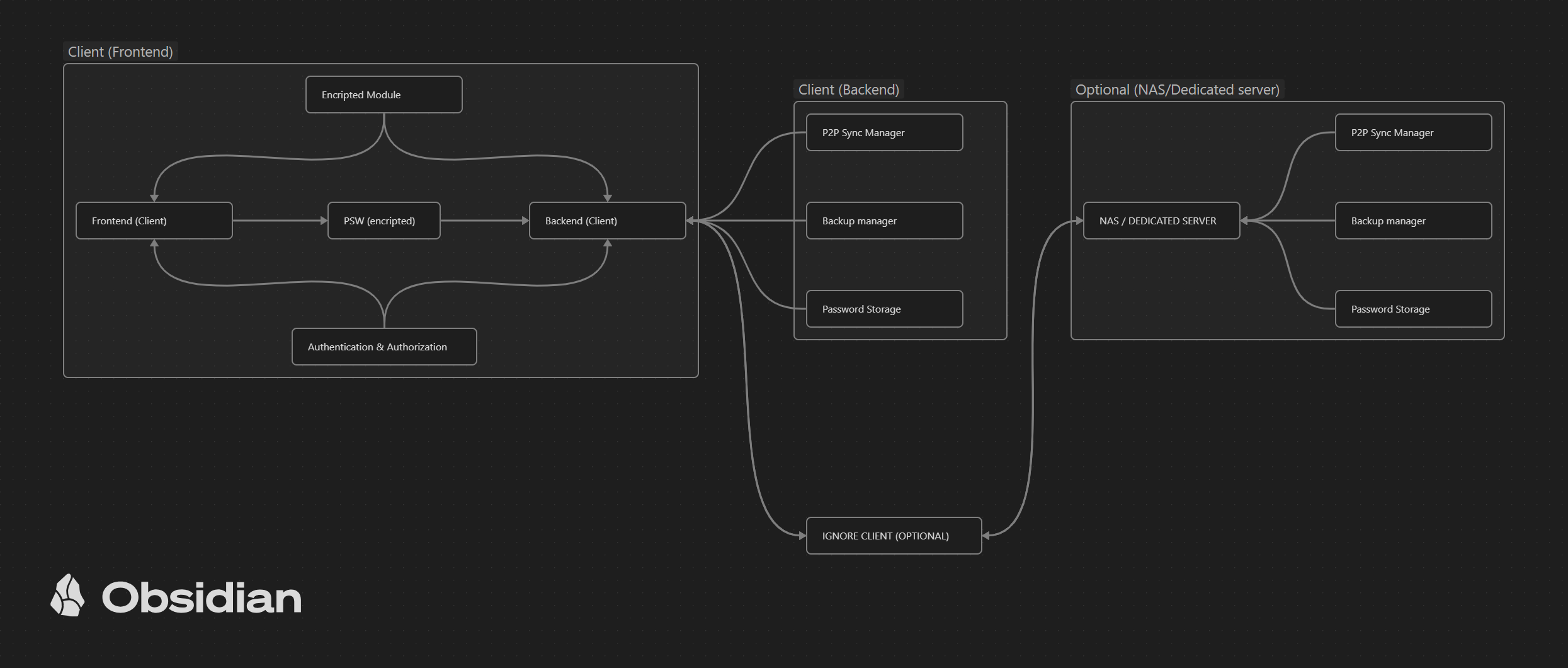
FortiVault is a decentralized password manager designed to keep your credentials secure by eliminating reliance on central servers. Built with a focus on privacy and security, FortiVault uses cutting-edge technology to ensure that your sensitive information is stored and synchronized safely across devices without the need for large data centers or third-party servers.
In recent years, data breaches have exposed millions of passwords and sensitive information from major databases. For instance:
- Equifax Data Breach (2017): Over 147 million records, including sensitive personal information, were compromised.
- Yahoo Data Breaches (2013-2014): A series of breaches resulted in over 3 billion accounts being compromised.
- LastPass Security Incident (2022): Exposed data from a password manager raised concerns about password security and encryption practices.
These incidents highlight the risks associated with storing personal data on centralized servers. Large data centers, while providing convenience, are also lucrative targets for cybercriminals. FortiVault mitigates these risks by employing a decentralized approach, ensuring that your passwords are stored and managed on your own devices, not in vulnerable data centers.
- Decentralized Storage: Passwords are stored locally on your device and synchronized across devices using a peer-to-peer network.
- Strong Encryption: AES encryption ensures that your data is securely encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance security with MFA, including biometric options.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Available for Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS.
- Backup and Recovery: Secure backups and recovery options to safeguard against data loss.
+------------------------------------------------------+
| FortiVault Architecture |
+------------------------------------------------------+
+---------------------------+ +---------------------------+
| | | |
| Client (Local App) |<---->| Dedicated Server/NAS |
| | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | | | | | |
| | Password Storage | | | | Password Storage | |
| | (Encrypted) | |<---->| | (Encrypted) | |
| | | | | | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | | | | | |
| | Backup Manager | | | | Backup Manager | |
| | (Local & Remote) | |<---->| | (Server Backup) | |
| | | | | | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ | (Server not encript client data because
| | | | | | | | the data already come to server encripted
| | Encryption Module | | | | Encryption Module | | so only client know how to decript
| | (AES-256, Argon2) | | | | (AES-256, Argon2) | | it will ensure that even if data leaks the
| | | | | | | | content will remain safe)
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | | | | | |
| | P2P Sync Manager | |<---->| | P2P Sync Manager | |
| | (libp2p) | | | | (libp2p) | |
| | | | | | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | | | | | |
| | Authentication | | | | Authentication | |
| | & Authorization | |<---->| | & Authorization | |
| | (MFA, JWT, etc.) | | | | (MFA, JWT, etc.) | |
| | | | | | | |
| +-----------------------+ | | +-----------------------+ |
| | | |
+---------------------------+ +---------------------------+
+-------------------------------+ +-------------------------------+
| User Interface | | Network & Security Layers |
+-------------------------------+ +-------------------------------+
| | | |
| +---------------------------+ | | +---------------------------+ |
| | Next.js Frontend | | | | TLS/SSL Encryption | |
| | (React, Tauri) | | | | Secure Communication | |
| +---------------------------+ | | +---------------------------+ |
| | | |
| +---------------------------+ | | +---------------------------+ |
| | API Communication | | | | API Security Layer | |
| | (Rust, Tauri) | | | | (JWT, OAuth2, etc.) | |
| +---------------------------+ | | +---------------------------+ |
+-------------------------------+ +-------------------------------+
Client (local application):
- Password Storage: Stores passwords in encrypted form locally on the device.
- Backup Manager: Manages local and remote backups. In case of dedicated servers, sync with them.
- Encryption module: Performs data encryption using AES-256 and key derivation using Argon2.
- P2P Sync Manager: Manages peer-to-peer synchronization between devices, ensuring that passwords are always up to date.
- Authentication and Authorization: Implements authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as MFA and JWT.
Dedicated Server/NAS:
- It works as a dedicated server where users can store their passwords, sync between devices and keep secure backups.
- It shares the same functionalities as the local client, but operates on a dedicated server.
User Interface:
- Next.js Frontend: User interface built with Next.js and React, integrated with Tauri to enable desktop functionality.
- API Communication: Communication between frontend and backend is done securely using Rust and Tauri.
Network and security layers:
- TLS/SSL encryption: Ensures that all communications between client and server are secure.
- API Security Layer: Protects APIs with mechanisms like JWT, OAuth2, and other security practices.
The FortiVault Password Manager is designed to securely store user passwords locally on the user's device, leveraging strong encryption methods and avoiding any form of cloud-based storage by default. This approach eliminates the risk of large-scale data breaches, such as the ones that have affected cloud-based password managers in the past.
However, for users who wish to synchronize their data across devices or set up their private servers, FortiVault offers a flexible option. Even in this scenario, the security model is designed to maintain data integrity and privacy, adhering to a "zero trust" principle. This document outlines the security architecture and data management model employed in FortiVault.
-
Client-Side Encryption:
All sensitive data, including passwords and user-specific information, are encrypted on the client side before being stored or transmitted. This ensures that no plaintext data is ever exposed to the server. -
Server as a Secure Storage and Distribution Service:
The server acts merely as a storage and synchronization service. It does not perform any encryption or decryption on behalf of the clients. The server's primary role is to ensure secure access control, data integrity, and efficient synchronization between devices. -
No Sensitive Data in Plaintext in the Database:
As SQLite databases can be easily opened by an attacker, it is essential not to store any sensitive data such as salts, IVs (Initialization Vectors), or keys in plaintext within the database. Instead, these sensitive encryption details are securely stored in an encrypted file that can only be accessed by the client. -
Local Encrypted File for Key Management:
Each client maintains an encrypted file locally that stores all encryption-related data (e.g., salts, IVs, and private keys). This file is only decrypted when needed by the client application, adding an additional layer of security. -
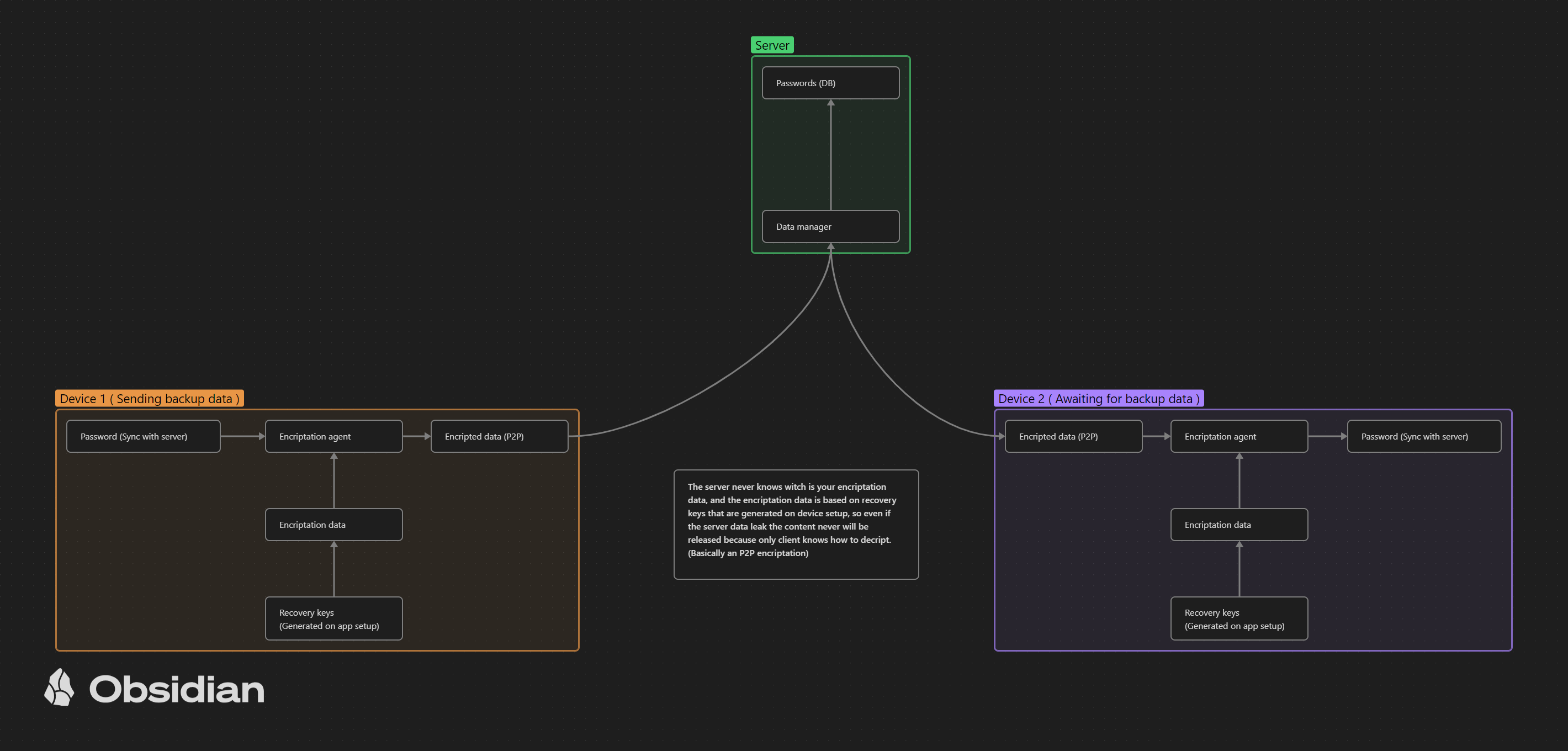
End-to-End Encryption for Data Synchronization:
When users choose to synchronize their data across devices via their private server, the client handles the encryption and decryption process. The server only stores and transmits encrypted data. This ensures that even if the server is compromised, the attacker cannot access the plaintext data. -
Reduced Server Responsibilities:
The server's role is limited to securely storing encrypted data and managing access control. It does not need to implement any encryption or decryption routines for client data, reducing complexity and potential vulnerabilities on the server side. -
Backup and Recovery Using Encrypted Keys:
The server, while not handling sensitive encryption, can facilitate data recovery and synchronization. Users can generate backup keys that allow them to recover their encrypted data from the server in case of device loss. However, only the client with the correct backup keys can decrypt and recover the data.
-
Reduced Attack Surface on the Server:
With the server not managing any sensitive encryption keys or data in plaintext, the potential attack surface is significantly minimized. This makes it harder for attackers to exploit server-side vulnerabilities. -
End-to-End Security:
All data is encrypted on the client side, ensuring that it remains secure throughout its lifecycle—from storage to transmission to retrieval. -
Total Control for Users:
Users maintain complete control over their data and encryption keys. This aligns with the principle of user autonomy and privacy, making the application trustworthy for security-conscious users. -
Flexibility in Deployment:
Users can choose to operate FortiVault entirely offline or set up their private server for additional functionality. This flexibility does not compromise security, as the core encryption and decryption processes remain on the client side.
To get started with FortiVault, follow these steps:
-
Clone the Repository:
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/fortivault.git
-
Install Dependencies: Navigate to the project directory and install dependencies for each microservice.
cd fortivault # Follow the installation instructions for each microservice
-
Build and Run: Build and run the application using the provided scripts or commands.
# Example command npm run start -
Configuration: Follow the configuration guidelines provided in the
docs/directory to set up your local environment and synchronize devices.
We welcome contributions from the community to help improve FortiVault. Here’s how you can get involved:
-
Report Issues: If you encounter any bugs or have suggestions for improvements, please open an issue.
-
Submit Pull Requests: Feel free to submit pull requests with bug fixes, new features, or improvements. Make sure to follow the contribution guidelines.
-
Join the Discussion: Engage with other contributors and developers on our discussion forum.
-
Spread the Word: Share FortiVault with others who might benefit from a more secure way to manage their passwords.
FortiVault is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.
Protect your credentials and join us in revolutionizing password management with FortiVault.