Fundamental tools for electrical engineers.
This is the avaliable functions in pyeletrica:
- sind
- cosd
- tand
- polar
- rect
- divI
- ZIbase
- Zparallel
- plot3vectors
- plotmho
- to_linecomp
- to_symcomp
- overcurrent_time
You can use the documentation to understand how the function works .
>>> import pyeletrica as elt
>>> help(elt.to_symcomp)
Help on function to_symcomp in module pyeletrica:
to_symcomp(Va, Vb, Vc, ndigits=3)
Calculate symmetric component vector from line vector.
parameters
----------
Va: array-like
[module, angle (degrees)]
Vb: array-like
[module, angle (degrees)]
Vc: array-like
[module, angle (degrees)]
ndigits: int
Precision in decimal digits.
Returns
-------
output : array-like
(V1, V2, V0), each vector being in array format with
[module, angle in degrees], where V1 is positive sequence,
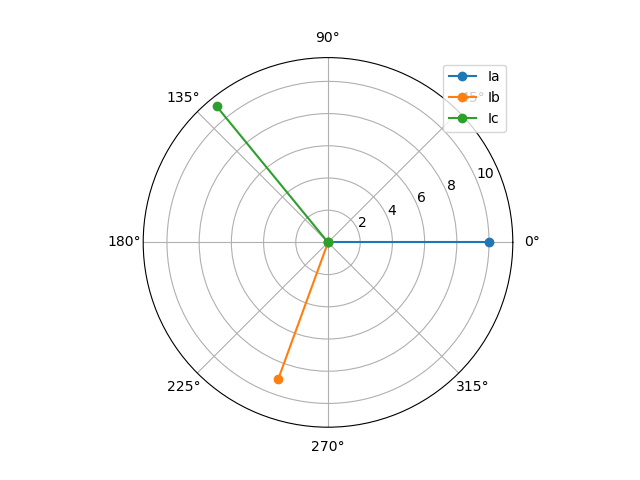
V2 negative sequence and V0 zero sequence.Calculate Symmetric Component from line quantities. Considering the currents Ia = 10∠0° amps, Ib = 9∠-110° amps and Ic = 10.93∠129.3° amps we get I1 = 9.945∠6.407° amps, I2 = 1.116∠0° amps and I0 = 0∠0° amps
In [1]:elt.to_symcomp([10,0],[9,-110],[10.93,129.3])
Out[1]: ([9.945, 6.407], [1.116, 0], [0, 0])Plot vectors.
In [1]: elt.plot3vectors([[10,0], [9,-110], [10.93,129.3]], ['Ia', 'Ib', 'Ic'])Calculate base impedance and base current from apparent power and voltage.
In [1]: Zbase, Ibase = elt.ZIbase(10e6, 69e3)
In [2]: Zbase
Out[2]: 83.67395205646751
In [3]: Ibase
Out[3]: 476.1Complex numbers computation. You must perform complex number operations in Python using the rectangular form.
In [1]: v_sum = elt.rect([10,120]) + elt.rect([10,-120])
In [2]: v_sum
Out[2]: (-10+0j)
In [3]: elt.polar(v_sum)
Out[3]: [10.0, 180.0]