-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Home
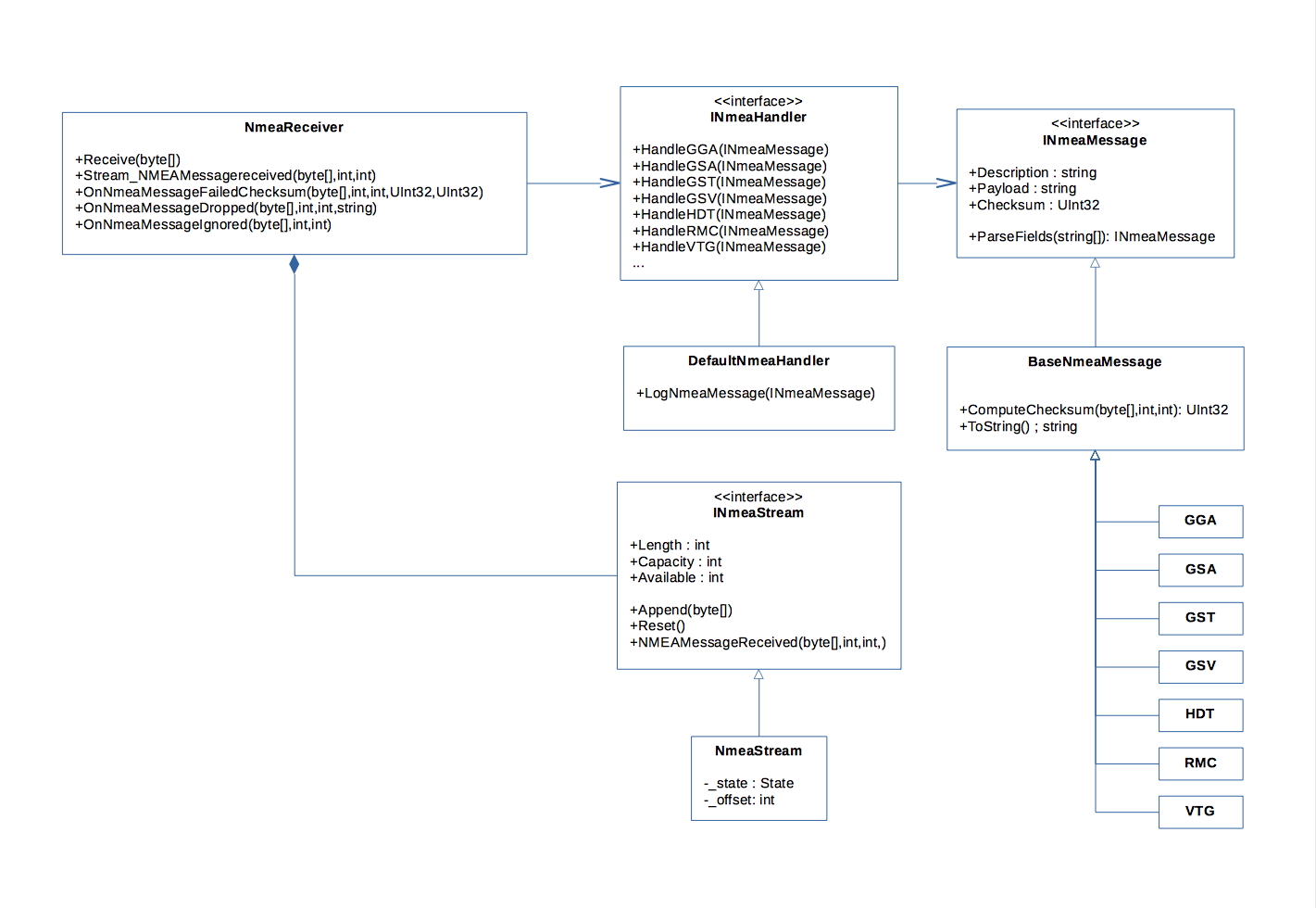
This is a basic NMEA-0183 parser that processes bytes fed into its API. When a complete NMEA sentence is successfully read, application-level handlers are invoked.
There are many implementations of NMEA-0183 parsers out there. This is not about reinventing the wheel, but as an exercise on my part to port NMEA parsing code that I wrote over 12 years ago in C++. The motivation to put this up on Github came after I was invited to apply for work with the condition that I pass a coding tests. Having been on the hiring end of the coding interview, I can say that coding tests are utterly useless when compared to actual code samples on Github. So here I am with samples that - at the very least - depicts my coding style.
This is a clean and fairly easy to extend implementation.
This is the simplest scenario: using the DefaultNmeaHandler class. DefaultNmeaHandler implements the contract INmeaHandler, which defines support for the following NMEA-0183 data types:
- GGA : Global Positioning System Fix Data
- GSA : Satellite status
- GSV : Satellites in view
- GST : GPS Pseudorange Noise Statistics
- HDT : NMEA heading log
- RMC : Recommended Minimum data for gps
- VTG : Track made good and ground speed
DefaultNmeaHandler implements the contract by invoking the event handler LogNmeaMessage each time a supported NMEA sentence is successfully parsed.
// ... Create an object to handle parsed NMEA messages
DefaultNmeaHandler nmeaHandler = new DefaultNmeaHandler();
nmeaHandler.set_OnLogNmeaMessageHandler( new DefaultNmeaHandler.OnLogNmeaMessageHandler() {
@Override
public void OnLogNmeaMessage( String msg ) {
Log.i("NmeaTester","New NMEA Message: " + msg );
}
} );
// ... Create the NMEA receiver
NmeaReceiver nmeaReceiver = new NmeaReceiver( nmeaHandler ) ;
// ... Attach handler for NMEA messages that fail NMEA checksum verification
nmeaReceiver.setMessageHandlers( new NmeaReceiver.MessageHandlers() {
@Override
public void OnNmeaMessageFailedChecksum( byte[] bytes, int index, int count, byte expected, byte actual ) {
String sentence = new String(bytes, index, count, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII ) ;
Log.e("NmeaTester", "Failed Checksum: " + sentence + "; expected "+expected+" but got " + actual );
}
@Override
public void OnNmeaMessageDropped( byte[] bytes, int index, int count, String reason ) {
String sentence = new String(bytes, index, count, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII ) ;
Log.i("NmeaTester","Bad Syntax: "+sentence+"; reason: "+reason );
}
@Override
public void OnNmeaMessageIgnored( byte[] bytes, int index, int count ) {
String sentence = new String(bytes, index, count, StandardCharsets.US_ASCII ) ;
Log.i("NmeaTester","Ignored: " + sentence ) ;
}
} ) ;
// ... Your byte receiving logic...
boolean keepReceiving = true ;
while ( keepReceiving ) {
byte [] bytesReceived = /* receive some bytes from socket, file, whatever... */
// ... Feed the bytes into the NMEA receiver
nmeaReceiver.Receive( bytesReceived ) ;
}
The above code will invoke the appropriate callbacks each time a NMEA sentence is received.