This project is dedicated to developing a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) leveraging advanced machine learning techniques and real-time data streaming. Key aspects include:
- Custom CSP Implementation: A Common Spatial Patterns algorithm for effective EEG signal processing.
- Feature Extraction: Extracting features from EEG data using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT).
- Ensemble Learning: A combination of various machine learning classifiers such as XGBoost, Random Forest, Logistic Regression, and Linear Discriminant Analysis, enhancing prediction accuracy.
- Kafka Integration: Utilizing Apache Kafka to establish a real-time data streaming platform, simulating live EEG data processing.
Using Physionet EEG Motor Movement/Imagery Dataset, we aim to develop a BCI that can predict a subject's task based on EEG data. The primary objective is to interpret EEG data to understand a subject's specific tasks or mental states, aiming to achieve high accuracy in real-time processing.
Subjects experiments are divided into 4 tasks. The goal is to predict the task number based on the EEG data.
Tasks are as follows:
- Open and close left or right fist
- Imagine opening and closing left or right fist
- Open and close both fists or both feet
- Imagine opening and closing both fists or both feet
The dataset is available on Physionet. Data are handled using MNE.
There are 109 subjects, each subject has 14 experimental runs (see here for more details).
The following steps are performed:
- Data preprocessing (filtering, downsampling, epoching)
- Feature extraction (FFT, CSP)
- Hyperparameters tuning (XGBoost, Random Forest, Logistic Regression, Linear Discriminant Analysis)
- Trying models on different intervals, with different feature extraction methods. Model selection with cross-validation and ensemble learning, best model is chosen based on accuracy (bucket of models method)
- Model training and saving
- Real-time prediction (Kafka integration with Docker)
-
Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Modify this line in BrainComputerInterface.py so that it points to the Physionet dataset folder on your computer:
mne.set_config( "MNE_DATASETS_EEGBCI_PATH", "/mnt/nfs/homes/jsemel/sgoinfre/mne_data" )
-
Find the best model and train it for one task (3-14) on one subject (1-109):
python mybci.py --task=<task_number> --subject=<subject_number> train
-
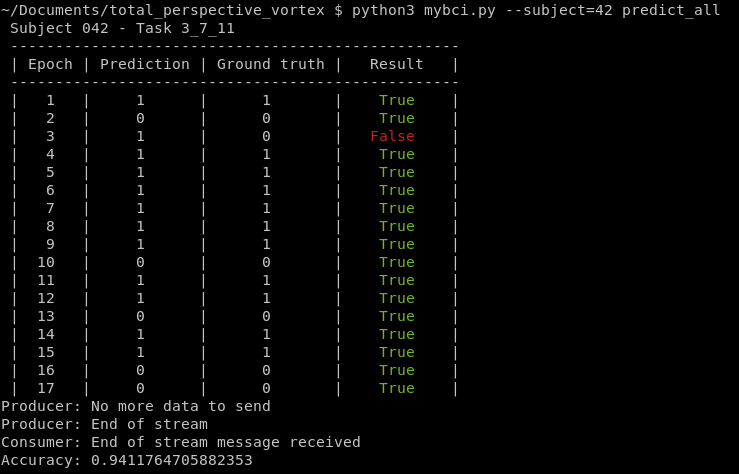
Stream predictions for one task (3-14) on one subject (1-109):
docker compose up -d python mybci.py --task=<task_number> --subject=<subject_number> predict
-
Find the best models and train them on all tasks for all subjects (/!\ This will create 436 models):
python mybci.py train_all
-
Print accuracy of saved models:
python mybci.py stats
-
Stream predictions for all tasks on one subject (1-109):
docker compose up -d python mybci.py --subject=<subject_number> predict_all