Introduction • Requirements • Tested Environments • Quick Start • How To Use • License
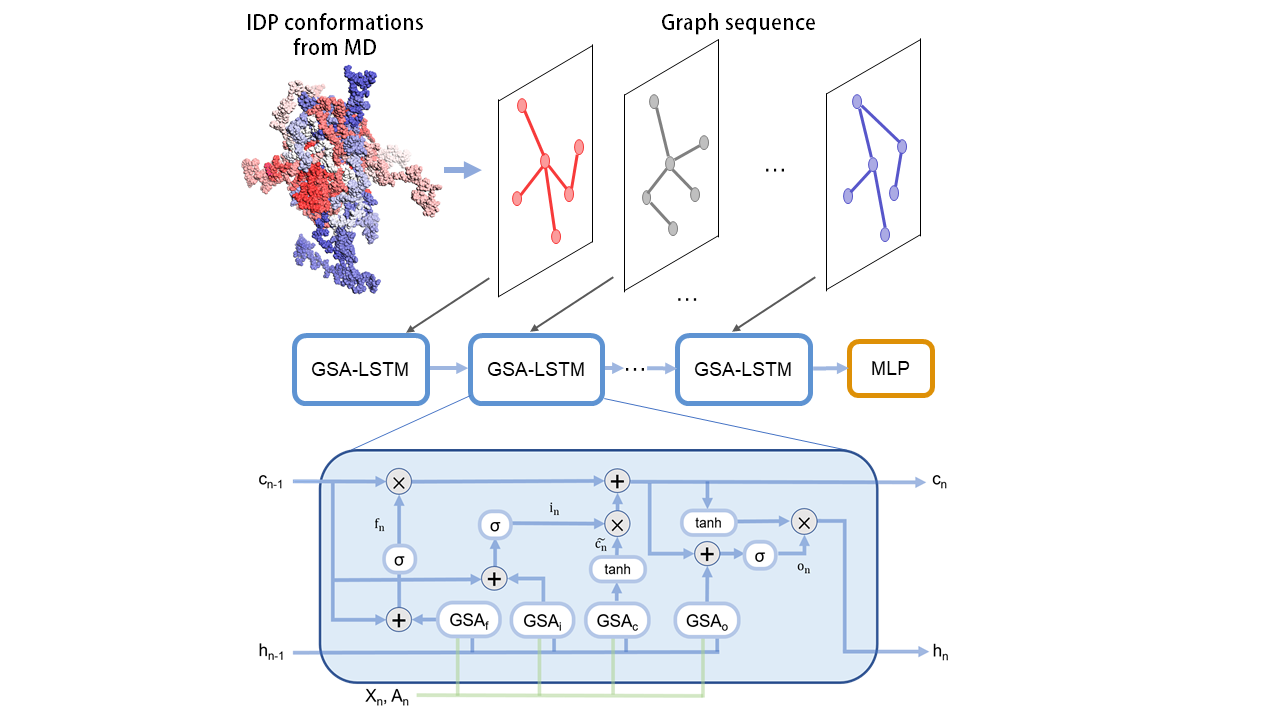
We present GSALIDP, a GraphSAGE LSTM Network for predicting the behavior of IDP interaction. GSALIDP integrates the graph sample and aggregate (GraphSAGE) network with the long short-term memory (LSTM) network. LSTM serves as the main framework of the model, and GraphSAGE is embedded within LSTM to extract the structural information of IDPs. The training data for GSALIDP is obtained from atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Multiple conformations of IDP is modeled as a dynamic graph to describe the fluctuation of its flexible conformation.
GSALIDP can effectively predict the interaction sites of IDP as well as the contact residue pairs between IDPs. Its performance to predict IDP interaction is on par with or even better than the conventional models to predict the interaction of structural proteins. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first machine-learning method to realize the prediction of interaction behavior of IDPs.
- Python 3.9.16
- numpy 1.25.0
- pandas 1.3.5
- scikit_learn 1.2.2
- torch 1.12.1
- torch_geometric 2.3.0
- torch_geometric_temporal 0.54.0
- tqdm 4.65.0
- Linux version 5.15.0-75-generic
- Ubuntu 20.04
To clone this repository, you'll need Git installed on your computer. From your command line:
# Clone this repository
$ git clone https://github.com/arnoldland/GSALIDP
# Go into the repository
$ cd GSALIDP
# Install dependencies
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
# Site predicion on the test set
$ python evaluate_test.py --ptype site- Create the contact graphs by raw data. (the contact graphs are already created and sorted in the ./contact_graph, so you can ignore this step.)
# create discrete contact graphs (you can ignore this step because the graphs are already established)
$ python create_graph_d.py - Evaluate the trained model on the test set.
# for site prediction
$ python evaluate_test.py --ptype site
# for pair prediction
$ python evaluate_test.py --ptype pair- Cross-Validation on the train set to choose the best epoche.
# for site cross-validation. Best model of each fold will be stored in the ./models/site_models folder
$ python train_full.py --cvtype site
# for pair cross-validation. Best model of each fold will be stored in the ./models/pair_models folder
$ python train_full.py --cvtype pair- After getting the best epoch of the Cross-Validation, you can train a new model on the full train set.
# for site train
$ python train_full.py --ttype site
# for pair train
$ python train_full.py --ttype pairMIT