TLJH plugin provides a JupyterHub service to build and use Docker images as user environments. The Docker images can be built locally using repo2docker or via the binderhub service.
This plugin requires The Littlest JupyterHub 1.0 or later (running on JupyterHub 4+).
During the TLJH installation process, use the following post-installation script:
#!/bin/bash
# install Docker
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository -y "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable"
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y docker-ce
sudo apt-get update
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg
NODE_MAJOR=21
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] https://deb.nodesource.com/node_$NODE_MAJOR.x nodistro main" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y nodejs
sudo npm install -g yarn
sudo modprobe fuse
# pull the repo2docker image
sudo docker pull gcr.io/nii-ap-ops/repo2docker:2024.10.0
sudo docker pull gcr.io/nii-ap-ops/rdmfs:2024.12.0
# install TLJH 1.0
curl -L https://tljh.jupyter.org/bootstrap.py \
| sudo python3 - \
--version 1.0.0 \
--admin admin:change-your-password \
--plugin git+https://github.com/RCOSDP/CS-tljh-repo2docker.git@master
# Workaround: upgrade to the latest version of jupyterhub
# Because an older version of jupyterhub is installed together with CS-binderhub,
# upgrade jupyterhub after the installation of the plugin
sudo /opt/tljh/hub/bin/pip install --upgrade jupyterhub\<5
# configure the plugin
cat <<'EOF' | sudo tee /opt/tljh/config/jupyterhub_config.d/repo2docker.py
from tljh_repo2docker import TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE
import sys
c.JupyterHub.allow_named_servers = True
c.JupyterHub.services.extend(
[
{
"name": "tljh_repo2docker",
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:6789", # URL must match the `ip` and `port` config
"command": [
sys.executable,
"-m",
"tljh_repo2docker",
"--ip",
"127.0.0.1",
"--port",
"6789"
],
"oauth_no_confirm": True,
"oauth_client_allowed_scopes": [
TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE, # Allows this service to check if users have its admin scope.
],
}
]
)
c.JupyterHub.custom_scopes = {
TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE: {
"description": "Admin access to tljh_repo2docker",
},
}
# Set required scopes for the service and users
c.JupyterHub.load_roles = [
{
"description": "Role for tljh_repo2docker service",
"name": "tljh-repo2docker-service",
"scopes": [
"read:users",
"read:roles:users",
"admin:servers",
"access:services!service=binder",
],
"services": ["tljh_repo2docker"],
},
{
"name": "user",
"scopes": [
"self",
# access to the serve page
"access:services!service=tljh_repo2docker",
],
},
{
"name": 'tljh-repo2docker-service-admin',
"groups": ["repo2docker"],
"scopes": [TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE],
},
]
c.JupyterHub.tornado_settings = {
"slow_spawn_timeout": 30
}
EOF
sudo systemctl restart jupyterhubApplying the above settings allows JupyterHub administrators or users in the repo2docker group to access the tljh_repo2docker service. See Configuration for information to customize the settings.
Refer to The Littlest JupyterHub documentation for more info on installing TLJH plugins.
This Python package is designed for deployment as a service managed by JupyterHub. The service runs its own Tornado server. Requests will be forwarded to it by the JupyterHub internal proxy from the standard URL https://{my-hub-url}/services/my-service/.
The available settings for this service are:
port: Port of the service; defaults to 6789ip: Internal IP of the service; defaults to 127.0.0.1default_memory_limit: Default memory limit of a user server; defaults toNonedefault_cpu_limit: Default CPU limit of a user server; defaults toNonemachine_profiles: Instead of entering directly the CPU and Memory value,tljh-repo2dockercan be configured with pre-defined machine profiles and users can only choose from the available option; defaults to[]binderhub_url: The optional URL of thebinderhubservice. If it is available,tljh-repo2dockerwill use this service to build images.db_url: The connection string of the database.tljh-repo2dockerneeds a database to store the image metadata. By default, it will create asqlitedatabase in the starting directory of the service. To use other databases (PostgreSQLorMySQL), users need to specify the connection string via this config and install the additional drivers (asyncpgoraiomysql).
This service requires the following scopes : read:users, admin:servers and read:roles:users. If binderhub service is used, access:services!service=binderis also needed. Here is an example of registering tljh_repo2docker's service with JupyterHub
# jupyterhub_config.py
from tljh_repo2docker import TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE
import sys
c.JupyterHub.services.extend(
[
{
"name": "tljh_repo2docker",
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:6789", # URL must match the `ip` and `port` config
"command": [
sys.executable,
"-m",
"tljh_repo2docker",
"--ip",
"127.0.0.1",
"--port",
"6789"
],
"oauth_no_confirm": True,
}
]
)
# Set required scopes for the service and users
c.JupyterHub.load_roles = [
{
"description": "Role for tljh_repo2docker service",
"name": "tljh-repo2docker-service",
"scopes": [
"read:users",
"read:roles:users",
"admin:servers",
"access:services!service=binder",
],
"services": ["tljh_repo2docker"],
},
{
"name": "user",
"scopes": [
"self",
# access to the serve page
"access:services!service=tljh_repo2docker",
],
},
]By default, only users with an admin role can access the environment builder page and APIs, by leveraging the RBAC system of JupyterHub, non-admin users can also be granted the access right.
Here is an example of the configuration
# jupyterhub_config.py
from tljh_repo2docker import TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE
import sys
c.JupyterHub.services.extend(
[
{
"name": "tljh_repo2docker",
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:6789",
"command": [
sys.executable,
"-m",
"tljh_repo2docker",
"--ip",
"127.0.0.1",
"--port",
"6789"
],
"oauth_no_confirm": True,
"oauth_client_allowed_scopes": [
TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE, # Allows this service to check if users have its admin scope.
],
}
]
)
c.JupyterHub.custom_scopes = {
TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE: {
"description": "Admin access to tljh_repo2docker",
},
}
c.JupyterHub.load_roles = [
... # Other role settings
{
"name": 'tljh-repo2docker-service-admin',
"users": ["alice"],
"scopes": [TLJH_R2D_ADMIN_SCOPE],
},
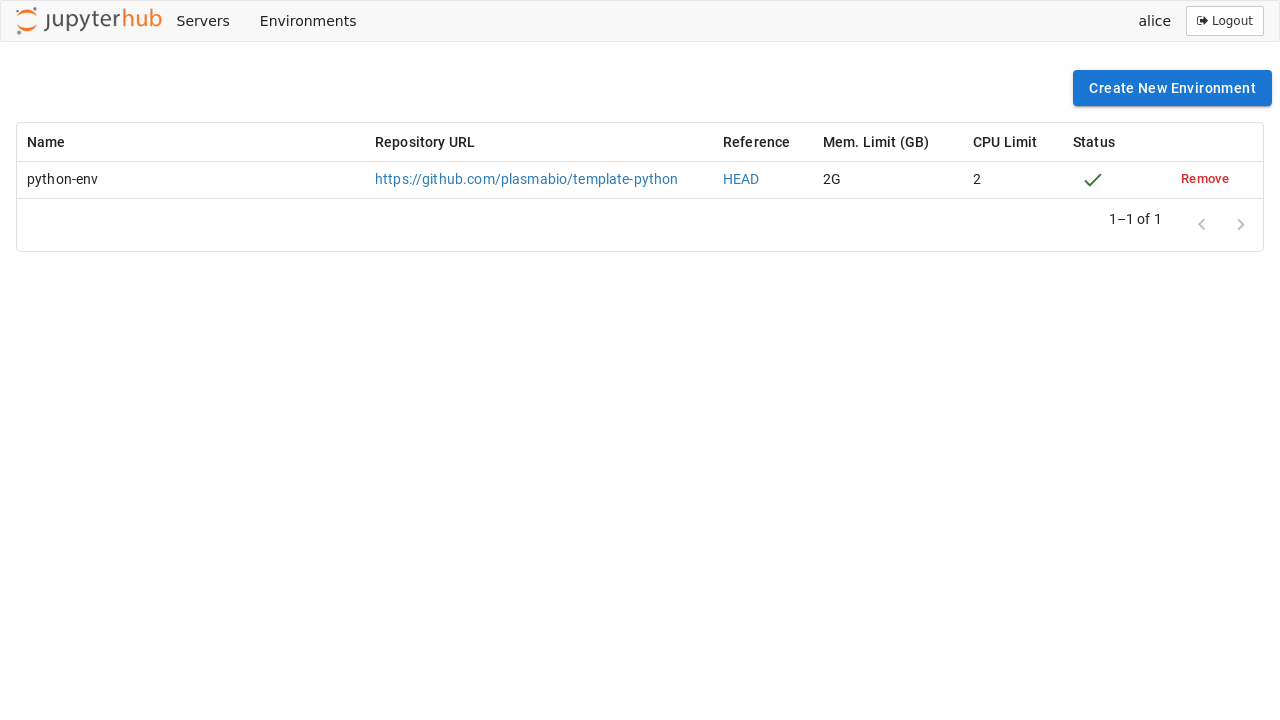
]The Environments page shows the list of built environments, as well as the ones currently being built:
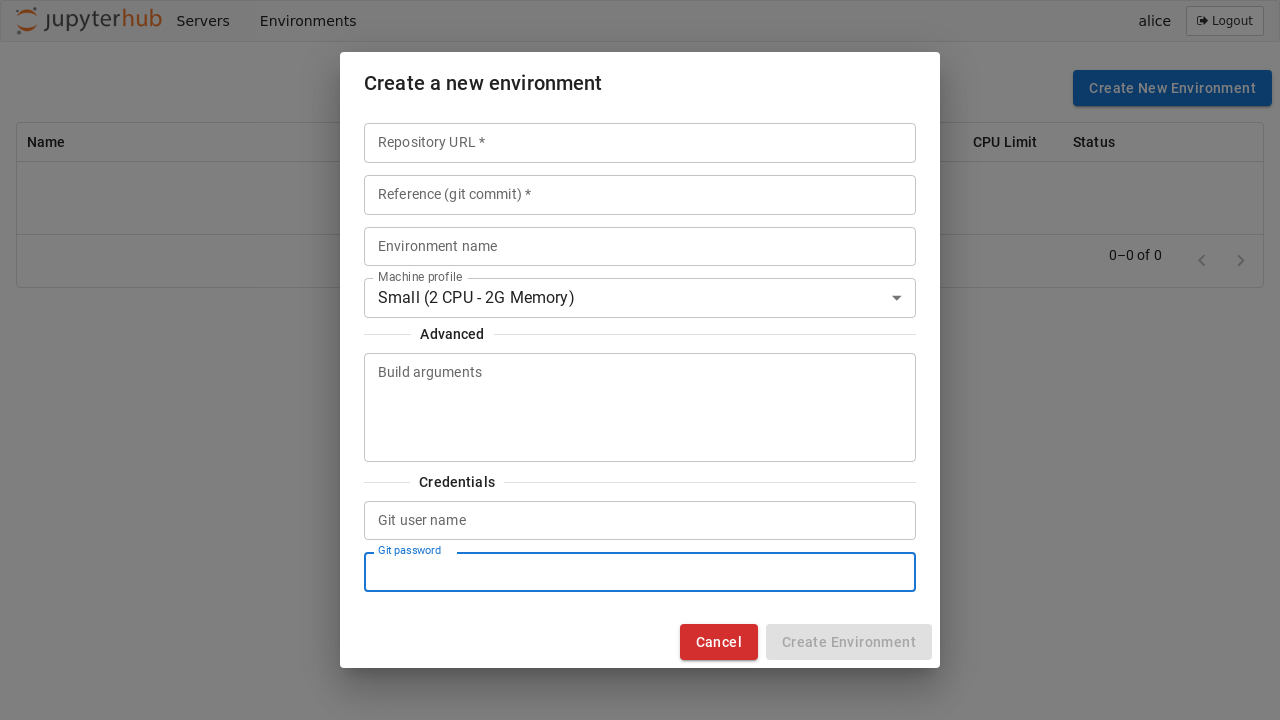
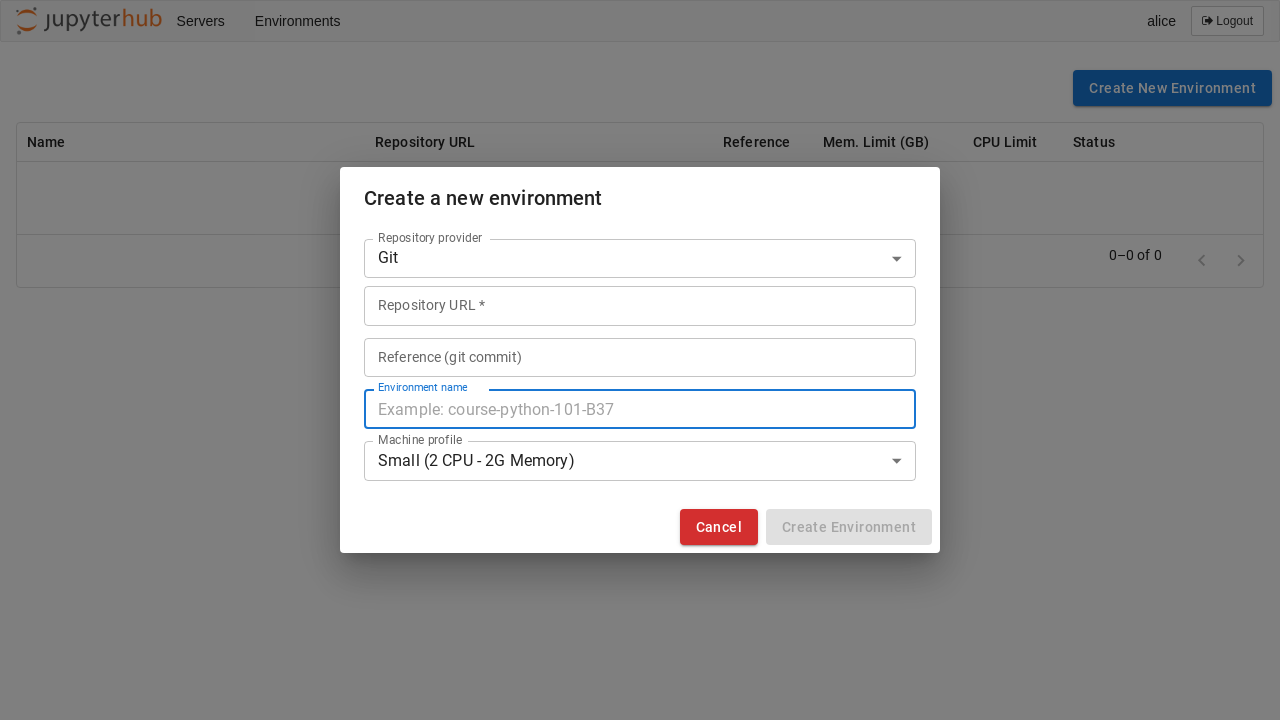
Just like on Binder, new environments can be added by clicking on the Add New button and providing a URL to the repository. Optional names, memory, and CPU limits can also be set for the environment:
Note
If the build backend is binderhub service, users need to select the repository provider and can not specify the custom build arguments
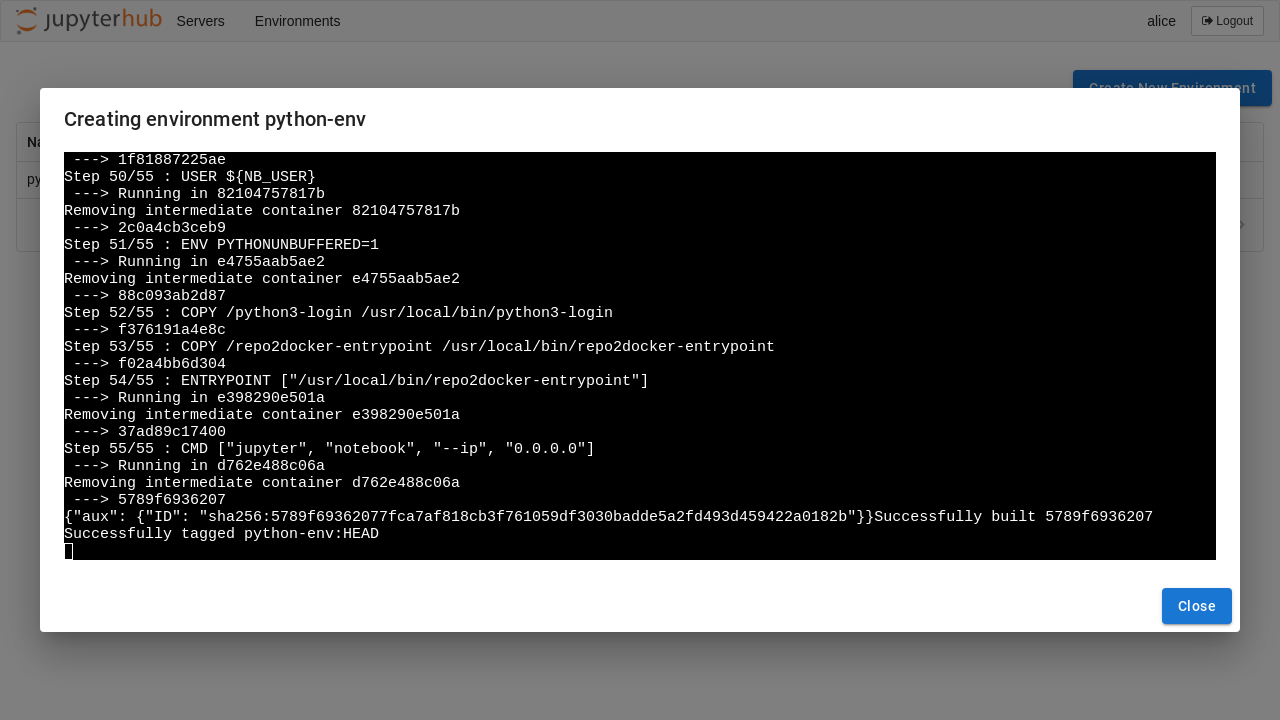
Clicking on the Logs button will open a new dialog with the build logs:
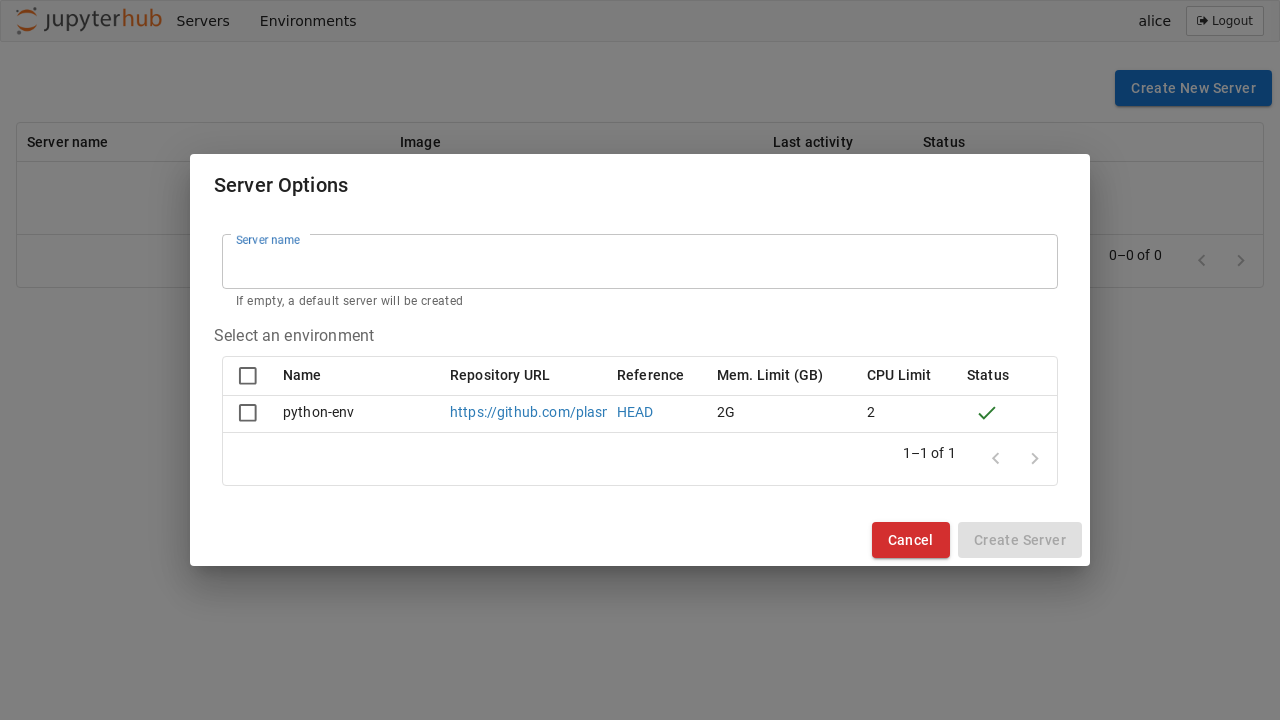
Once ready, the environments can be selected from the JupyterHub spawn page:
tljh-repo2docker also supports building environments from private repositories.
It is possible to provide the username and password in the Credentials section of the form:
On GitHub and GitLab, a user might have to first create an access token with read access to use as the password:
Note
The binderhub build backend does not support configuring private repositories credentials from the interface.
Instead of entering directly the CPU and Memory value, tljh-repo2docker can be configured with pre-defined machine profiles and users can only choose from the available options. The following configuration will add 3 machines with labels Small, Medium and Large to the profile list:
c.JupyterHub.services.extend(
[
{
"name": "tljh_repo2docker",
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:6789",
"command": [
sys.executable,
"-m",
"tljh_repo2docker",
"--ip",
"127.0.0.1",
"--port",
"6789",
"--machine_profiles",
'{"label": "Small", "cpu": 2, "memory": 2}',
"--machine_profiles",
'{"label": "Medium", "cpu": 4, "memory": 4}',
"--machine_profiles",
'{"label": "Large", "cpu": 8, "memory": 8}'
],
"oauth_no_confirm": True,
}
]
)tljh-repo2docker is currently developed as part of the Plasma project.
See the Plasma documentation on user environments for more info.
See: https://repo2docker.readthedocs.io/en/latest/howto/jupyterhub_images.html
Check out the instructions in DEPLOYMENT.md to set up the deployment.
Check out the instructions in CONTRIBUTING.md to set up a local environment.