- Object Page - Content Area
- General Features
- Forms
- Table
- Chart
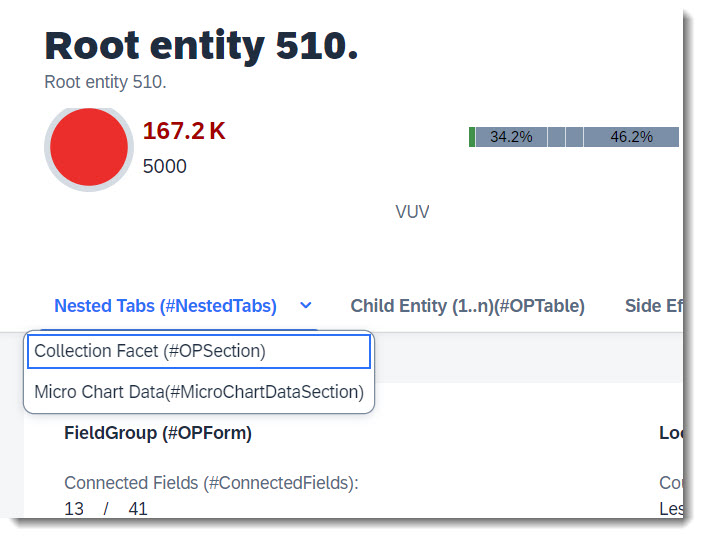
Multiple sub tabs can be placed underneath a main tab, called nesting. User can click on an expand button to show a drop down list of sub tabs. All that is needed is to define a Collection facet (main tab) and assign other Collection facets (the sub tabs) to it.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #NestedTabs (Main Tab)
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #COLLECTION,
label: 'Nested Tabs (#NestedTabs)',
id: 'Nested'
},
// Search Term #OPSection (Sub tab, take note of parentID)
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #COLLECTION,
label: 'Collection Facet (#OPSection)',
id: 'collectionFacetSection',
parentId: 'Nested'
},
// Search Term #MicroChartDataSection (Sub tab, take note of parentID)
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #COLLECTION,
label: 'Micro Chart Data(#MicroChartDataSection)',
id: 'chartDataCollection',
parentId: 'Nested'
}
]
Search term: #DisplayTextAndID
Instead of showing unreadable long IDs, there is the option to replace the ID with another text property from the entity, for example a name property. The @ObjectModel.text.element annotation specifies which value should be displayed instead of the original value.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Criticality
@ObjectModel.text.element: ['Name']
key code as Code,
name as Name,
The @UI.textArrangement annotation defines how the new text is displayed. The options are #TextOnly, #TextFirst, #TextLast, #TextSeparate.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #DisplayTextAndID
@UI.textArrangement: #TEXT_FIRST,
CriticalityCode;
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model: Providing Text by Text Elements in the Same Entity
Search term: #HidingContent
Any header facet, section or data field can be hidden with the annotation @UI.xx.hidden. The annotation supports either fixed boolean values or values from a referenced property, as shown below.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #HidingContent
@UI.facet: [
{
purpose: #HEADER, // or #STANDARD
type: #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
label: 'Section Visible when in Edit(#HidingContent)',
targetQualifier: 'ShowWhenInEdit',
hidden: #( IsActiveEntity )
}
]
@UI.fieldGroup: [ { qualifier: 'ShowWhenInEdit' }] // Search Term #HidingContent
StringProperty;
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model: Hiding Fields Dynamically on the Object Page
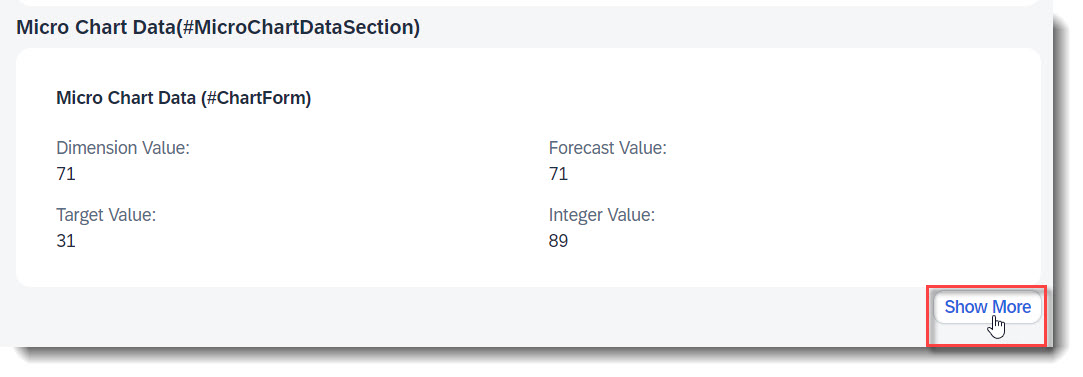
Search term: #Preview
A reference facet in a collection facet is not shown after loading the app, when the reference facet has the @UI.facet.isPartOfPreview annotation and it is set to false. The sub section is then hidden beneath a "Show more" button on the UI.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #Preview
@UI.facet: [
{
purpose: #STANDARD
type: #COLLECTION,
label: 'Micro Chart Data(#MicroChartDataSection)',
id: 'chartDataCollection'
},
{
parentId : 'chartDataCollection',
label : 'Chart Data Preview (#Preview)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'chartDataPreview',
isPartOfPreview: false
}
]
@UI.fieldGroup: [ { qualifier: 'chartDataPreview' }] // Search Term #Preview
IntegerValue;
Search term: #MultiInputField
It is possible to have a multi input field which displays values from an association. When the values are from a child entity with delete capability, you are able to delete the entity in edit mode, directly from the multi input field.
It is not necessary to use the @UI.fieldGroup annotation to display the field, it is just annotated as such in the app to group and display it. It is however necessary, to use the datafield attribute value to set the source of the input, in this case the field StringProperty via the association _Child.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
{
// Search Term #OPForm
purpose: #HEADER, // or #STANDARD
label : 'FieldGroup (#OPForm)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'OPForm',
id: 'SubSectionID'
}
]
// Search Term #MultiInputField
@UI.fieldGroup: [
{
label: 'Multi Input Field (#MultiInputField)',
qualifier: 'OPForm',
value: '_Child.StringProperty',
position: 40
}
]
Child;
Search term: #PresentationVariant-Child
A presentation variant defines how the result of a queried collection of entities is shaped and how this result is displayed, for example as a list report or a chart (@UI.presentationVariant.visualizations), the sorting order (@UI.presentationVariant.sortOrder), or the number of items (@UI.presentationVariant.maxItems) to display per segment.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #PresentationVariant-Child
@UI.presentationVariant: [
{
qualifier: 'pVariant',
maxItems: 5,
sortOrder: [
{
by: 'StringProperty',
direction: #DESC
}
],
visualizations: [{type: #AS_LINEITEM}]
}
]
To use presentation variant for a child entity in the object page, it is necessary to annotate @UI.facet with the correct type in the root entity: #PRESENTATIONVARIANT_REFERENCE instead of #LINEITEM_REFERENCE.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #OPTable, #PresentationVariant-Child
@UI.facet: [
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #PRESENTATIONVARIANT_REFERENCE,
targetElement: '_Child',
targetQualifier: 'pVariant',
label: 'Child Entity (1..n)(#OPTable)',
id: 'childEntitiesSection'
}
]
Search term: #SelectionVariant-Child
With a selection variant, you can define how the fields of an entity set should be filtered. The attribute text is the title of the view and filter contains all filter parameters.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #SelectionVariant
@UI.selectionVariant: [
{
qualifier: 'sVariant',
text: 'SelectionVariant (Positive criticality)',
filter: 'CriticalityCode EQ 3'
}
]
Search term: #SelectionPresentationVariant-Child
A SelectionPresentationVariant bundles a Selection Variant and a Presentation Variant.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #SelectionPresentationVariant-Child
@UI.selectionPresentationVariant: [
{
qualifier: 'ChildSP',
presentationVariantQualifier: 'pVariant',
selectionVariantQualifier: 'sVariant'
}
]
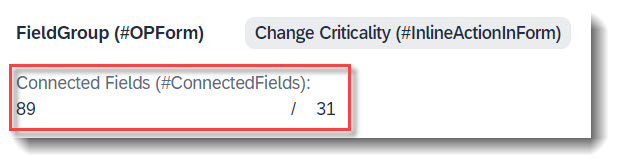
Search term: #ConnectedFields
When two properties are semantically connected, they can be displayed next to each other under one label, to show their data relation. The connected field is defined with the annotation @UI.connectedFields. The attribute template is a string which defines in which order the properties are displayed and what is displayed between both properties, for example a slash.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #ConnectedFields
@UI.connectedFields: [
{
qualifier: 'ConnectedFields',
groupLabel: 'Connected Fields (#ConnectedFields)',
name: 'integer',
template: '{integer} / {target}'
}
]
IntegerValue;
// Search Term #ConnectedFields
@UI.connectedFields: [
{
qualifier: 'ConnectedFields',
name: 'target'
}
]
TargetValue;
The connected field can only be displayed in a form using @UI.fieldGroup or in a #STANDARD facet. They cannot be rendered in a table with @UI.lineItem, with @UI.identification or in header facets.
@UI.facet: [
{
// Search Term #OPForm
purpose : #STANDARD,
label : 'FieldGroup (#OPForm)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'OPForm',
id: 'SubSectionID'
}
]
// Search Term #ConnectedFields
@UI.fieldGroup: [
{
qualifier: 'OPForm',
type: #AS_CONNECTED_FIELDS,
valueQualifier: 'ConnectedFields',
position: 10
}
]
IntegerValue;
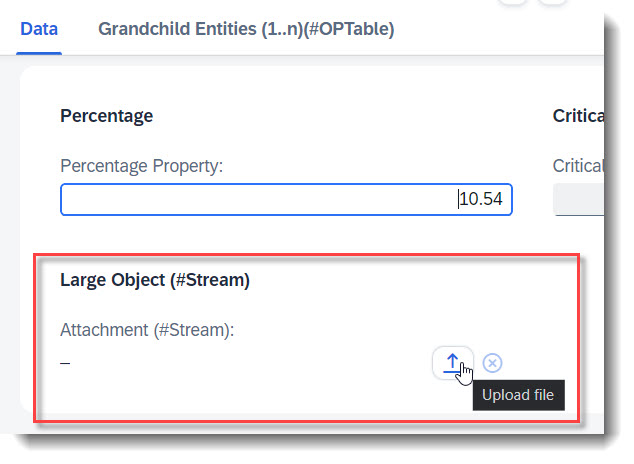
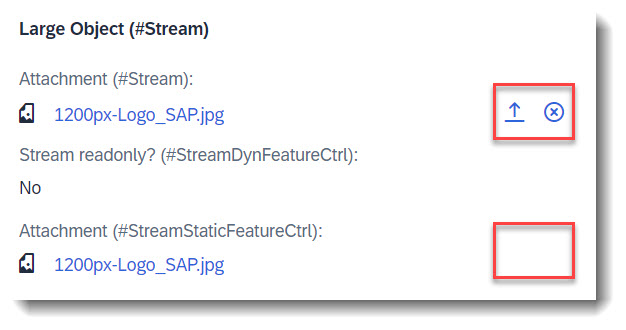
Search term: #Stream
You can enable your RAP application for maintaining large objects (LOBs). By doing so, you provide end users the option to incorporate external binary files or text files when editing entity instances. First the appropriate fields should be added into the database table and the CDS view, and also the annotations @Semantics.largeObject and @Semantics.mimeType. To show it in a standard or header facet, you will need annotation @UI.facet. Lastly, you should also update the mapping and the draft table in your behaviour definition.
Note
Source: Database Table /DMO/FSA_ChildA
stream_filename : abap.char(128);
stream_mimetype : abap.char(128);
stream_file : abap.rawstring(0);
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
StreamFilename, // Search Term #Stream
// Search Term #Stream
@Semantics.largeObject: {
acceptableMimeTypes: [ 'image/*', 'application/*' ],
cacheControl.maxAge: #MEDIUM,
contentDispositionPreference: #INLINE, // #ATTACHMENT - download as file
// #INLINE - open in new window
fileName: 'StreamFilename',
mimeType: 'StreamMimeType'
}
StreamFile,
// Search Term #Stream
@Semantics.mimeType: true
StreamMimeType,
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #Stream
@UI.facet: [
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #COLLECTION,
id: 'Collection',
label: 'Data'
},
{
purpose: #STANDARD
type: #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'Stream',
label: 'Large Object (#Stream)',
parentId: 'Collection'
}
]
// Search Term #Stream
@UI.hidden: true
StreamMimeType;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 10, qualifier: 'Stream', label: 'Attachment (#Stream)' }] // Search Term #Stream
StreamFile;
// Search Term #Stream
@UI.hidden: true
StreamFilename;
Note
Source: BDEF /DMO/FSA_R_ROOTTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_ChildTP alias Child {
...
mapping for /dmo/fsa_child_a {
..
StreamFile = stream_file;
StreamFilename = stream_filename;
StreamMimeType = stream_mimetype;
}
More Information on data modelling for Large Object: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Working with Large Objects
Search term: #StreamStaticFeatureCtrl
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release.
It is possible to enable static field control for your large object property/attachment. This is done by adding the control in the behaviour definition.
In our example, we have set the stream property to readonly.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #StreamStaticFeatureCtrl
@Semantics.largeObject: {
acceptableMimeTypes: [ 'image/*', 'application/*' ],
cacheControl.maxAge: #MEDIUM,
contentDispositionPreference: #ATTACHMENT , // #ATTACHMENT - download as file
// #INLINE - open in new window
fileName: 'StreamFilename',
mimeType: 'StreamMimeType'
}
StreamFileReadonly,
StreamFilename,
@Semantics.mimeType: true
StreamMimeType,
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #StreamStaticFeatureCtrl
@UI: {
fieldGroup: [
{
position: 30,
qualifier: 'Stream',
label: 'Attachment (#StreamStaticFeatureCtrl)'
}
]
}
StreamFileReadonly;
// Search Term #Stream
@UI.hidden: true
StreamMimeType;
// Search Term #Stream
@UI.hidden: true
StreamFilename;
Note
Source: BDEF /DMO/FSA_R_ROOTTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_ChildTP alias Child .. {
field ( readonly ) StreamFileReadonly; // Search Term #StreamStaticFeatureCtrl
}
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Static Feature Control
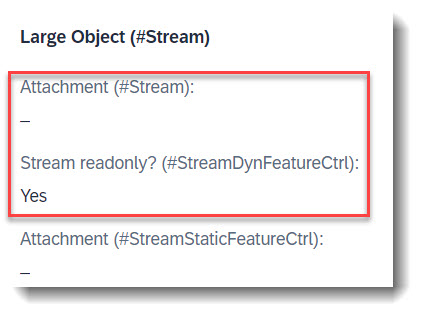
Search term: #StreamDynamicFeatureCtrl
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release.
It is possible to enable dynamic field control for your large object property/attachment. This is done by adding the control in the behaviour definition.
In our example, we set the stream property to readonly, when the boolean property StreamIsReadOnly is set to true. This can only be done when creating a new child instance, as the property StreamIsReadOnly itself has field control readonly : update, mandatory : create.
Note
Source: Database Table /DMO/FSA_ChildA
stream_filename : abap.char(128);
stream_mimetype : abap.char(128);
stream_file : abap.rawstring(0);
stream_is_readonly : abap_boolean;
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
StreamIsReadOnly, // Search Term #StreamDynamicFeatureCtrl
StreamFilename, // Search Term #Stream
// Search Term #Stream
@Semantics.largeObject: {
acceptableMimeTypes: [ 'image/*', 'application/*' ],
cacheControl.maxAge: #MEDIUM,
contentDispositionPreference: #INLINE, // #ATTACHMENT - download as file
// #INLINE - open in new window
fileName: 'StreamFilename',
mimeType: 'StreamMimeType'
}
StreamFile,
// Search Term #Stream
@Semantics.mimeType: true
StreamMimeType,
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #StreamDynamicFeatureCtrl
@UI: {
fieldGroup: [
{
position: 10,
qualifier: 'Stream',
label: 'Stream readonly? (#StreamDynFeatureCtrl)'
}
]
}
@EndUserText: {
label: 'Stream readonly? Caution - cannot be changed after create',
quickInfo: 'Stream readonly?'
}
StreamIsReadOnly;
// Search Term #Stream
@UI.hidden: true
StreamMimeType;
@UI: {
// Search Term #Stream
fieldGroup: [
{
position: 10,
qualifier: 'Stream',
label: 'Attachment (#Stream)'
}
]
}
StreamFile;
// Search Term #Stream
@UI.hidden: true
StreamFilename;
Note
Source: BDEF /DMO/FSA_R_ROOTTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_ChildTP alias Child ... {
field ( readonly : update, mandatory : create ) StreamIsReadOnly;
...
mapping for /dmo/fsa_child_a {
StreamFile = stream_file;
StreamFilename = stream_filename;
StreamMimeType = stream_mimetype;
}
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Implementation /DMO/FSA_BP_R_ROOTTP
CLASS lhc_child IMPLEMENTATION.
METHOD get_instance_features.
READ ENTITIES OF /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP IN LOCAL MODE
ENTITY Child
FIELDS ( StreamIsReadOnly )
WITH CORRESPONDING #( keys )
RESULT DATA(children).
result = VALUE #( FOR child IN children
( %tky = child-%tky
%field-StreamFile = COND #( WHEN child-StreamIsReadOnly = abap_true
THEN if_abap_behv=>fc-f-read_only
ELSE if_abap_behv=>fc-f-unrestricted )
) ).
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Dynamic Feature Control
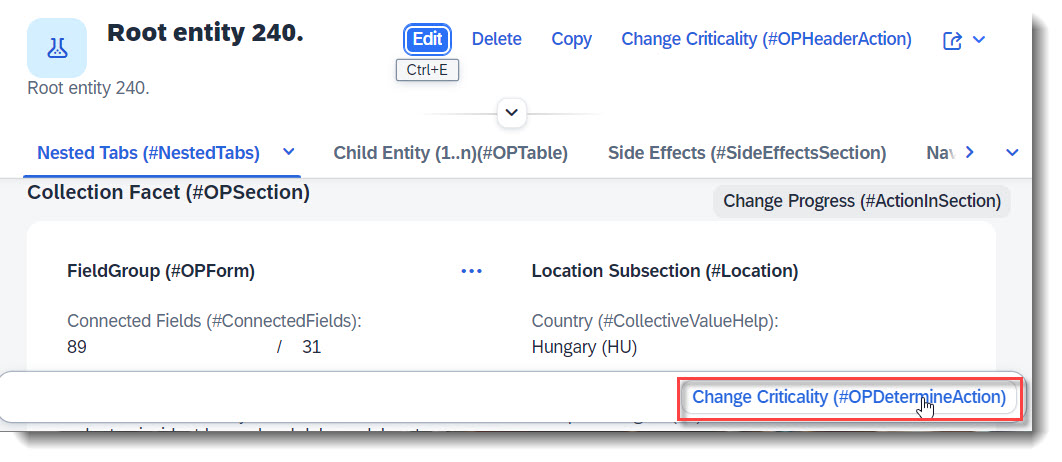
Search term: #OPDetermineAction
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
Determining actions are used to trigger actions directly using the context of the page in the object page, like an action that completes a process step (e.g. approve, reject). The action button will appear at the footer of the object page. This only works with @UI.identification and keyword determining: true.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.identification: [
// Search Term #OPDetermineAction
{
type: #FOR_ACTION,
label: 'Change Criticality (#OPDetermineAction)',
criticality: 'CriticalityCode',
dataAction: 'changeCriticality',
determining: true
}
]
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
action changeCriticality parameter /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeCriticalityP result [1] $self;
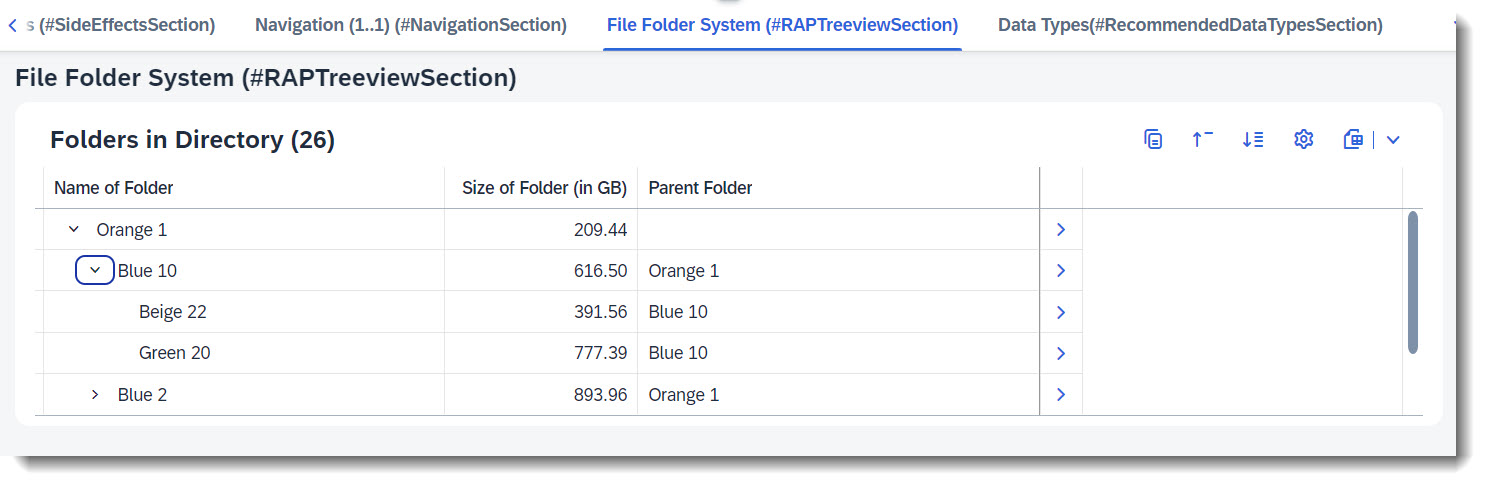
Search term: #RAPTreeview, #RAPTreeviewSection
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release.
ABAP CDS allows for the structuring of data in hierarchies. For RAP, it is possible to display this CDS Hierarchy as a readonly treeview in the SAP Fiori UI, either as a list report which has a different implementation (an example can be found in ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model: Implementing Treeviews) or in the object page, which will be described hereafter.
The example implemented here represents a file folder system. Each folder has a parent folder, which is itself a 'normal' folder, and the topmost/root folder does not have a parent. Each folder is named with a combination of colour and number, and the name is used to sort the hiearchy. The root entity will serve as a 'directory' so that each instance has its own hierarchy which can be displayed in the object page.
To implement this you would need the following artifacts:
The root_id contains the id of the directory, in this case the root instance. parent_folder contains the folder_id of the parent.
Note
Source: Database table /DMO/FSA_FLDR_A
define table /dmo/fsa_fldr_a {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key root_id : sysuuid_x16 not null;
key folder_id : sysuuid_c22 not null;
parent_folder : sysuuid_c22;
folder_name : abap.char(1024);
folder_size : abap.dec(10,2);
}
It serves as the source for the hierarchy, has a self-association and an association to the root entity, the directory. Annotations depicting how the treeview is shown in UI is also declared here. The most important annotation, @OData.hierarchy.recursiveHierarchy is required to specify the hierarchy.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Folder
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #NOT_REQUIRED
@EndUserText.label: '(Hierarchy) Folder'
// Search Term #RAPTreeview
@OData.hierarchy.recursiveHierarchy: [{ entity.name: '/DMO/FSA_I_FolderHN' }]
@UI: {
headerInfo: {
typeName: 'Folder in Directory',
typeNamePlural: 'Folders in Directory',
title.value: 'FolderName'
},
presentationVariant: [
{
sortOrder: [{ by: 'FolderName', direction: #ASC }],
visualizations: [{type: #AS_LINEITEM}]
}
]
}
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Folder
as select from /dmo/fsa_fldr_a
association to one /DMO/FSA_I_Root as _Directory on $projection.RootId = _Directory.ID
association of many to one /DMO/FSA_I_Folder as _ParentFolder on $projection.RootId = _ParentFolder.RootId
and $projection.ParentFolder = _ParentFolder.FolderId
{
@UI.facet: [{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #IDENTIFICATION_REFERENCE,
label: 'Folder (#RAPTreeview)',
position: 10
}]
@UI.hidden: true
key root_id as RootId,
@UI.hidden: true
key folder_id as FolderId,
@UI: {
lineItem: [{
position: 30,
value: '_ParentFolder.FolderName',
label: 'Parent Folder'
}],
identification: [{
position: 30,
value: '_ParentFolder.FolderName',
label: 'Parent Folder'
}]
}
@EndUserText.label : 'Parent Folder'
parent_folder as ParentFolder,
@UI: {
lineItem: [{ position: 10 }],
identification: [{ position: 10 }]
}
@EndUserText.label : 'Name of Folder'
folder_name as FolderName,
@UI: {
lineItem: [{ position: 20 }],
identification: [{ position: 20 }]
}
@EndUserText.label : 'Size of Folder (in GB)'
folder_size as FolderSize,
_Directory,
_ParentFolder
}
The source of the hierarchy is /DMO/FSA_I_Folder. The parent of a node is defined via association _ParentFolder, which is a self-association. The hierarchy is filtered with parameter P_Directory, which is the ID of the root instance so that the correct hierarchy is shown in the object page of the instance. The topmost node is the one with an initial ParentFolder and the hierarchy is sorted by FolderName.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_FolderHN
define hierarchy /DMO/FSA_I_FolderHN
with parameters
P_Directory : sysuuid_x16
as parent child hierarchy (
source /DMO/FSA_I_Folder
child to parent association _ParentFolder
directory _Directory filter by
RootId = $parameters.P_Directory
start where ParentFolder is initial
siblings order by FolderName
)
{
key RootId,
key FolderId,
ParentFolder
}
The following artifacts must be modified:
An association to the hierarchy must be included in the root entity, since the root entity serves as a directory. The association _Folder need to be exposed up until the consumption view /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Root
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Root
...
association of exact one to many /DMO/FSA_I_Folder as _Folder // Search Term #RAPTreeview
on $projection.ID = _Folder.RootId
{
...
_Folder,
...
}
A facet is added to show the treeview as a list report within the object page.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_FolderTP
annotate entity /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP with
{
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #RAPTreeviewSection
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #LINEITEM_REFERENCE,
label: 'File Folder System (#RAPTreeviewSection)',
targetElement: '_Folder'
}
]
}
The hierarchy CDS View should be exposed in the service.
Note
Source: Service Definition /DMO/UI_FeatureShowcaseApp
define service /DMO/UI_FeatureShowcaseApp {
...
expose /DMO/FSA_I_Folder as Folder;
}
More Information:
- ABAP Data Models: CDS Hierarchies
- ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model: Implementing Treeviews
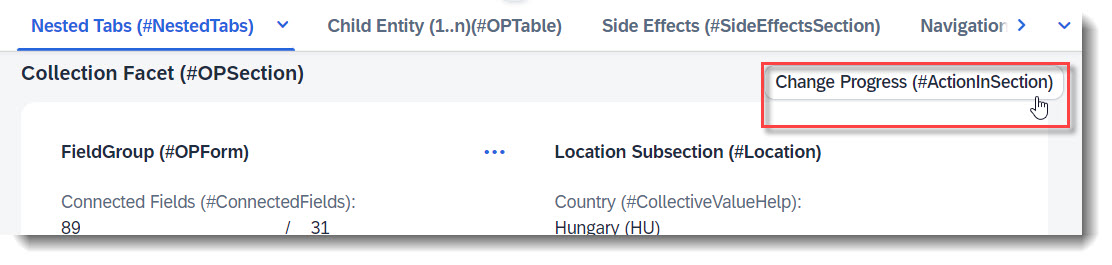
Search term: #ActionInSection
Sections can have their own actions, which show up in the upper right corner of the section by default. This is done through annotation @UI.facet.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #OPForm
{
purpose : #HEADER, // or #STANDARD,
label : 'FieldGroup (#OPForm)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'OPForm',
id: 'SubSectionID'
}
]
// Search Term #ActionInSection
@UI.fieldGroup: [
{
qualifier: 'OPForm',
dataAction: 'changeProgress',
type: #FOR_ACTION,
emphasized: true,
criticality: 'CriticalityCode',
label: 'Change Progress (#ActionInSection)'
}
]
LastChangedAt;
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
action changeProgress parameter /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeProgressP result [1] $self;
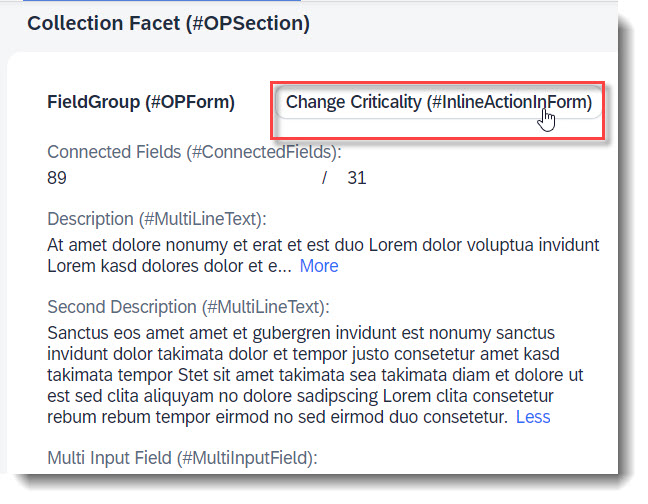
Search term: #InlineActionInForm
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
Forms can also have their own actions, which show up in the upper right corner of the form by default. This is done through annotation @UI.facet and UI.fieldGroup.inline: true.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #OPForm
{
purpose : #HEADER, // or #STANDARD,
label : 'FieldGroup (#OPForm)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'OPForm',
id: 'SubSectionID'
}
]
// Search Term #InlineActionInForm
@UI.fieldGroup: [
{
qualifier: 'OPForm',
dataAction: 'changeCriticality',
type: #FOR_ACTION,
emphasized: true,
inline: true,
label: 'Change Criticality (#InlineActionInForm)'
}
]
LastChangedAt;
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
action changeProgress parameter /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeProgressP result [1] $self;
Search term: #SectionNavigation, #FormNavigation
External or intent based navigations are added in the App using @UI.fieldGroup. Depending on the type used (#FOR_INTENT_BASED_NAVIGATION or #WITH_INTENT_BASED_NAVIGATION), the navigation will either be rendered as a button at the section toolbar or a link.
An intent is the combination of an action and semantic object. There are 2 ways to achieve this.
Associating the semantic object using @Consumption.semanticObject and keyword semanticObjectAction in the UI anotation.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #OPForm
{
purpose : #HEADER, // or #STANDARD,
label : 'FieldGroup (#OPForm)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'OPForm',
id: 'SubSectionID'
}
]
@Consumption.semanticObject: 'FeatureShowcaseNavigation'
@UI: {
fieldGroup: [
// Search Term #SectionNavigation ( Button )
{
qualifier: 'OPForm',
label: 'IntentBased Navi (#SectionNavigation)',
type: #FOR_INTENT_BASED_NAVIGATION,
semanticObjectAction: 'manage'
},
// Search Term #FormNavigation ( Link )
{
qualifier: 'OPForm',
label: 'IntentBased Navi (#FormNavigation)',
type: #WITH_INTENT_BASED_NAVIGATION,
value: 'NavigationID',
semanticObjectAction: 'manage',
position: 50
}
]
}
NavigationID;
Search term: #UISemanticObject
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
Associating the semantic object using keywords semanticObject, semanticObjectAction in the UI anotation.
Additionally you may set the binding if different values are to be used. You can use either localElement for a property in the CDS view, or localParameter for a CDS parameter.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #HeaderCollectionFacet
{
purpose: #HEADER,
id: 'FacetCollection',
type: #COLLECTION
},
// Search Term #HeaderFieldGroup
{
parentId : 'FacetCollection',
label : 'General Data (#HeaderFieldGroup)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'HeaderData'
}
]
@UI: {
fieldGroup: [
// Search Term #UISemanticObject
{
qualifier: 'HeaderData',
position: 40,
label: 'IntentBased Navi (#UISemanticObject)',
type: #WITH_INTENT_BASED_NAVIGATION,
semanticObject: 'FeatureShowcaseContact',
semanticObjectAction: 'manage',
semanticObjectBinding: [{ localElement: 'Country', element: 'Country' }]
}
]
}
ContactID;
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model: Based on Intent
Search term: #OPTable
Table sections are most commonly for child entities or other associated entities. The implementation consists of two parts. First the associated or child entity needs the @UI.lineItem annotation. This defines which fields are displayed.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_GrandchildTP
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 10 }] // Search Term #OPTable
StringProperty;
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
Secondly the @UI.facet annotation needs to be added
// Search Term #OPTable
@UI.facet: [
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #LINEITEM_REFERENCE,
targetElement: '_Grandchild',
label: 'Grandchild Entities (1..n)(#OPTable)'
}
]
Additionally it is also possible to show a table in a facet using the type #SELECTIONPRESENTATIONVARIANT_REFERENCE.
First the associated or child entity needs @UI.presentationVariant, @UI.selectionVariant, @UI.selectionPresentationvariant and @UI.lineItem annotation. This defines which fields are displayed.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #OPTable
@UI: {
// Search Term #PresentationVariant-Child
presentationVariant: [
{
qualifier: 'pVariant',
sortOrder: [
{
by: 'StringProperty',
direction: #DESC
}
],
visualizations: [{type: #AS_LINEITEM}]
}
],
// Search Term #SelectionVariant-Child
selectionVariant: [
{
qualifier: 'sVariant',
text: 'SelectionVariant (Positive criticality)',
filter: 'CriticalityCode EQ 3'
}
],
// Search Term #SelectionPresentationVariant-Child
selectionPresentationVariant: [
{
presentationVariantQualifier: 'pVariant',
selectionVariantQualifier: 'sVariant'
}
]
}
annotate entity /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
with
{
...
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 10 }] // Search Term #OPTable
StringProperty;
@UI.lineItem: [{ position: 20 }] // Search Term #OPTable
FieldWithPercent;
@UI.lineItem: [{
position: 30,
criticality: 'CriticalityCode'
}]
BooleanProperty;
}
Secondly the @UI.facet annotation needs to be added.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #OPTable, #PresentationVariant-Child, #SelectionPresentationVariant-Child, #SelectionVariant-Child
@UI.facet: [
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #SELECTIONPRESENTATIONVARIANT_REFERENCE,
targetElement: '_Child',
label: 'Child Entity (1..n)(#OPTable)',
id: 'childEntitiesSection'
}
]
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model: Tables
Search term: #OPTableTitle
The title of an Object Page table is the attribute typeNamePlural of the @UI.headerInfo annotation.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #HeaderInfo
@UI.headerInfo: {
...
typeNamePlural: 'Root Entities (#OPTableTitle)', // Search Term #OPTableTitle
...
}
If the section title and the table title are identical or the @UI.headerInfo annotation is not given, the table title will not be displayed. Also if the table is the only content in a subsection and has a title, the subsections title will not be displayed.
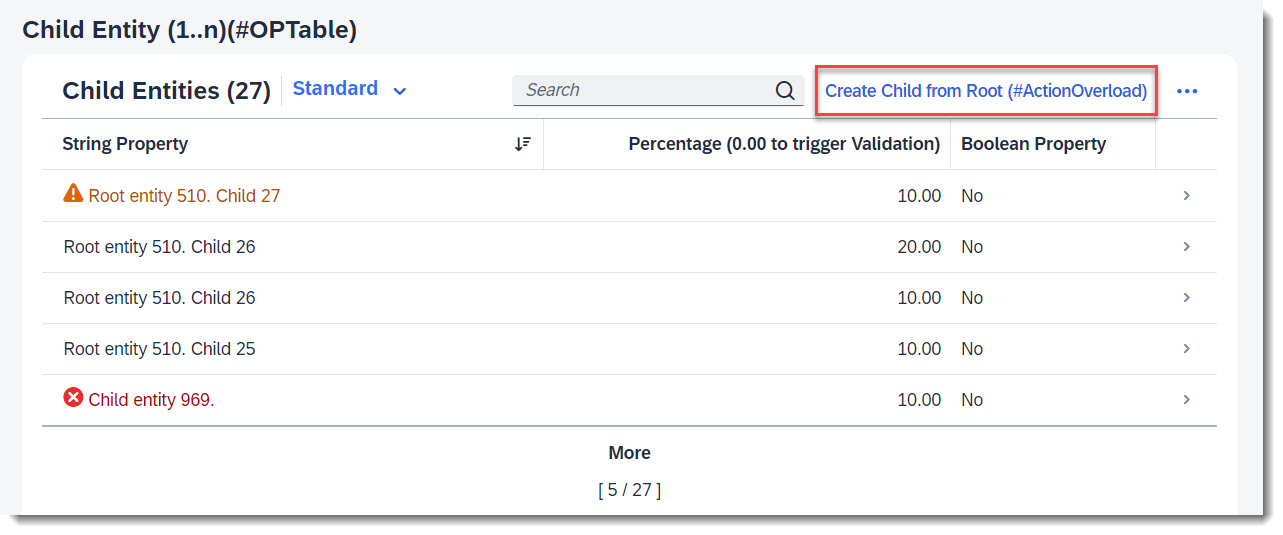
Search term: #ActionOverload
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
Action overload means to add an action bound to another entity, to the object page list table of a child entity. The action is defined in the behaviour definition, and the UI annotation to add the action is defined in the other entity's CDS view or metadata extension.
The example given here, is an action button displayed at the Child entity table in section Child Entity (1..n)(#OPTable), that calls a Root action to create a new Child instance.
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP alias Root
{
action ( features : instance ) createChildFromRoot result [0..1] entity /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP;
}
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChildTP
// Search Term #ActionOverload
@UI.lineItem: [
{
type: #FOR_ACTION,
dataAction: '/DMO/FSA_C_RootTP.createChildFromRoot',
label: 'Create Child from Root (#ActionOverload)'
}
]
StringProperty;
Search term: #ChartSection
As an alternative to micro charts in the header, charts are also possible as sections. However the implementation is more complex. As aggregation is not yet available for V4 services, which this app is based on, the following shows only an example of how a chart should be annotated.
First the entity needs @Aggregation.default annotations, which defines which aggregation methods are supported. This can only be done on views that are not transactional.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Chart
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Chart
as select from zfsa_chart_a
...
{
key id as ID,
...
@EndUserText.label : 'Minimal Net Amount'
@Aggregation.default: #MIN
integer_value as MinAmount,
@EndUserText.label : 'Maximal Net Amount'
@Aggregation.default: #MAX
integer_value as MaxAmount,
@EndUserText.label : 'Average Net Amount'
@Aggregation.default: #AVG
integer_value as AvgAmount,
...
}
After that the @UI.chart can be defined. Please note, that the attribute measures contains the properties of the aggregation methods. If it is just a property of the entity, like "integerValue", the chart won't be displayed. The first property in the attribute dimensions has the default dimension. The second property is the category into which a drill down is possible.
The added actions to the attribute actions are shown in the chart toolbar.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_C_ChartTP
// Search Term #ChartSection
@UI.chart: [
{
qualifier: 'Test',
title: 'Chart (#ChartSection)',
chartType: #COLUMN,
dimensions: ['Dimensions', 'CriticalityCode'],
measures: ['MaxAmount'],
dimensionAttributes: [
{
dimension: 'Dimensions',
role: #CATEGORY
},
{
dimension: 'CriticalityCode',
role: #CATEGORY
}
],
measureAttributes: [
{
measure: 'MaxAmount',
role: #AXIS_1
}
],
actions: [{ type: #FOR_ACTION, dataAction: 'updateChart', label: 'Action at Chart' }]
}
]
Lastly the chart needs to be added to the @UI.facet annotation.
:warning: This section is commented out in the Feature Showcase App as Aggregation annotations are still not yet available in V4 services
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search term #ChartSection
@UI.facet: [
{
id: 'chart',
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #CHART_REFERENCE,
targetElement: '_Chart',
label: 'Chart (#ChartSection)'
}
]
For semantic coloring of a dimension, the dimension property "CriticalityCode" is annotated with @UI.valueCriticality, where possible values of the property are matched against a criticality.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_ChartTP
// Search Term #ChartSection
@UI.valueCriticality: [
{
value: '1',
criticality: #NEGATIVE
},
{
value: '2',
criticality: #CRITICAL
},
{
value: '3',
criticality: #POSITIVE
}
]
CriticalityCode;
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model: Visualizing Data with Charts