Python 3.8 or higher
Once you have cloned the repository, install the requirements.
pip install -r requirements.txtInstall **lolapy** from git using pip
```bash
pip install "git+https://github.com/alejamp/lola-py-sdk.git"npm install -g prompter-cliset env variables for prompter server url
export PROMPTER_SERVER_URL=[PROMPTER_SERVER_URL]Then execute prompter and select Login. Use your username and password.
Execute prompter then from menu select Assistant -> Create New. Input the assistant name and description. Keep lola as agent.
Execute prompter then from menu select Channel -> Register New. Then input the token.
Publish a prompt by running prompter --prompt=<prompt> --id=<prompt-id> --publish in your terminal. Note that the prompt must be a valid Handlebars template. See Handlebars for more information.
If no promptId is provided, the file name will be used as the promptId. If the prompt is already published, it will be updated.
Lola2 utilizes Handlebars templates to generate prompts. The output is a HTML like named PML, Prompt Markup Language. The PML is then rendered on each customer's message using a context object.
VS Code has a handlebars extension that can be used for syntax highlighting and snippets. Check recommended extensions for this project.
Prompts context variables are:
- date: current date
- state: current conversation state. This is an object that contains any assistant implementation related data. For example, if the assistant is a ticketing assistant, the state may contain the selected movie, the selected seats, etc.
- message: the customer's last message to the assistant. Useful for embeddings queries.
In handlebars, you can use the {{#if}} helper to conditionally render a block. For example, if you want to render the customer's name if the state variable name exists.
Conditionals do not supports operations, so you can't do something like {{#if state.name == 'John'}}.
In future versions, we will add support for operations.
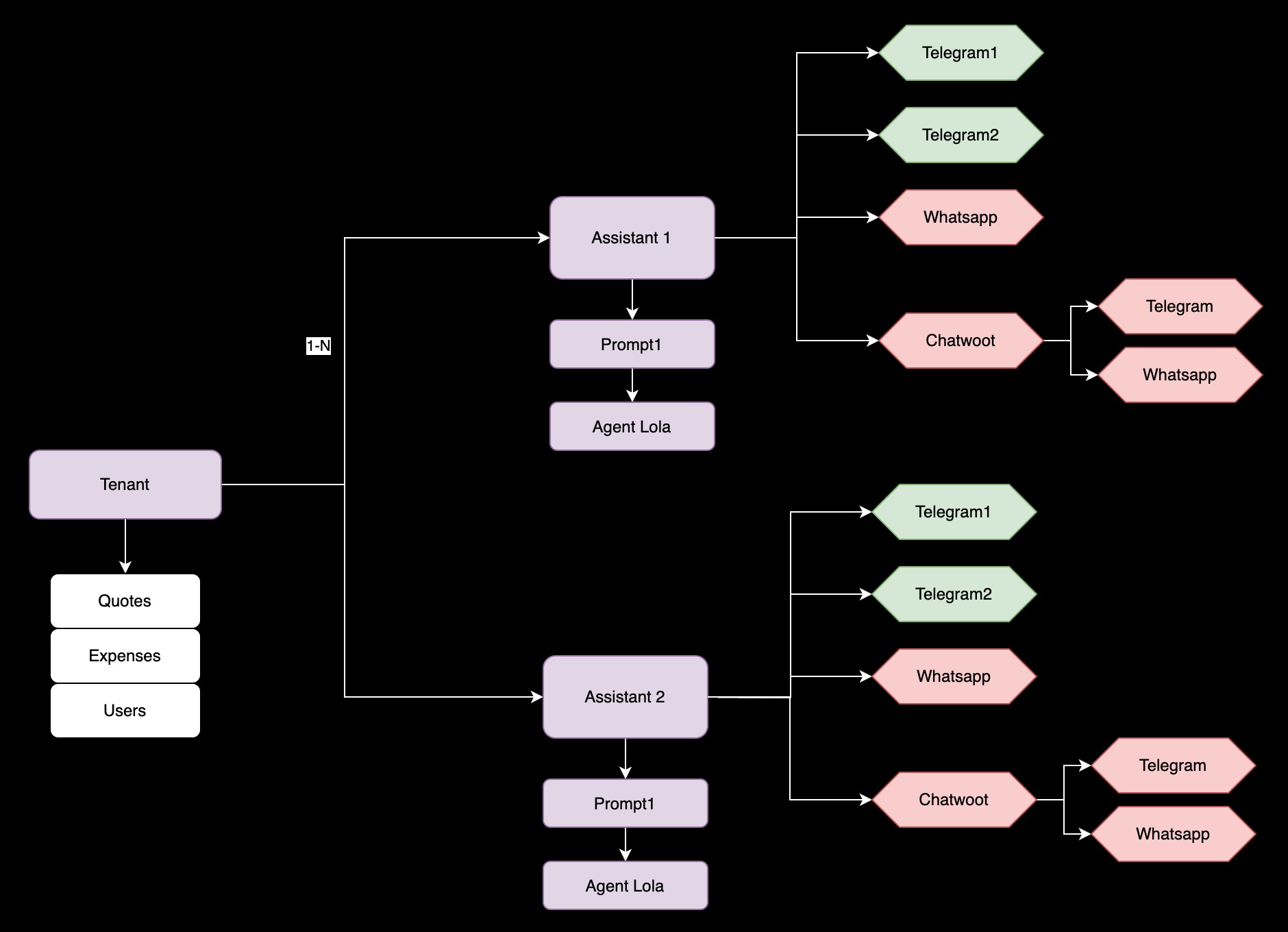
The assistant is the main component of the architecture. It is responsible for handling the customer's messages and generating the responses. It defines the Prompt and the NLP Agent to use. It also provides the token needed bu lolapy to connect to and gather events and command from the customer's conversation.
An assistant can have multiple channels. A channel is a way to connect to the customer. For example, a Telegram channel, a Facebook Messenger channel, a WhatsApp channel, etc. Each channel has its own conversation state, so the assistant must be able to handle multiple conversation states.
A Tenant is can have multiple assistants. For example, a tenant can have a ticketing assistant, a banking assistant, a food delivery assistant, etc. Each assistant can have multiple channels.
Tenant is the main entity. It is the owner of the assistants and channels. It also provides the token needed by prompter-cli to connect to the prompter server and administrate the assistants and channels.
Upload/publish prompt, in the same directory as the prompt:
prompter --prompt=prompt.hbr --id=<prompt-id> --publish
Upload text to semantic store aka embedings
Embeddings can be uploaded by running prompter --embed=<file> --collection=<collection-name> in your terminal. Embeddings must be a text file, it supports Mark Down and Json.
you can specifiy chunkSize by running prompter --embed=<file> --collection=<collection-name> --chunkSize=<chunkSize> in your terminal. The default chunkSize is 1000.
prompter --embed=hway.txtExecute prompter then select Embeddings from menu then Query.