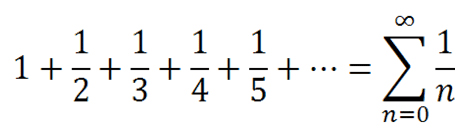I gathered the JAVA projects I created during bootcamp here. 👉 Patika.dev 👈
- Zodiac Animal Programme
- Leap Years Programme
- Password Control Programme
- Average
- Sum of even Numbers
- Exponent Calculator
- Combination
- Exponent
- Armstrong Number
- Sum Of Digits
- Harmonic Series
- Print Diamond
- ATM Project
- Find GCD and LCM
- Finding MIN and MAX from given number in Java
- Perfect Number
- Inverted Triangle
- Prime Number
- Fibonacci Series
- Palindromic Number
- Recursive Fibonacci Numbers
- Calculator
- Metot Exponent
- Recursive Prime Numbers
- Print Pattern
- Student Grading System
- Box Players
- Salary Employee
- Harmonic Means
- Near Highter Smaller
- Letter B
- Dublicate
- Take Array
- Number Game
- Matrix To Transpose
- Palindrome
- Minesweeper Game
There are 12 zodiac signs and the order goes like this: Rat, Ox, Tiger, Rabbit, Dragon, Snake, Horse, Goat, Monkey, Rooster, Dog and Pig. The program find your Chinese zodiac animal in Java.
To be a leap year, the year number must be divisible by four – except for end-of-century years, which must be divisible by 400.
Customer account login password control with while loop.
Program that calculates the average of numbers divisible by 3 and 4 from numbers 0 to the number entered with Java loops.
A program that accepts input from the user until a single number is entered with Java loops and adds even and multiples of 4 from the entered values and prints it on the screen.
Power of 4 Calculator and Power of 5 Calculator
Program that prints powers of 4 and 5 up to the number entered with Java loops.
Program to calculate combination with Java.
The number of r-combinations from a given of n elements is often denoted in elementary combinatorics texts by C(n,r).
C(n,r) = n! / (r! * (n-r)!)
Program that calculates exponential numbers with values entered by the user in Java (For Loop)
Java program determines whether the integer entered is a Narcissistic / Armstrong number or not.
In number theory, a narcissistic number (also known as a pluperfect digital invariant (an Armstrong number (after Michael F. Armstrong) or a plus perfect number) in a given number base b is a number that is the sum of its own digits each raised to the power of the number of digits.
Program to calculate the sum of digits of a number.
In mathematics, the harmonic series is the infinite series formed by summing all positive unit fractions:
👉 more information about Harmonic series
Java Program to Generate Harmonic Series
Java program to print diamond star pattern.
Using for loop.
ATM Project Java.
In the ATM program, the user has to select an option from the options displayed on the screen. The options are related to withdraw the money, deposit the money, check the balance, and exit.
To withdraw the money, we simply get the withdrawal amount from the user and remove that amount from the total balance and print the successful message.
To deposit the money, we simply get the deposit amount from the user, add it to the total balance and print the successful message.
To check balance, we simply print the total balance of the user.
GCD or the Greatest Common Divisor of two given numbers A and B is the highest number dividing both A and B completely, i.e., leaving remainder 0 in each case. LCM or the Least Common Multiple of two given numbers A and B is the Least number which can be divided by both A and B, leaving remainder 0 in each case.
LCM(A, B) = (a * b) / GCD(A, B)
Java program that finds the MAX and MIN numbers entered from user.
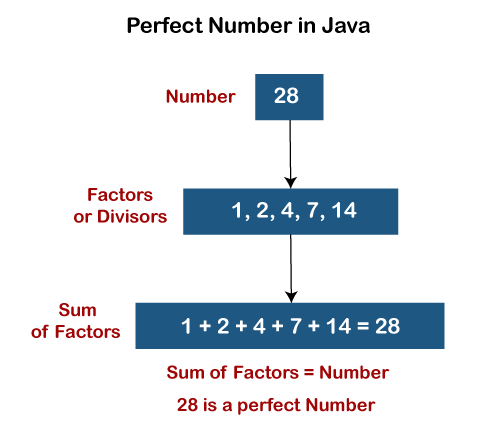
In number theory, a perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive divisors, excluding the number itself.
For instance, 6 has divisors 1, 2 and 3 (excluding itself), and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6, so 6 is a perfect number. 👉 More information
Inverted triangle in Java using loops.
Prime Number Program in Java.
Fibonacci series in Java
In fibonacci series, next number is the sum of previous two numbers for example 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55 etc. The first two numbers of fibonacci series are 0 and 1.
A palindromic number (also known as a numeral palindrome or a numeric palindrome) is a number (such as 16461) that remains the same when its digits are reversed. In other words, it has reflectional symmetry across a vertical axis. The term palindromic is derived from palindrome, which refers to a word (such as rotor or racecar) whose spelling is unchanged when its letters are reversed. The first 30 palindromic numbers (in decimal) are:
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 101, 111, 121, 131, 141, 151, 161, 171, 181, 191, 202, …
Java program to check whether a number is prime or not using recursion.
Object Oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that relies on the concept of classes and objects.
A class is an abstract blueprint used to create more specific, concrete objects. Classes often represent broad categories, like Car or Dog that share attributes. These classes define what attributes an instance of this type will have, like color, but not the value of those attributes for a specific object.
Classes can also contain functions, called methods available only to objects of that type. These functions are defined within the class and perform some action helpful to that specific type of object.
- OOP models complex things as reproducible, simple structures
- Reusable, OOP objects can be used across programs
- Allows for class-specific behavior through polymorphism
- Easier to debug, classes often contain all applicable information to them
- Secure, protects information through encapsulation
👉 For More
Don't Repeat Yourself!
In software engineering and computer science, abstraction is:
- The process of removing physical, spatial, or temporal details or attributes in the study of objects or systems to focus attention on details of greater importance; it is similar in nature to the process of generalization;
- the creation of abstract concept-objects by mirroring common features or attributes of various non-abstract objects or systems of study – the result of the process of abstraction.
Abstraction, in general, is a fundamental concept in computer science and software development. The process of abstraction can also be referred to as modeling and is closely related to the concepts of theory and design. Models can also be considered types of abstractions per their generalization of aspects of reality.
👉 For More
- Qualifications : name, code, prefix, note, Teacher
- Methods : Course() , addTeacher() , printTeacher()
- Qualifications : name, mpno, branch
- Methods : Teacher()
- Qualifications : name, stuNo, classes, course1, course2, course3, avarage, isPass
- Methods : Student(), addBulkExamNote(), isPass(), calcAvarage(), printNote()
An array in Java is a group of like-typed variables referred to by a common name. Arrays in Java work differently than they do in C/C++. Following are some important points about Java arrays.
- In Java, all arrays are dynamically allocated. (discussed below)
- Since arrays are objects in Java, we can find their length using the object property length. This is different from C/C++, where we find length using sizeof.
- A Java array variable can also be declared like other variables with [] after the data type.
- The variables in the array are ordered, and each has an index beginning from 0.
- Java array can be also be used as a static field, a local variable, or a method parameter.
- The size of an array must be specified by int or short value and not long.
- The direct superclass of an array type is Object.
- Every array type implements the interfaces Cloneable and java.io.Serializable.
An array can contain primitives (int, char, etc.) and object (or non-primitive) references of a class depending on the definition of the array. In the case of primitive data types, the actual values are stored in contiguous memory locations. In the case of class objects, the actual objects are stored in a heap segment.
👉 For More
Get the size of the array and the elements of the array from the user Java.