- Word Search II
困难
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-search-ii/
Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
Example 1:
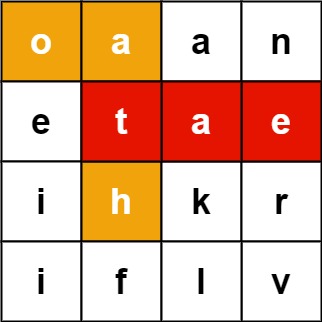
Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
Output: ["eat","oath"]
Example 2:
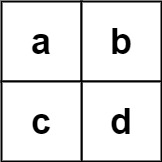
Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
Output: []
Constraints:
m == board.length
n == board[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 12
board[i][j] is a lowercase English letter.
1 <= words.length <= 3 * 104
1 <= words[i].length <= 10
words[i] consists of lowercase English letters.
All the strings of words are unique.
相关企业
- 优步 Uber|33
- 亚马逊 Amazon|31
- 思科 Cisco|12
- 微软 Microsoft|9
- 谷歌 Google|6
- Facebook|5
- Indeed|4
- 苹果 Apple|3
相关标签
- Trie
- Array
- String
- Backtracking
- Matrix
相似题目
- Word Search 中等
- Unique Paths III 困难
隐藏提示1
- You would need to optimize your backtracking to pass the larger test. Could you stop backtracking earlier?
隐藏提示2
- If the current candidate does not exist in all words' prefix, you could stop backtracking immediately. What kind of data structure could answer such query efficiently? Does a hash table work? Why or why not? How about a Trie? If you would like to learn how to implement a basic trie, please work on this problem: Implement Trie (Prefix Tree) first.
A: for 词典里的每个单词 { check 单词是否在矩阵里 } (sol 1)
B: for 矩阵的每个单词 { check 单词是否在词典里} (sol 2) prefix map, or data structure called "trie"
for each word call 79.word search solution to solve
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
if not board:
return []
rowleng = len(board)
colleng = len(board[0])
founded_words = []
for word in words:
visited = [[False] * colleng for _ in range(rowleng)]
found = False
for i in range(rowleng):
for j in range(colleng):
if board[i][j] == word[0]:
visited[i][j] = True
found = self.dfs(board, i, j, word, 1, [board[i][j]], visited, rowleng, colleng)
visited[i][j] = False
if found:
founded_words.append(word)
break
if found:
break
return founded_words
def dfs(self, board, i, j, word, wordindex, currsubset, visited, rowleng, colleng):
# print("".join(currsubset), word, wordindex)
if wordindex > len(word):
return False
if "".join(currsubset) == word:
return True
for offsetx, offsety in [[0,1], [0,-1],[1,0],[-1,0]]:
newx, newy = i + offsetx, j + offsety
if not (0 <= newx <= rowleng-1 and 0 <= newy <= colleng-1) or visited[newx][newy]:
continue
newletter = board[newx][newy]
if newletter == word[wordindex]:
currsubset.append(newletter)
visited[newx][newy] = True
found = self.dfs(board, newx, newy, word, wordindex+1, currsubset, visited, rowleng, colleng)
currsubset.pop()
visited[newx][newy] = False
if found:
return True
return Falseclass Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
if not board:
return []
rowleng = len(board)
colleng = len(board[0])
prefix_is_word = self.setupPrefix(words)
resultsset = set()
visited = [[False] * colleng for _ in range(rowleng)]
for i in range(rowleng):
for j in range(colleng):
if board[i][j] in prefix_is_word:
visited[i][j] = True
self.dfs(board, i, j, board[i][j], prefix_is_word, resultsset, visited, rowleng, colleng)
visited[i][j] = False
return list(resultsset)
def dfs(self, board, i, j, currsubsetstr, prefix_is_word, resultsset, visited, rowleng, colleng):
if currsubsetstr not in prefix_is_word:
return
if prefix_is_word[currsubsetstr]:
resultsset.add(currsubsetstr)
for offsetx, offsety in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
newx, newy = i + offsetx, j + offsety
if not (0 <= newx <= rowleng-1 and 0 <= newy <= colleng-1) or visited[newx][newy]:
continue
visited[newx][newy] = True
self.dfs(board, newx, newy, currsubsetstr+board[newx][newy], prefix_is_word, resultsset, visited, rowleng, colleng)
visited[newx][newy] = False
def setupPrefix(self, words):
prefix_is_word = {}
for word in words:
for i in range(len(word)):
prefix_is_word[word[:i+1]] = False
for word in words:
prefix_is_word[word] = True
return prefix_is_wordsimilar to sol2 but replace prefix map with trie
使用了 Trie 的版本
考点:
- 字典树
- dfs
- tip:trie树,一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种。典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。
题解:
- 首先建立字典树,字典树从root开始,每个节点利用hashmap动态开点,利用字母的公共前缀建树。
- 遍历字母矩阵,将字母矩阵的每个字母,从root开始dfs搜索,搜索到底部时,将字符串存入答案返回即可。
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.children = dict()
self.is_end_of_word = False # 是否是单词最后一个字母
self.word = None # 为了方便也保存下完整单词
class Trie:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.root = TrieNode()
def add(self, word): #字典树插入单词
currnode = self.root
for letter in word:
if letter not in currnode.children:
currnode.children[letter] = TrieNode() #在此节点申请节点
currnode = currnode.children[letter] #继续遍历
currnode.is_end_of_word = True #last letter marked as end of word
currnode.word = word #存入单词
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
if not board:
return []
rowleng = len(board)
colleng = len(board[0])
trie = Trie()
for word in words:
trie.add(word)
resultsset = set()
visited = [[False] * colleng for _ in range(rowleng)]
for i in range(rowleng):
for j in range(colleng):
if board[i][j] in trie.root.children: # root.children are all possible starting letters
visited[i][j] = True
self.dfs(board, i, j, trie.root.children.get(board[i][j]), trie, resultsset, visited, rowleng, colleng)
visited[i][j] = False
return list(resultsset)
def dfs(self, board, i, j, node, trie, resultsset, visited, rowleng, colleng):
if node is None:
return
if node.is_end_of_word:
resultsset.add(node.word)
for offsetx, offsety in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
newx, newy = i + offsetx, j + offsety
if not (0 <= newx <= rowleng-1 and 0 <= newy <= colleng-1) or visited[newx][newy]:
continue
visited[newx][newy] = True
self.dfs(board, newx, newy, node.children.get(board[newx][newy]), trie, resultsset, visited, rowleng, colleng)
visited[newx][newy] = False