In SAPUI5, the Descriptor for Applications (often referred to as the "app descriptor" or "manifest.json") is a JSON file that is used to configure and describe various aspects of a SAPUI5 application. This file is a key component of the SAPUI5 framework and plays a crucial role in defining the behavior, structure, and properties of your application. It allows you to set up the application's metadata, define its routing, specify the resources it requires, and configure other application-specific settings.
The manifest.json file typically contains information like:
-
Application Metadata: This includes the application's name, version, description, and other metadata.
-
Root View and Pages: You can define the root view of your application and specify other views/pages that make up the application.
-
Routing: You can configure routing in the manifest to define how different URLs map to views or components in your application.
-
Dependencies and Resources: You can specify which libraries and modules your application depends on and define the resources it requires.
-
UI5 Configuration: Configure settings specific to the SAPUI5 framework.
-
Settings and Features: Define various settings and features for your application.
The manifest.json file makes it easier to manage and configure your SAPUI5 application because it centralizes all this information in one place. It is usually located in the root directory of your application and is loaded by the SAPUI5 framework when the application starts. By using the manifest, you can keep your application's configuration organized and maintainable.
In SAP UI5, both the Component.js and Manifest.json files play crucial roles in the application's configuration and startup. Here's a comparison of the two:
-
Component.js: This is the first point of entry for any SAP UI5 application. When SAP UI5 runs the application, it searches for the
Component.jsfile in your application workspace because this file is the starting point from where SAP UI5 starts to run your application². In older versions of UI5, all configuration was placed inside theComponent.js. -
Manifest.json: This is an application descriptor or a configuration file for your SAP UI5 application². The
Manifest.jsonfile contains all the resources and other configurations that your app requires². In recent versions of UI5, the configuration has been moved fromComponent.jstoManifest.json. This change has several advantages, such as improving the startup performance of the application² and allowing for more efficient loading and better performance since only the required resources are loaded.
The Component.js file also tells SAP UI5 where to find the Manifest.json file. As seen in many SAPUI5 applications, there is a manifest: "json" line in the metadata section of Component.js, which tells SAPUI5 that there is a manifest.json file in the application at the same directory level as the Component.js.
Refer to /webapp/manifest.json
The manifest.json file in SAP UI5 is a descriptor file that provides a centralized, machine-readable and easy-to-access location for all the metadata related to an application, component, or library. The code you've shared can be divided into three main parts:
-
sap.app: This section contains application-specific information such as the application ID, type, version, title, and description. The
idis the unique identifier of the application. Thetypeindicates the type of the component, which is "application" in this case. TheapplicationVersionspecifies the version of the application. -
sap.ui: This section contains UI technology-specific metadata. It specifies the technology used (UI5 in this case), the device types supported by the application (desktop, tablet, phone), and any supported themes.
-
sap.ui5: This section contains SAPUI5-specific metadata. It includes:
dependencies: Specifies the minimum UI5 version required and any library dependencies.models: Defines the models available to the application. In this case, an i18n model for internationalization is defined.rootView: Specifies the root view of the application.contentDensities: Specifies whether the app supports compact and cozy content densities.
Each of these sections plays a crucial role in defining how your SAP UI5 application behaves and interacts with various devices and libraries.
Refer to /webapp/Component.js
-
sap.ui.define: This is the SAP UI5 module loader. It loads the specified modules and calls a function with the loaded modules as its arguments. -
The array
["sap/ui/core/UIComponent", "sap/ui/model/json/JSONModel"]specifies the modules to be loaded. In this case, it's loading theUIComponentmodule fromsap/ui/coreand theJSONModelmodule fromsap/ui/model/json. -
The function
(UIComponent, JSONModel) {...}is called after the modules are loaded. The loaded modules are passed as arguments to this function. -
Inside this function, a new UI5 component is defined by extending the base
UIComponentclass. This is done using theUIComponent.extendmethod. -
The
metadataobject defines metadata for this component. It specifies that this component implements thesap.ui.core.IAsyncContentCreationinterface and that it uses a JSON manifest. -
The
initmethod is a lifecycle method that is called when the component is initialized. Inside this method:- It first calls the parent class's (UIComponent) init method using
UIComponent.prototype.init.apply(this, arguments);. - Then it creates a new JSON model with some data (
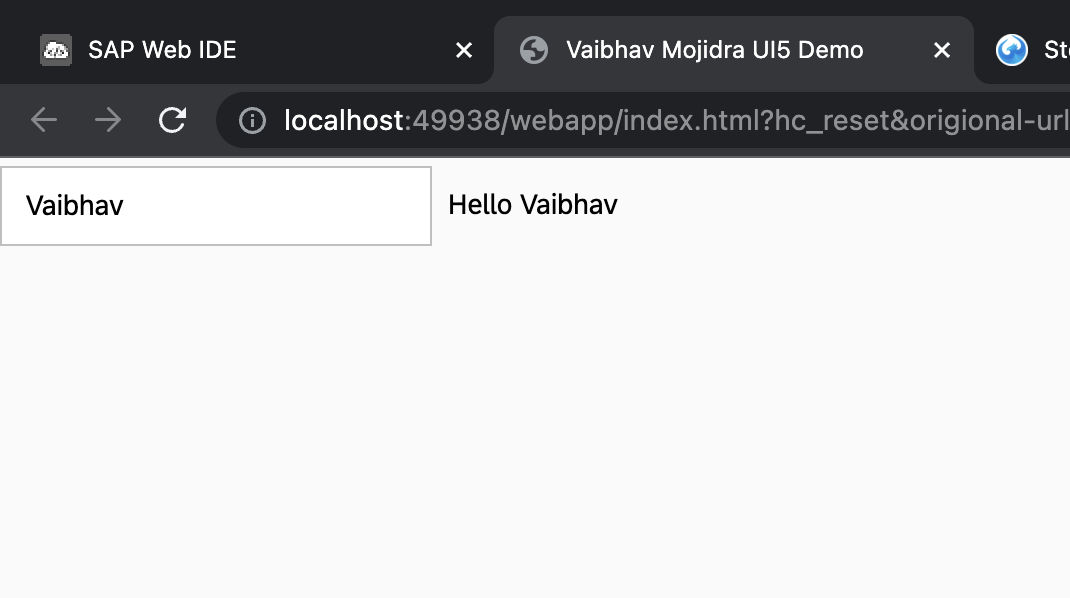
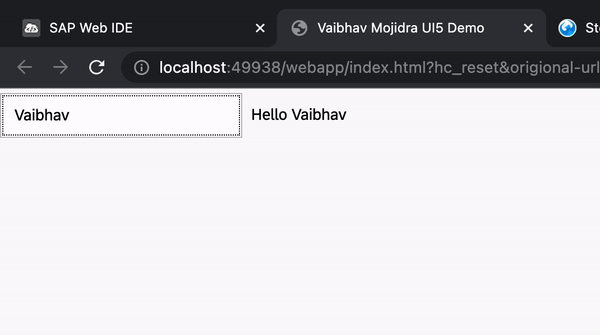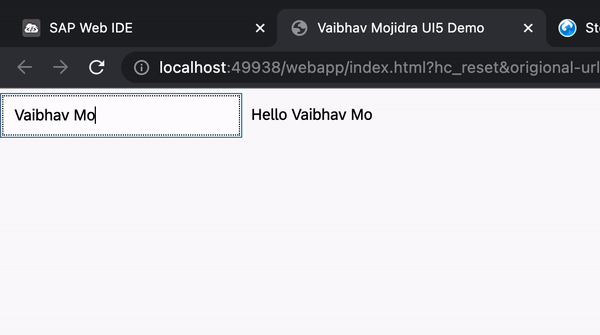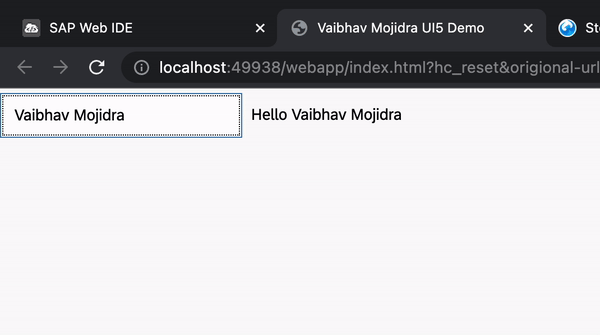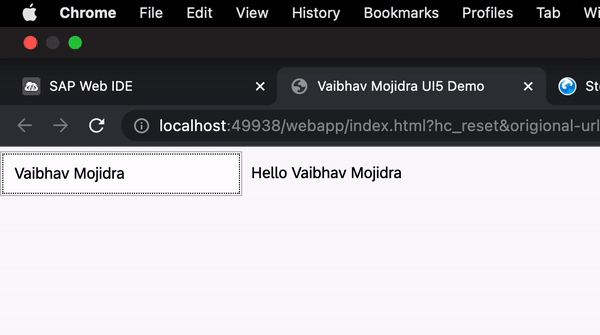
{name:"Vaibhav"}) and sets this model on the component usingthis.setModel(oModel);.
- It first calls the parent class's (UIComponent) init method using
In this app the bootstrapping is done by index.html from there it loads Component.js which loads manifest.json.
Why we don't have index.js, controller.js? Because loading of View is done from Manifest.json which is load from Component.js which is loaded by index.html so no need of index.js for loading the component.js explicitly. And controller.js not there because we don't have any clicks event it do have 2 way binding directly from XML so no need of handler.