Dependencies: SDL2, gcc.
local lazypath = vim.fn.stdpath("data") .. "/lazy/lazy.nvim"
if not (vim.uv or vim.loop).fs_stat(lazypath) then
vim.fn.system({
"git",
"clone",
"--filter=blob:none",
"https://github.com/folke/lazy.nvim.git",
"--branch=stable", -- latest stable release
lazypath,
})
end
vim.opt.rtp:prepend(lazypath)How to run :
gcc % -o %< -lm -I/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX.sdk/System/Library/Frameworks/SDL2.framework/Headers -Wl,-rpath,/Library/Frameworks -F/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX.sdk/System/Library/Frameworks -framework SDL2Manipulation of contact management in C language. Pair:
-
Belkacemi Abderrahim – (Rahim444)
LinkedIn Profile -
Aoudia Nour Islam (islam5603)
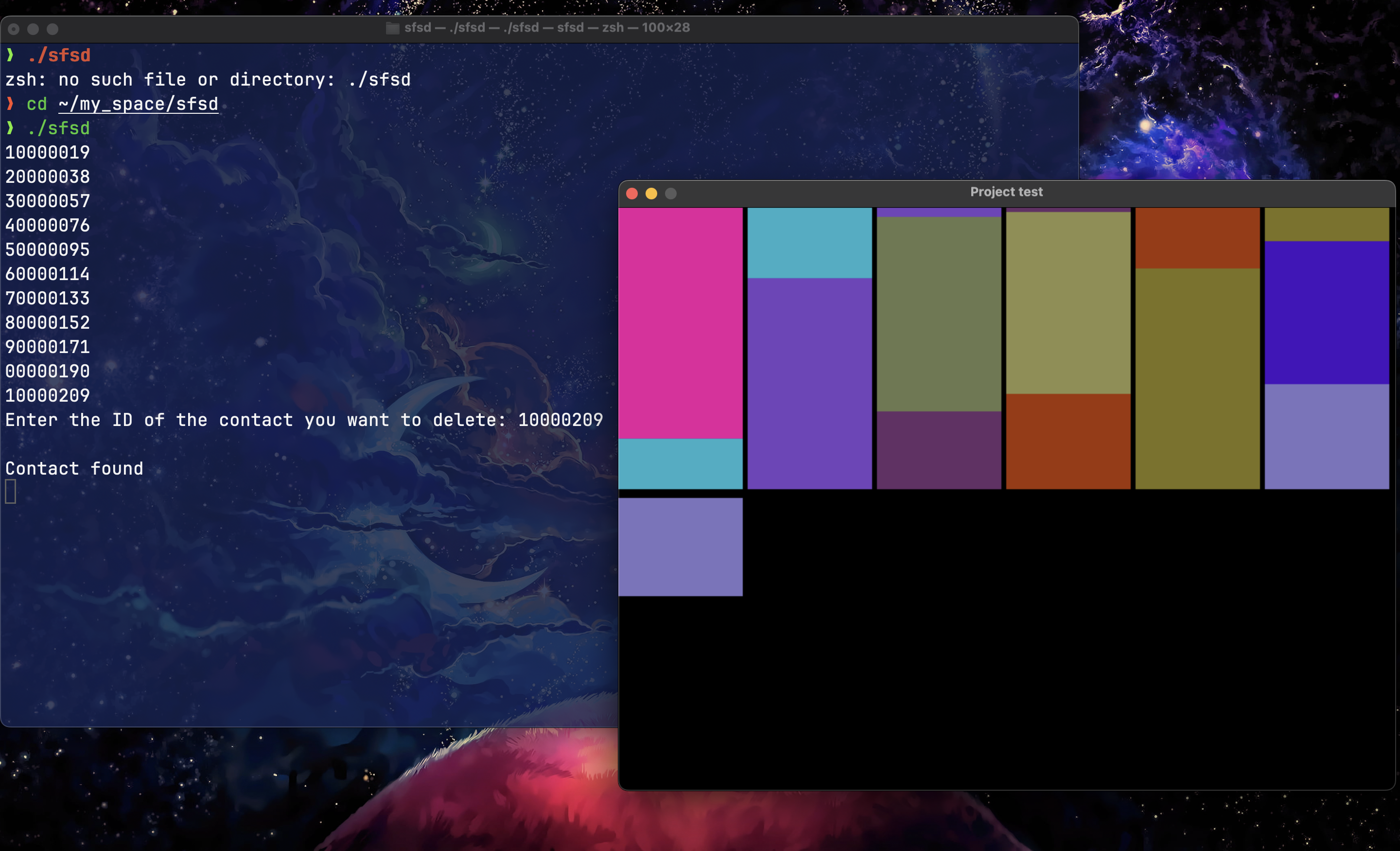
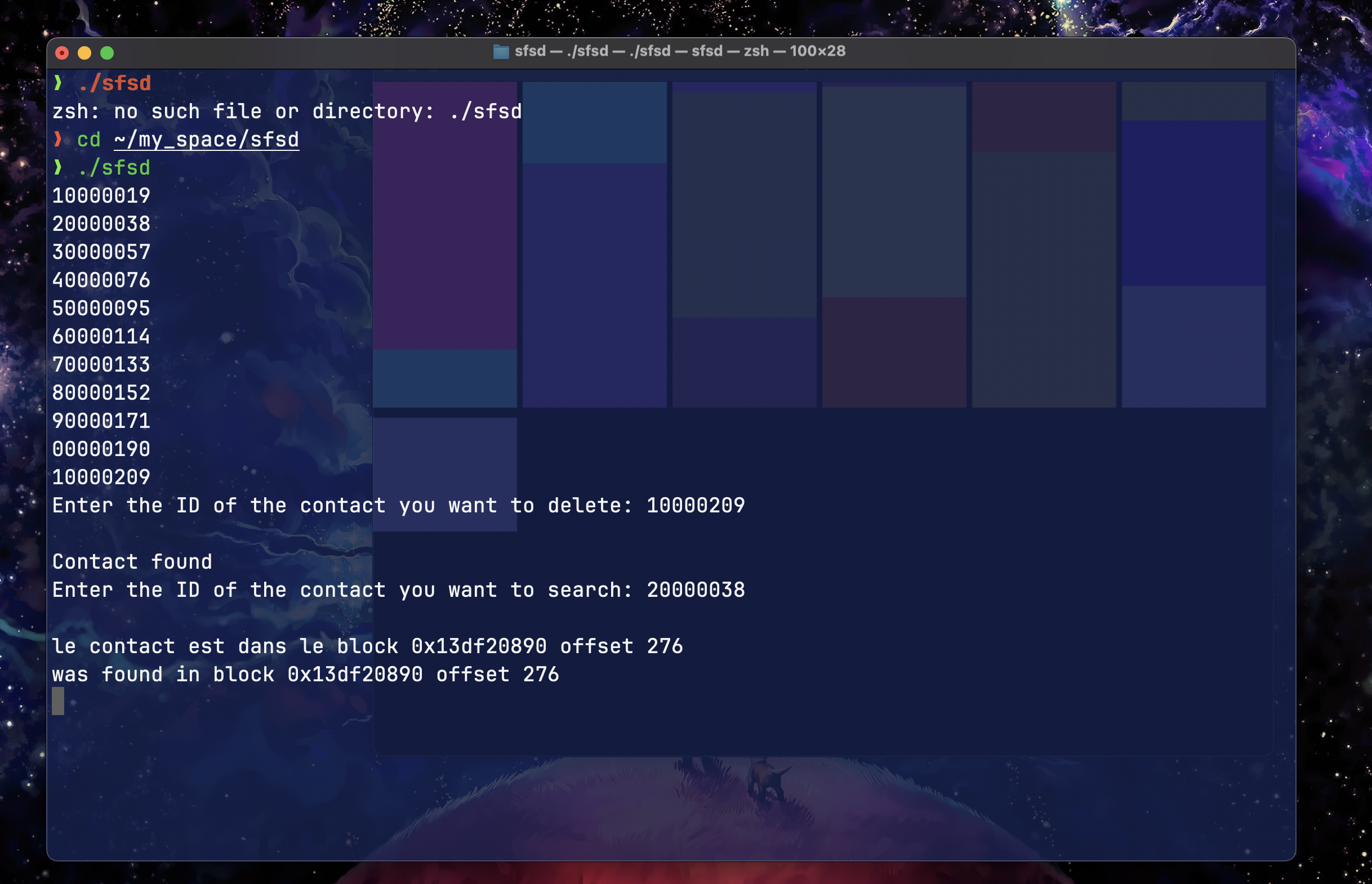
Our project involves implementing a contact management system using a binary file named 'Contacts.bin'. This file adopts an LVC structure (Chained Organization, variable record format, and overlapping). This approach offers particular flexibility to efficiently manage a large number of contacts.
-
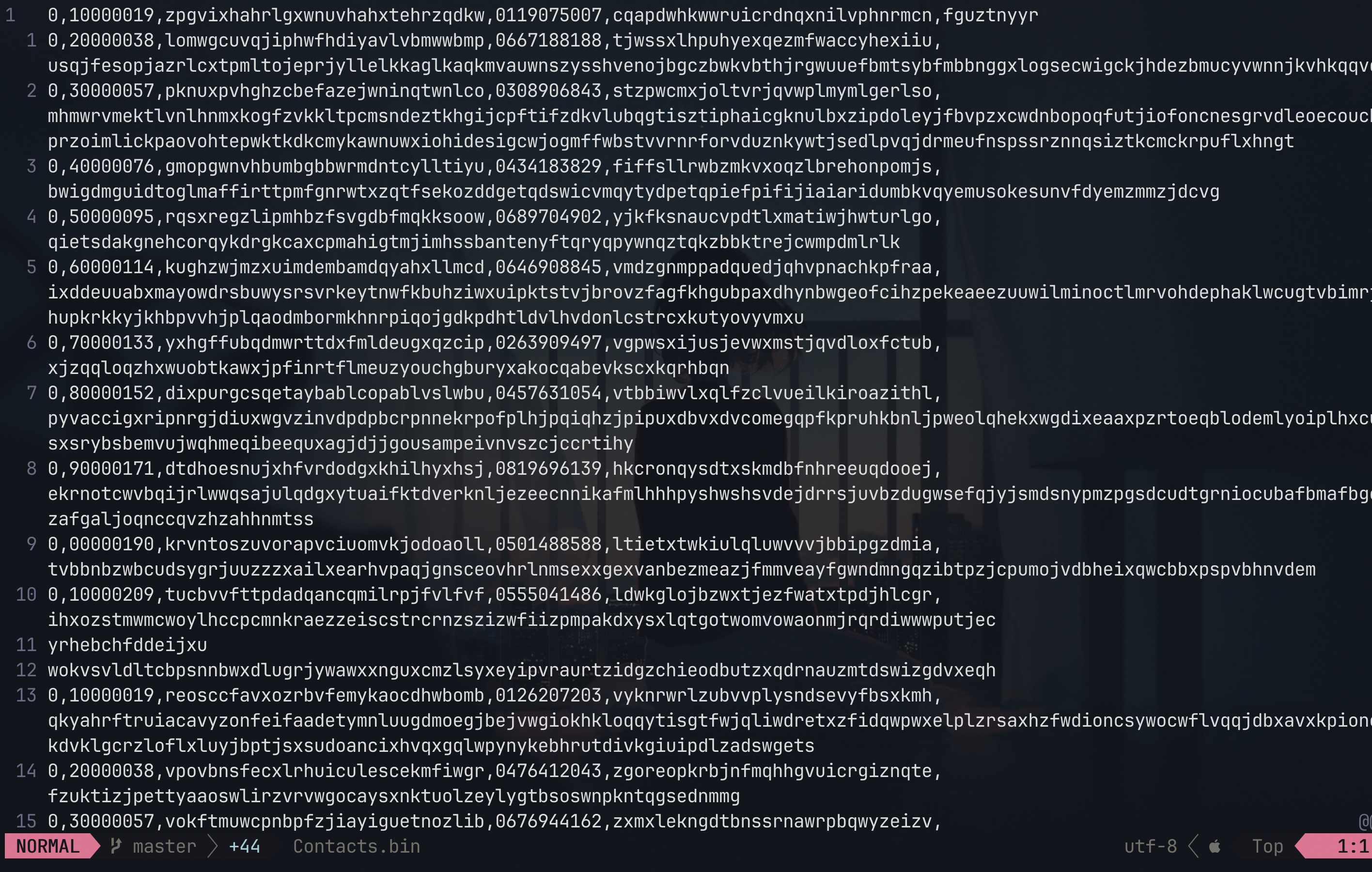
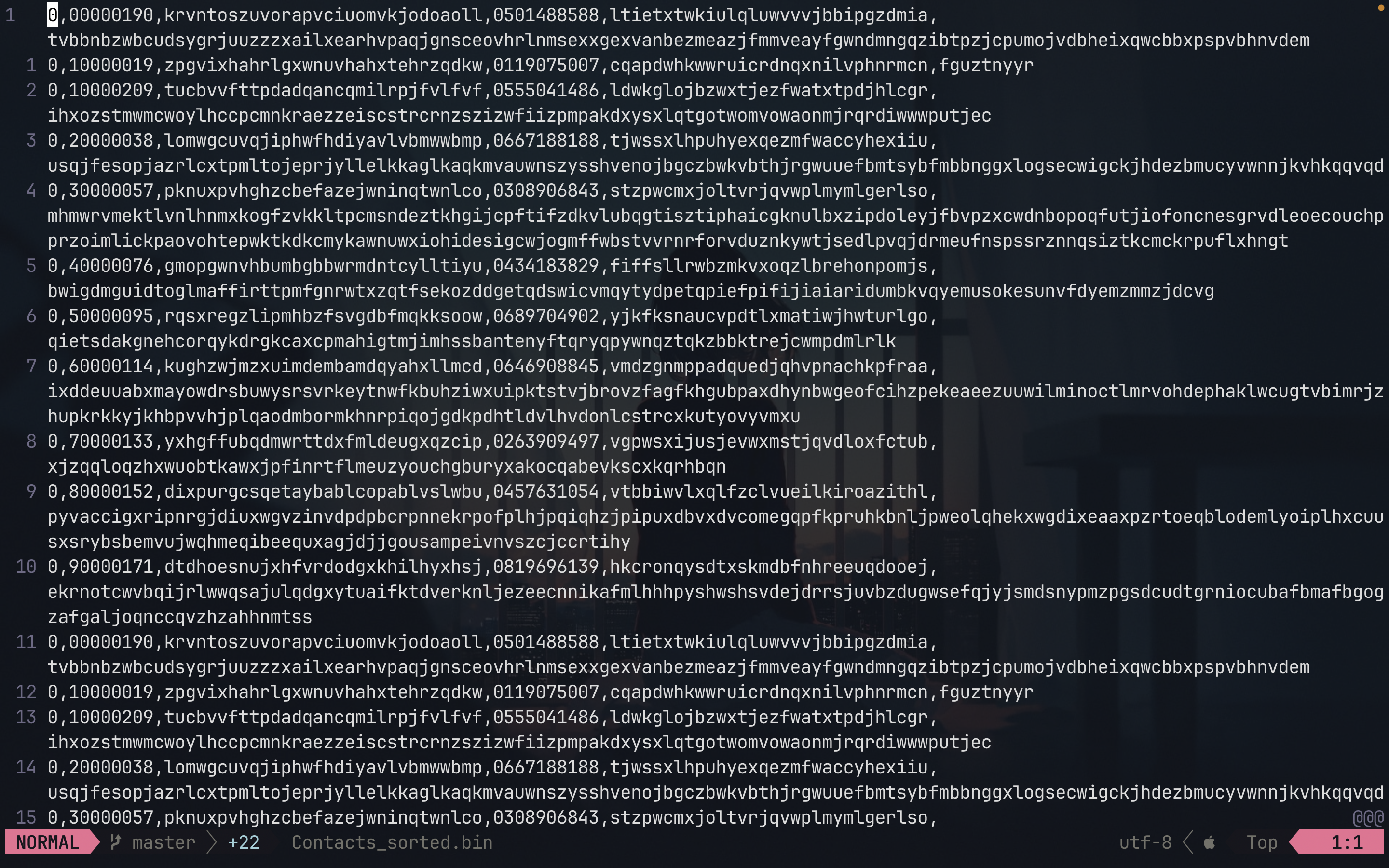
Contact: The Contact structure is designed to store information about a contact, including an identifier (iD), a name (name), a phone number (phoneNumber), an email address (email), and the possibility to include additional variable-length information (otherInfo). Each field is sized to accommodate the maximum expected size, with margins for string termination characters. The use of a pointer for otherInfo suggests dynamic memory management for storing additional details.
-
Block: The Block structure is intended to organize and store contacts efficiently. Each block is identified by a number (blockNumber) and keeps track of the space occupied in characters (occupiedSpace). A character array named Contacts is used to store contacts, although the specific size is not specified. A pointer to the next block (nextBlock) allows for the creation of a linked list of blocks, facilitating dynamic memory management to store a large number of contacts optimally.
-
FileInfo: The FileInfo structure centrally manages a sequence of blocks, probably organized in a linked list to store contacts. The main elements include a pointer to the first block (firstBlock), the total number of blocks in the sequence (totalSize), the total number of contacts stored (contactSize), as well as statistics on operations performed, such as the number of contacts added (addedContacts) and the number of contacts deleted (deletedContacts).
-
IndexFile: The IndexFile structure is designed to index data blocks in a file. Each index element is associated with a file identifier (id), a pointer to the corresponding block (Pblock), and an offset within the block (offset). The linked list (next) allows for dynamic management of index elements, thus facilitating flexible organization of multiple index entries in a file structure.
- SDL2/SDL.h: The <SDL2/SDL.h> library in C language, known as SDL (Simple DirectMedia Layer), offers powerful features for multimedia development. It enables the creation of graphic windows, user input management, graphic rendering, sound and music playback, as well as time and event management. SDL also facilitates working with threads for concurrent task management. Including <SDL2/SDL.h> in the code indicates the use of these features, but also requires linking with the SDL library during compilation for proper functionality.