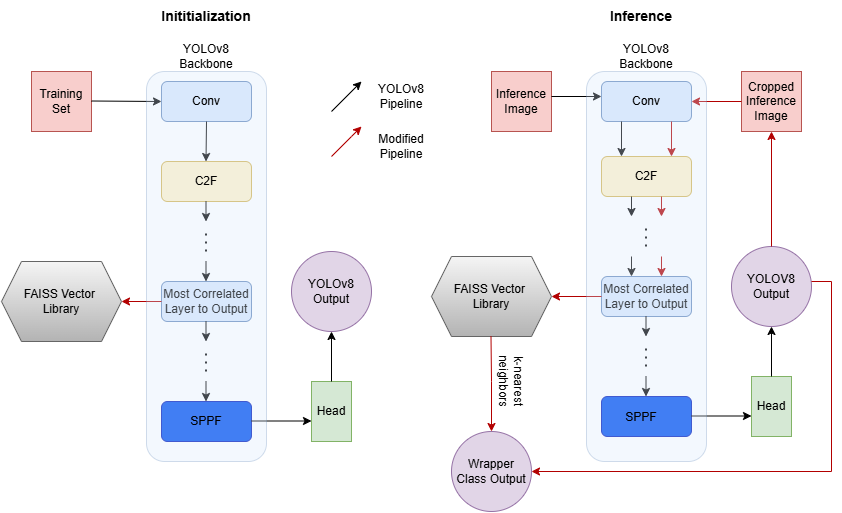
This project demonstrates how to add post-hoc interpretability to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) using vector libraries. By mapping the training set to the vector space of the most relevant layer, we can retrieve the k-nearest neighbors for inference images, providing insight into the model's output.
We developed a wrapper class that take a trained CNN (YOLOv8) and its training set as inputs. This class enable us to:
- Map the training set to the vector space of the most relevant layer to the model's output
- Reduce dimensionality using Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
- Retrieve the k-nearest neighbors for inference images
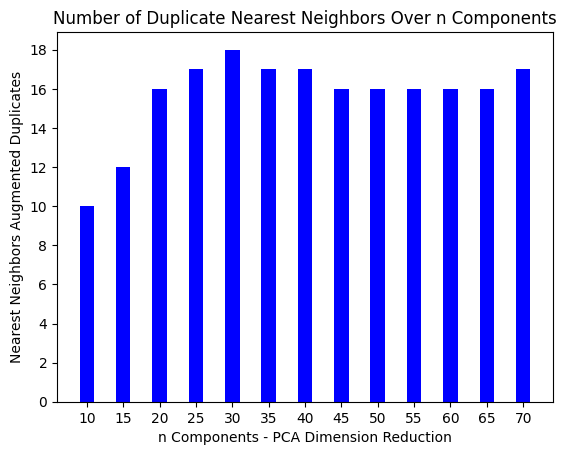
We tested our approach on the YOLOv8m model using the BR35H brain tumor dataset. Our results show that layer 210, with PCA dimension reduction to 30, provides the most reliable results for identifying the most influential training images for a given inference prediction.
Ensure the necessary dependencies are installed in your python environment.
pip install -r requirements.txt
For the YOLOv8 wrapper, a data.yaml file with following format should be created for the dataset as follows:
path: /path/to/dataset
train: /path/to/train/images
val: /path/to/validate/images
test: /path/to/test/images
names:
0: tumor
The weights of a trained YOLOv8m model will need to be already obtained and saved. To instantiate an instance of the InterpretableYOLOTest class:
data_yaml_path = 'path/to/data.yaml'
weights_path = 'path/to/weights.pt'
weights = torch.load(model_path)
weights = model['model'].float()
weights.eval()
target_layer_index = 210 # default parameter value for InterpretableYOLOTest
pca_components = 30 # default parameter value for InterpretableYOLOTest
model = InterpretableYOLOTest(data_yaml_path, model=weights, target_layer_index=target_layer_index, pca_components=pca_components)To perform infernce on an image:
image_path = 'path/to/inference/image'
k = 6 # k nearest neighbors
result = model.single_image_inference(image_path, k=k)
print(result)The output is a dictionary that contains the class, confidence score, bounding box coordinates, file names of the k-nearest neighbors from the training set, and the distance of each neighbor to the inference image.
{'model_prediction': 0,
'confidence_score': 0.8937316536903381,
'bounding_box': array([ 0.55639, 0.59689, 0.15373, 0.20179]),
'nearest_neighbors': ['y132.jpg', 'y105.jpg', 'y328.jpg', 'y451.jpg', 'y249.jpg', 'y349.jpg'],
'distances': array([[ 57.989, 73.775, 206.04, 245.18, 319.35, 343.15]],
dtype=float32)}
You can find the full paper here.