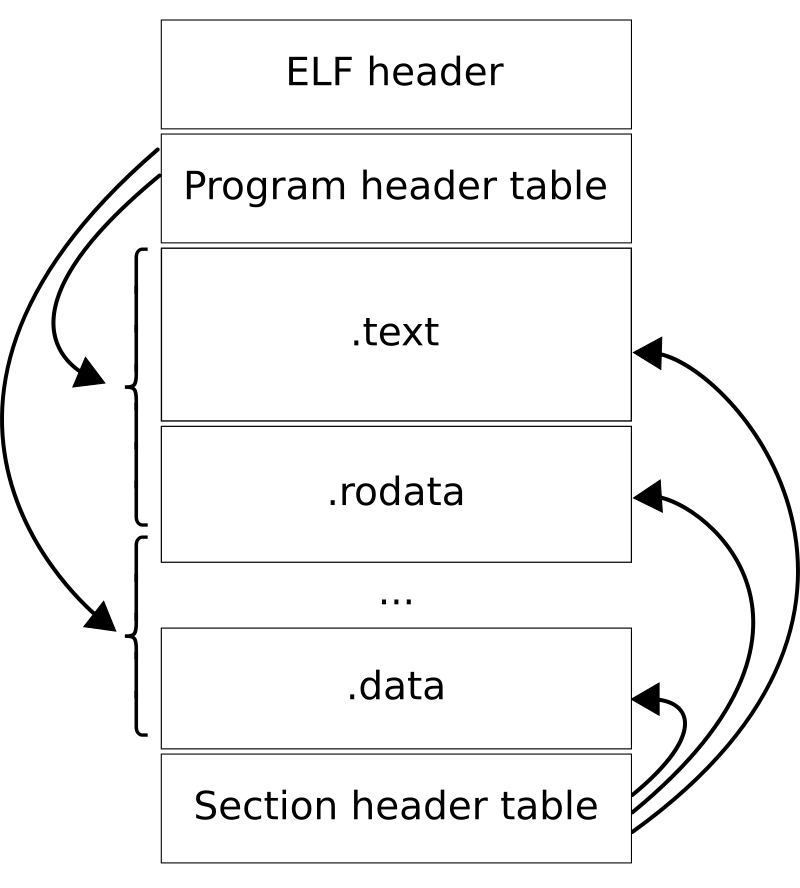
This contiguous block of memory is logically divided into various types parts of memory as given below
-
The ELF file format contains the ELF headers followed by the following data
- Program Header Table
- Section Header Table
- Data which is referred by the entries in the program header table or section header table.
$ objdump --file-headers foo # shows the summary ELF file headers for foo
foo: file format elf64-x86-64
architecture: i386:x86-64, flags 0x00000150:
HAS_SYMS, DYNAMIC, D_PAGED
start address 0x00000000000004f0- Interesting thing to note here is the last attribute called the start address. It is the address of the function which calls the main in the assembly langauge code generate by defualt. This speical function is called as _start function
$ objdump -p foo | less # prints the program headers
foo: file format elf64-x86-64
Program Header:
PHDR off 0x0000000000000040 vaddr 0x0000000000000040 paddr 0x0000000000000040 align 2**3
filesz 0x00000000000001f8 memsz 0x00000000000001f8 flags r--
INTERP off 0x0000000000000238 vaddr 0x0000000000000238 paddr 0x0000000000000238 align 2**0
filesz 0x000000000000001c memsz 0x000000000000001c flags r--
LOAD off 0x0000000000000000 vaddr 0x0000000000000000 paddr 0x0000000000000000 align 2**21
filesz 0x0000000000000820 memsz 0x0000000000000820 flags r-x
LOAD off 0x0000000000000df0 vaddr 0x0000000000200df0 paddr 0x0000000000200df0 align 2**21
filesz 0x0000000000000220 memsz 0x0000000000000228 flags rw-
DYNAMIC off 0x0000000000000e00 vaddr 0x0000000000200e00 paddr 0x0000000000200e00 align 2**3
filesz 0x00000000000001c0 memsz 0x00000000000001c0 flags rw-
NOTE off 0x0000000000000254 vaddr 0x0000000000000254 paddr 0x0000000000000254 align 2**2
filesz 0x0000000000000044 memsz 0x0000000000000044 flags r--
EH_FRAME off 0x00000000000006b4 vaddr 0x00000000000006b4 paddr 0x00000000000006b4 align 2**2
filesz 0x0000000000000044 memsz 0x0000000000000044 flags r--
STACK off 0x0000000000000000 vaddr 0x0000000000000000 paddr 0x0000000000000000 align 2**4
filesz 0x0000000000000000 memsz 0x0000000000000000 flags rw-
RELRO off 0x0000000000000df0 vaddr 0x0000000000200df0 paddr 0x0000000000200df0 align 2**0
filesz 0x0000000000000210 memsz 0x0000000000000210 flags r--
$ objdump -x foo # this shows all headers along with symbol table for foo